As organisations rely more and more on the internet, they face the risk of complex and evolved cyber threats. Open source AI and ML based cyber security solutions are the need of the hour to counter these threats.
Did you know that 57.6 per cent of the world’s population uses social media today, with average daily usage being 2 hours and 27 minutes? There are 5.29 billion unique mobile users across the globe currently, which is equal to two-thirds of the world population. By 2025, the amount of data generated each day is expected to reach 463 exabytes globally.
The rise of internet usage leads to security concerns like cyber attacks and cyber threats. A cyber attack can use malware or ransomware to gain access to data, disrupt digital operations or misuse information. These threats are not only complex but are also difficult to detect. A cyber security practice is required to control these threats and attacks across the organisation.
Cyber security is a technology or process to protect networks, devices, information, programs and data from attacks, damages and unauthorised access. There are many ways to protect data and infrastructure, including intrusion detection, malware protection, and more.
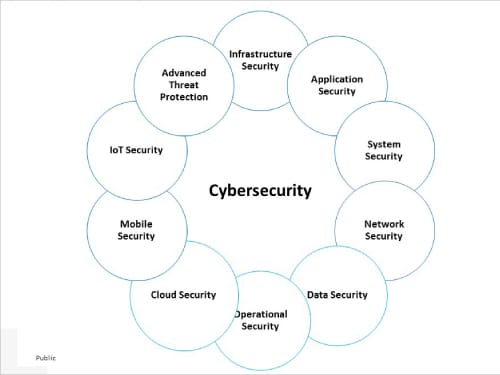
Classification of cyber security
Cyber security encompasses all the measures taken to protect an entity from cyber threats and secure data. It can be broadly classified into the following distinct security areas:
- Infrastructure security, covering DNS security, mail security, security information and event management
- Application security, which focuses on preventing malware from infecting software and devices
- System security addresses Windows/Linux server security, and vulnerability and patch management
- Network security safeguards a computer network from intruders
- Data security, both in storage and in transport, which uses automated data encryption and data leakage prevention techniques
- Operational security refers to the procedures and actions used to manage and secure digital assets
- Cloud security needs to be continuously monitored and updated to safeguard data from attacks
- Mobile security helps in authentication and on-boarding, rogue access point detection, and managing wireless secure protocols
- Internet of Things (IoT) security protects products and services against threats
- Advanced threat protection covers botnet protection, malware analysis and anti-malware solutions, forensic solutions and automated security analysis
Industry trends in cyber security
According to a Grandview research report, the artificial intelligence component of the global cyber security market reached US$ 13.29 billion in 2021. It is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 24.3 per cent from 2022 to 2030 to reach US$ 93.75 billion by 2030.
Mobile banking malware or assaults are on the rise (by 50 per cent), making portable devices a target for hackers. All our photographs, financial transactions, emails, and interactions put us in danger.
Another industry report says that organisations will be increasingly afraid to stack their security measures in 2023 because of these cyber security developments. They are likely to spend more than ever on asset protection this year, with estimates of US$ 100 billion or more.
Some key players operating in artificial intelligence in the cyber security market include:
- Acalvio Technologies, Inc.
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- Cylance Inc. (BlackBerry)
- Darktrace
- FireEye, Inc.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- Intel Corporation
- LexisNexis
- Micron Technology, Inc.
Core concepts of AI and ML in cyber security
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a simulation of the human intelligence process by computers. It helps in identifying vulnerabilities, threats, and attacks in cyber space. This is the umbrella discipline under which fall machine learning and deep learning.
Machine learning (ML) uses existing behaviour patterns, making decisions based on past data and conclusions. ML consists of the programs developed to access the data stored on the system and make it more intelligent by studying the patterns and providing better support through continuous learning. There are three types of ML algorithms.
- Supervised learning: In this system both the input and the desired output data are provided. Input and output data are labelled for classification to provide a learning basis for future data processing. The term supervised learning comes from the idea that an algorithm is learning from a training data set, which can be thought of as the teacher. Data sets are labelled so that patterns can be detected and used to label new sets.
- Unsupervised learning: This involves the training of an AI algorithm using information that is neither classified nor labelled, and allowing the algorithm to act on that information without guidance. Data sets aren’t labelled and are sorted according to similarities or differences.
- Reinforcement learning: This training method is based on rewarding desired behaviours and/or punishing undesired ones. Data sets aren’t labelled but, after performing an action or several actions, the AI system is given feedback.
Deep learning (DL) is a type of ML algorithm that uses neural networks (NN), a modelling approach inspired by how our brains work. It comprises millions of neurons, connected to each other, organised in hundreds or more layers.
To address complex cyber attacks and threats, several organisations are implementing AI and ML based security solutions and technologies.
AI and ML have evolved as an optimal solution in cyber security, with solution techniques/algorithms being applied across all market sectors. They play a crucial role in the development of automated security systems, natural language processing, face recognition, and autonomous threat detection.
| Feature | Open source tool/product | Remarks |
| Malware detection and identification | REMnux, OpenEDR |
REMnux is a free Linux toolkit for reverse engineering and analysing malware. OpenEDR helps organisations to secure their infrastructure against malware, ransomware, data breaches and other threats. |
| Threat analysis | Nmap, Metasploit |
Nmap provides methods to find open ports, detect host devices, verify active network services, fingerprint operating systems and locate potential backdoors. Metasploit helps security professionals perform simulation attacks to find loopholes in a system. |
| Spam detection | FortiClient | FortiClient reduces the risk of malware, and blocks spam URLs as well as exploit kits. |
| Network intrusion detection | Security Onion, Snort, PfSense, OSSEC |
Security Onion provides network monitoring via full packet capture, host-based and network-based intrusion detection systems, log indexing, and search and data visualisation features. Snort is capable of real-time traffic analysis and logging. PfSense is configured for intrusion detection and prevention, traffic shaping, load balancing and content filtering. |
| Phishing detection | Gophish | Gophish provides a full-featured toolkit for security administrators to build their own phishing campaigns. |
| Asset discovery | AlienVault, OSSIM |
OSSIM offers end-to-end security information and event management through asset discovery, behavioural monitoring, and event correlation. |
| Incident response | OpenVAS, Nikto |
OpenVAS is an all-in-one vulnerability scanner. It tests for security issues, misconfigured systems and outdated software. |
| SQL injection flaw detection | Sqlmap | Sqlmap automates detecting and exploiting SQL injection flaws of database servers, enabling a remote hacker to take control. |
Popular AI/ML approaches to cyber security
Some of the most prominent and popular ways in which AI and ML detect cyber threats are described below briefly.
Malware detection and identification: In this approach, AI and ML algorithms help in identifying malicious files and filter them before they reach the end user. Many different AI and ML approaches have been used to detect malware. These solutions can detect, respond, and remediate in real-time. Most prominent among these are:
- Machine learning and data mining to look for malware source code repositories using a technique called ‘SourceFinder’ and analyse them based on characteristics and properties
- Machine learning to look for a particular string within files that could indicate the presence of malware or malicious code and classify them
- Usage of AI/ML to detect patterns in binary executable files and determine if they are malicious
- Utilising visual binary patterns identified in the code and a type of self-organising network that adapts over time
Behavioural threat analysis: Threat analysis is a cyber security strategy that aims to assess an organisation’s security protocols, processes and procedures to identify threats, vulnerabilities, and gather knowledge of a potential attack in advance. A threat analysis consists of the information and assets that need to be protected in terms of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Some of the techniques used to identify the threats are:
- ML techniques called user and event behavioural analytics (UEBA) to analyse and recognise typical behaviours and patterns in user accounts and endpoints. These can detect security incidents that violate predefined operational rules, employ novel attack patterns, or span multiple organisational systems and data sources.
- Semi-supervised learning is another approach used for threat detection.
Spam detection: Spam emails may have inappropriate contents, links and attachments, which can lead to security issues. Uninvited bulk emails generally belong to the category of spam. AI and ML models can be used to detect spam by analysing the content of the mail/message and looking for patterns.
AI is able to detect that messages are spam without requiring any human intervention. Some of the spam detection algorithms are:
- Bayes algorithm that helps to filter out some spam emails
- AI and ML based spam detection unsupervised text mining model used to detect the possibility of false reviews
Network intrusion detection: AI and ML based intrusion detection systems (IDS) develop intelligent systems to detect, classify, and respond to cyber attacks. IDSs identify malicious behaviour and stop it before it causes any damage.
An IDS is usually configured with a set of rules such as use of certain words in the subject line of an email message or sending of too many messages in a given time period. It helps to generate alerts when it detects an event related to an attack or intrusion attempt.
IDS can be implemented as a standalone system or as an add-on module to security software — for example, antivirus programs.
IDS responses can be categorised into two main types:
- Active defence: An active defence is ‘real-time’ defence where the system initiates an action at the moment of detection rather than waiting for a report from another system.
- Passive defence: In this type of defence, IDS only responds after receiving and processing information that an intrusion attempt has taken place.
The goal of an AI and ML based algorithm is to optimise certain features and improve its classifiers, so that it reduces the number of false alarms that come up while trying to identify an intruder.
Phishing detection system: An AI based system detects phishing emails by analysing the content of the email and comparing it with a database of known phishing emails. The phishing detection system (PDS) can also detect if the sender is spoofing another person’s identity.
PDS can also be used with voice, video, and image messages. The system activates when users receive a suspicious email or when they send an email containing personal information. Some of the features of the PDS are:
- Automatically detects email phishing scams
- Stores emails with malicious content in a quarantine folder
- Triggers user notifications when the system detects a new virus in an email
- Maintains detailed logs of all email activity
- Detects emails that contain phishing links
- Automatically generates a report of every detected email
The goal of the PDS is to automatically detect and report emails that contain phishing links.
Automated processes that optimise human analysis: Automated processes can be set up by analysing reports on past actions generated by security analysts to identify and respond to certain attacks successfully. AI algorithms use this knowledge to build a model, which can be used later for identifying similar cyber activities. Using this model, AI algorithms respond to attacks without human interference.
Incident response system: AI and ML based systems help in providing incident responses, enabling organisations to manage security alerts appropriately. AI automated incident responses mitigate vulnerabilities and deliver faster responses to such events.
Fraud detection: AI and ML based systems can be used to create models to recognise fraud-related patterns. As more data is fed to the system, the AI model becomes more accurate.
Asset discovery: AI and ML can be used for automating the discovery of all key devices and applications. This can play a huge role in mitigating risks.
Key open source AI and ML cyber security tools
Open source cyber security tools help organisations to protect their devices, data, and user landscapes from internal and external threats. These tools can be proactive or reactive, allowing organisations to test systems and check for vulnerabilities or monitor active systems to pre-empt incoming attacks.
Cyber security tools have the following important features:
- Business-need alignment and organisation readiness
- Highly scalable
- Support heterogeneous environments and can adapt easily
- Have proper industry support for technology
- Integrate easily with an organisation’s systems and tools
- Table 1 highlights the most popular and important open source AI and ML based cyber security tools.
Benefits of AI and ML in cyber security
Integrating AI and ML into a cyber security system has quite a few benefits:
- Ability to detect nuanced attacks, strengthen security, and enhance incident response
Improves the detection and response cycle time - Organisations can rapidly quantify risks and accelerate analyst decision-making with data-driven mitigation measures
- Prevents and mitigates cyber security breaches and malicious attacks
- Improved workforce experience
- Improved customer satisfaction and brand reputation due to heightened cyber security protection and increased trust in the organisation’s security protocols
Cyber threats have become innovative and are constantly evolving. Also, data is filled with new patterns that are hard to capture and analyse manually. AI and ML offer a powerful way of identifying vulnerabilities, threats and attacks across organisations as well as social media. AI and ML algorithms help to detect and analyse enormous amounts of data, and the solutions they offer are more robust, flexible, and scalable.
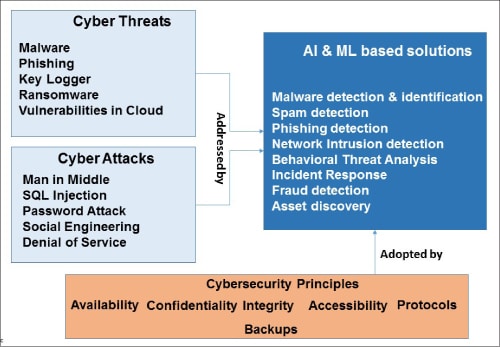
The main targets of AI and ML based algorithms for cyber security are malware detection, network intrusion detection, and phishing and spam detection. Some of the major adopters of AI and ML based cyber security solutions are Google, IBM, Juniper Networks, Apple, Amazon, and Balbix. More and more companies are joining this bandwagon.
To sum up, integrating AI and ML into your cyber security solutions today is not an option but a necessity if you want to counter the emerging complex security threats.
Acknowledgements
Dr Behara would like to thank Santosh Shinde of BTIS, Enterprise Architecture division of HCL Technologies Ltd for giving the required time and support in many ways when this article was being written as part of Architecture Practice efforts.