Spring AI is transforming Java programming by enabling developers to build AI-infused solutions seamlessly.
Spring AI provides a comprehensive framework that simplifies the integration of AI capabilities into Java applications. By leveraging its power, developers can create intelligent solutions with minimal overhead, ensuring efficiency and scalability.
Chat completion models and SpringAI
Chat completion models, powered by natural language processing (NLP), enhance user interactions by predicting and generating human-like responses. In a Java Spring Boot application, you can utilise Spring AI to integrate a chat completion model to augment customer service. For instance, in the banking sector, a chatbot can be developed to assist customers with their queries, providing timely and accurate responses based on historical data and context.
As an example, the following code will create a service that uses the ChatAI component to generate a response based on the user’s input message.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springai.chat.CompletionRequest;
import com.springai.chat.CompletionResponse;
import com.springai.chat.ChatAI;
@Service
public class ChatCompletionService {
@Autowired
private ChatAI chatAI;
public String getChatCompletion(String userMessage) {
CompletionRequest request = new CompletionRequest(userMessage);
CompletionResponse response = chatAI.complete(request);
return response.getCompletion();
}
}
Embedding models
Embedding models transform text into numerical vectors that capture the semantic meaning of words. These embeddings can be employed for various tasks such as document similarity, recommendation systems, and sentiment analysis. Within a retail application, Spring AI can be used to implement a recommendation engine that suggests products to customers based on their past purchases and browsing behaviour.
The example code given below creates a Spring service that processes the sentiment of the given document text using the SentimentAI component of the Spring AI framework.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springai.sentiment.SentimentRequest;
import com.springai.sentiment.SentimentResponse;
import com.springai.sentiment.SentimentAI;
@Service
public class SentimentAnalysisService {
@Autowired
private SentimentAI sentimentAI;
public String analyzeSentiment(String documentText) {
SentimentRequest request = new SentimentRequest(documentText);
SentimentResponse response = sentimentAI.analyze(request);
return response.getSentiment();
}
}
Text to image model
The text to image model generates images from textual descriptions, opening new avenues for creative and engaging content. In the insurance industry, this can be particularly useful for generating visual representations of complex policy documents. Spring AI enables developers to incorporate this functionality, allowing users to visualise policy details effortlessly.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springai.image.TextExtractionRequest;
import com.springai.image.TextExtractionResponse;
import com.springai.image.ImageAI;
@Service
public class ChequeProcessingService {
@Autowired
private ImageAI imageAI;
public String extractChequeText(byte[] chequeImage) {
TextExtractionRequest request = new TextExtractionRequest(chequeImage);
TextExtractionResponse response = imageAI.extractText(request);
return response.getExtractedText();
}
}
This example code creates a service that extracts text from an image of a cheque in a bank using the ImageAI component in the Spring AI framework. This extracted text can be used for cheque processing and database updates for transactions.
Audio transcription models
Audio transcription models convert spoken language into text. This capability is essential for creating accessible content and automating documentation processes. In healthcare, for instance, Spring AI can be leveraged to transcribe doctor-patient conversations, ensuring accurate record-keeping and enhancing patient care.
Here is an example code using AudioAI API in the Spring AI framework to transcribe audio to text (from a streaming byte array to text string):
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springai.audio.TranscriptionRequest;
import com.springai.audio.TranscriptionResponse;
import com.springai.audio.AudioAI;
@Service
public class AudioTranscriptionService {
@Autowired
private AudioAI audioAI;
public String transcribeAudio(byte[] audioFile) {
TranscriptionRequest request = new TranscriptionRequest(audioFile);
TranscriptionResponse response = audioAI.transcribe(request);
return response.getTranscription();
}
}
Text to speech models
Text to speech models convert written text into spoken words, providing a means to create auditory content. This is especially beneficial in the wealth management industry, where financial advisors can use these to generate voice-based reports for clients, making complex financial information more accessible and comprehensible.
Here is an example code to create a service that converts the input text to speech using the SpeechAI component of the Spring AI framework.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springai.speech.TextToSpeechRequest;
import com.springai.speech.TextToSpeechResponse;
import com.springai.speech.SpeechAI;
@Service
public class TextToSpeechService {
@Autowired
private SpeechAI speechAI;
public byte[] convertTextToSpeech(String text) {
TextToSpeechRequest request = new TextToSpeechRequest(text);
TextToSpeechResponse response = speechAI.convert(request);
return response.getSpeechAudio();
}
}
Moderation models
Moderation models help ensure that content adheres to community guidelines by identifying and filtering inappropriate material. In a social media platform within the retail industry, Spring AI can be employed to automatically moderate user-generated content, maintaining a safe and friendly environment for all users. The code example given below uses ModerationAI of the Spring AI framework to create a service that checks whether the given advertisement text is appropriate for children.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springai.moderation.ModerationRequest;
import com.springai.moderation.ModerationResponse;
import com.springai.moderation.ModerationAI;
@Service
public class ContentModerationService {
@Autowired
private ModerationAI moderationAI;
public boolean isContentAppropriate(String advertisementText) {
ModerationRequest request = new ModerationRequest(advertisementText);
ModerationResponse response = moderationAI.moderate(request);
return response.isAppropriate();
}
}
Advanced features of Spring AI
In addition to its portable service abstractions that help developers to start building agentic AI applications, Spring AI provides several advanced features that make it a great choice for building intelligent AI applications using the Java framework.
Observability
Spring AI emphasises observability to help developers monitor and debug AI workflows. The Spring Boot Starter Actuator provides metrics such as token usage, model used, etc, and supports integration with external monitoring systems such as Zipkin, Splunk and DataDog, thus enabling visibility into model behaviour and system performance.
Chat Memory
Chat Memory allows Spring AI applications to maintain conversational context across interactions. The PromptChatMemoryAdvisor manages pre- and post- requests to the model, which makes this feature essential for building agentic AI systems that require continuity and coherence in multi-turn dialogues. Chat Memory can be configured to be used in-memory or can store history in a database.
Retrieval augmented generation with vector stores
Spring AI uses an advisor called QuestionAnswerAdvisor so the ChatClient knows it must consult the vector store for supporting documents before sending the request to the model.
Structured output
Spring AI can be configured such that the model map returns data to a strongly typed object, which can return the model response in JSON for programmatic access.
Local function tools
Spring AI can annotate any local function with @Tool and @ToolParam with descriptions in human language so that it can be invoked by an LLM as needed. This is a great re-use of existing libraries within a genAI application
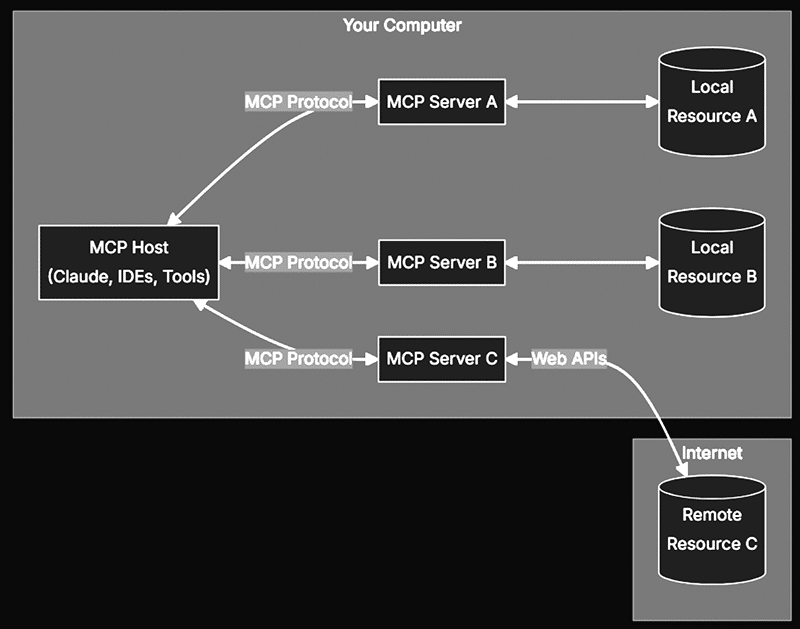
Model Context Protocol
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a standardised protocol that enables AI models to interact with external tools and resources in a structured way, regardless of the language in which they were written.
There are three flavours of MCP that Spring AI supports: STDIO, servlet based SSE, and WebFlux or WebMVC based HTTP streaming. You can easily configure the MCP server by adding the MCP information in application.properties.
Spring AI provides client and server starters to facilitate MCP integration. One interesting capability of MCP is its ability to dynamically update available tools at runtime. MCP servers can add or remove tools without restarting, MCP clients can detect these changes, and AI models can immediately use the new capabilities.
Building new age web applications with Spring AI
Spring AI’s integration with Java Spring Boot provides a powerful combination for developing modern web applications across various industries.
Banking
In the banking sector, Spring AI can be employed to enhance customer service through intelligent chatbots, streamline loan approval processes with automated document analysis, and improve fraud detection using predictive models.
Insurance
Insurance companies can leverage Spring AI to automate claims processing, generate personalised policy recommendations, and provide virtual assistants that guide customers through complex insurance products.
Retail
Retailers can utilise Spring AI to create personalised shopping experiences, automate inventory management with predictive analytics, and develop visual search engines that allow customers to find products using images.
Healthcare
In healthcare, Spring AI can be used to develop virtual health assistants, automate medical transcription, and implement predictive models that aid in disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
Wealth management
Wealth management firms can employ Spring AI to generate personalised investment strategies, create voice-based financial reports, and develop intelligent advisory systems that assist clients in making informed financial decisions.
The challenges
Spring AI incorporates generative AI within the Spring ecosystem. Integrating advanced features like retrieval augmented generation, tool calling, and Model Context Protocol is complex. Developers must understand both Spring Boot and core AI concepts such as embeddings and vector databases. While Spring AI supports over 20 models, switching between them may require configuration changes due to differing capabilities and output formats. Defining tools with annotations is easy, but managing tool logic, prompt design, and error handling can be complicated. Observability and debugging lack standardised tools, requiring integration with monitoring systems. Security features exist but demand careful setup. Finally, mastering agentic workflows, streaming responses, and structured outputs, along with evolving documentation, adds to the learning curve.
Handling non-functional requirements (NFR)
Non-functional requirements (NFRs) describe the operational characteristics of software systems, naming standards related to aspects other than specific functionalities. Addressing non-functional requirements is a key aspect of developing and maintaining AI systems. Spring AI provides a framework designed to address these requirements, including performance, scalability, reliability, maintainability, security, and usability. Focusing on NFRs enables developers to create AI solutions that meet diverse user needs. For AI systems developed with Spring AI, addressing NFRs helps ensure effective operation in various conditions.
Performance
Performance remains a critical NFR, especially for AI systems managing large datasets and complex computations. Spring AI ensures high performance through:
- Optimised libraries: Employing advanced machine learning libraries and data processing frameworks.
- Parallel processing: Supporting multi-threaded and distributed computing environments for handling extensive data volumes.
Scalability
Scalability is essential for accommodating growing workloads and evolving user demands. Spring AI addresses this need with:
- Microservices architecture: Organising applications as separate, independently deployable modules or services.
- Cloud-native capabilities: Utilising cloud infrastructure for dynamic scaling and efficient resource allocation.
- Load balancing: Spreads tasks over multiple nodes to improve efficiency and avoid overload.
Reliability
Consistent delivery of accurate and timely results defines the reliability of AI systems. Spring AI enhances reliability through:
- Robust error handling: Implementing comprehensive mechanisms for error detection and recovery.
- Testing and validation: Applying rigorous testing methodologies to ensure model accuracy and system stability.
- Continuous monitoring: Proactively monitoring system health and performance to rapidly identify and resolve issues.
Maintainability
Long-term viability depends on the ease of system maintenance and updates. Spring AI promotes maintainability by using:
- Modular designs: Adopting a modular approach that facilitates straightforward updates and enhancements.
- Documentation: Providing thorough documentation and clear maintenance guidelines.
- Version control: Leveraging version control systems to monitor changes and support collaborative development.
Security
Protecting sensitive information and maintaining user trust is paramount. Spring AI incorporates robust security measures, including:
- Authentication and authorisation: Restricting access exclusively to authorised users.
- Data encryption: Securing data during transmission and storage.
- Vulnerability management: Conducting regular assessments to identify and mitigate security risks.
Usability
Usability ensures that AI solutions are accessible and effective for all users. Spring AI advances usability with:
- User-friendly interfaces: Developing interfaces that prioritise clarity and ease of use.
- Accessibility: Ensuring adherence to accessibility standards to accommodate users with disabilities.
- Feedback mechanisms: Integrating user feedback to drive continuous improvement.
By providing comprehensive support for advanced AI models, Spring AI empowers developers to build intelligent, scalable, and efficient solutions across various industries. As we continue to embrace the future of AI-driven development, Spring AI offers the tools and framework necessary to stay ahead in the ever-evolving technological landscape.
Disclaimer: This article expresses the views of the authors and not of the organisation they work in.
















































































