The use of mobile computers is spreading faster than any other consumer technology in history. Smartphones outsell PCs. Touchscreens outnumber keyboards.
As per the Strategy Analytics Research Report on Global Mobile Workforce Forecast Update 2012-2018, worldwide, the mobile workforce is predicted to increase from 1.26 billion in 2013, accounting for 36.4 per cent of the global workforce, to 1.67 billion in 2018, accounting for 41 per cent of the global workforce.
Clearly, mobile apps are now being viewed by enterprises as core drivers that improve operational efficiency and have qualified as business-critical technology. However, app delivery is less about the technical aspects of programming and more about an apps business impact, design, integration, deployment and management.
This article will delve into the major challenges involved in designing, developing, deploying and maintaining mobile apps for enterprises, and how mobile application development platforms (MADP) solve some of these challenges.
Enterprise mobile apps: The challenges
Enterprise mobile apps involve some specific challenges that need to be addressed right in the planning and design phases. Later discoveries of one or more of these challenges have resulted in many enterprises having to re-plan and redesign their mobility solution roadmap. Lets take a deeper look at these challenges.
BYOD and device diversity
The Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) trend has penetrated enterprises everywhere. If your enterprise mobile app is to support the BYOD strategy, then an altogether different level of challenges needs to be addressed. The target device spectrum grows exponentially when considering BYOD, with new devices entering the market and reaching your target users every day. Keeping track of mobile platforms, versions and new device models (on a variety of platform versions and differing configurations) makes supporting BYOD for your enterprise app a big challenge, without a well-planned approach.
Even if you do not opt for BYOD, the target device spectrum may be limited yet heterogeneous. Diverse mobile platforms (Android, iOS, etc), along with the dynamics they bring in, makes app development for supporting multiple platforms complex. Further, apart from the variety of devices that currently exist, more keep arriving in the market for each of the mobile platforms, thereby imposing the need for an enterprise to ensure that the mobile apps not only support required mobile platforms, but also work well on the target device spectrum per platform.
Enterprise data access
An enterprise mobile app may need to access data stored in a variety of heterogeneous data sources at the enterprise backend. For instance, the sales teams data may reside in the SalesForce CRM while the financial data resides in Oracle. Integrating with a variety of standard and custom data sources may be a big need when creating an enterprise mobile app. It would require considerable time and energy to enable the mobile app to directly access the variety of data sources being used at the enterprise backend.
Enterprise data security
With legacy systems and related security ecosystems, enterprise IT heads can remain relaxed because all the enterprises data resides in and is mostly used from within the enterprise premises and via enterprise-owned devices like laptops, desktops, etc.
With mobility, data not only crosses beyond the enterprise premises, but often also resides on the users’ personal mobile devices for offline access. Further, enterprise data communication happens mostly over untrusted networks on these mobile devices, which creates the risk of enterprise data being stolen or tampered with. Also, confidential enterprise data may also get copied, printed, etc. Other malicious apps may invade the enterprise app sandbox and access its data. The user may lose the device containing enterprise data, leading to a leak of the confidential data residing in the device. Developing a robust and reliable solution to secure both enterprise data at rest and data-on-the-move pertaining to the app (while not violating the users privacy) is very crucial.
Remote management
Any loophole in an apps life cycle and its data management can make an enterprise vulnerable to mismanagement of app versions, users and their devices. For instance, the app should support a way to enforce app data wiping if a user is leaving the company or has lost the device. Further, if the enterprise wants to make a previous app version obsolete and prohibit its use, then it should be able to enforce specific app version updates as mandatory on the target user base.
Only complete control and management of the apps life cycle, together with the installed app and its data, can ensure the solution generates the desired return on investment (RoI) for an enterprise.
User adoption
In todays mobility era, an apps success depends, to a great extent, on its user experience. Streamlined use cases, ease of use, shorter workflows, a focus on only what the user needs in the current context, and a respect for screen size contribute to a better user experience. The better the user experience, the higher the chances of more users adopting the app. And the lower the user adoption, the higher the chance of an enterprise failing in its mobile app journey.
Enterprise mobility, as a segment, has been maturing over the past few years, and now there are solution suites available to address these challenges effectively. Enterprise mobility management (EMM) and the mobile application development platform (MADP) are well known solutions in the market. In this article, we will have a look at MADP and how it solves some of these challenges.
The solution: MADP
According to Gartner, A MADP enables an enterprise to design, develop, test, deploy, distribute, analyse and manage a portfolio of cross-platform mobile apps on a range of devices running Android and iOS, and to address the requirements of diverse use cases including external-facing and internal-facing scenarios.
There are generic MADPs available in the market as products or by service providers as their solution catalysts. Whether to use a generic MADP or opt for a custom one largely depends on the complexity of your enterprises ecosystem, its time-to-market needs, security concerns and customisation requirements.
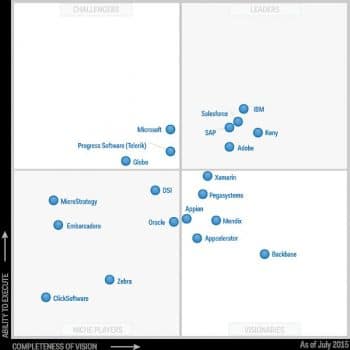
Figure 1 shows the market leading MADPs, as per Gartners Magic Quadrant for MADPs, July 2015.
As per this report, the MADP market continues to mature, moving away from the tech-centric position of the past towards a more business-aligned approach, expanding support for the app development life cycle and offering more robust and scalable capabilities.
As with all Magic Quadrants, vendors in the Leaders quadrant are not necessarily the best for all projects or enterprises. Depending on an enterprises needs, a vendor in any quadrant could be the best for an enterprise. Some platforms may be a better fit with an organisation’s particular skill sets. Consider the match between the skills available and those required by each MADP evaluated. Also consider the cost and complexity of the vendor’s offering, and whether this aligns with benefits expected during the estimated life span of the product.
Some enterprises may prefer custom MADP, to address specific concerns related to vendor lock-in, the nature of the solution, security, roadmap demands, long-term costs, etc. For developing custom MADP, enterprises can consider leveraging a mix of freeware or open source components and custom components.
Recommendation: Before deciding on which open source tools and libraries to leverage, a precise check on their capabilities, roadmap, support services and costing, long term plans, customisation possibilities and licence type will help you in taking the most appropriate decision.
The MADP advantage
Enterprises leverage MADPs to get the benefits of one or more of the following salient features.
Excellent support for cross-platform mobile app development
This feature addresses the mobile platform diversity challenge by providing a way to write selected or common code/scripts for mobile app development targeted at all platforms. Internally, the platform may use a variety of approaches to convert the common code to platform-specific apps.
Many MADPs like PhoneGap provide a hybrid development framework, which provides the best of the Web (also known as thin client) and native (also known as thick client) approaches. It facilitates communication between the Web and the native parts of the app along with other rich features. This paradigm is characterised by the reuse of Web parts across mobile platforms while balancing the native approach benefits.
There are also MADPs like Appcelerator, which consist of inbuilt converters to convert the common script written by MADP developers into platform-specific native apps. In short, MADPs help to optimise the time, effort and cost of maintaining apps for multiple platforms.
Recommendation: MADPs differ in their support for specific mobile platforms and scripting languages, and come with their own limitations. An enterprise must analyse its existing or long-term preferred skill sets, vendor binding limitations and target mobile platforms to better judge which MADP suits it the best. It would also help to get a complete overview of the vendor MADP roadmap and match it with your enterprises mobile app feature needs, in case you choose a standard MADP solution.
The standard MADP solutions roadmap and features are influenced by a variety of factors and your enterprise feature requirements may or may not match with them. This is why a large number of enterprises prefer customised MADPs to avoid vendor binding and to gain complete control as per their app roadmap, while keeping the solution simple and targeted to their specific needs.
Easy integration with standard enterprise data sources
This feature addresses the enterprise data access challenge to a large extent. Enterprise data sources may be standard like SAP, SalesForce, JDEdwards, etc, or customised.
While MADPs provide loosely coupled and clean ways to integrate standard data sources, if custom data source integration is required, it would consume effort and time, depending on the complexity of integration.
Recommendation: Different MADPs feature integration with different sets of data sources. An enterprise looking for a MADP must map its specific data source integration needs with the data sources supported by MADPs, to take an appropriate decision.
Always think in terms of the future roadmap in order to cover the bigger picture of the mobility solution.
The power to manage the mobile apps lifecycle
This feature addresses the remote management challenge to some extent. While enterprises have a collection of apps planned or rolled out for different target user bases, rolling out and managing multiple apps for multiple platforms together with multiple versions of each becomes a huge challenge for the enterprise.
MADP solves this challenge by helping to design, develop, test, deploy, distribute, analyse and manage a portfolio of cross-platform mobile apps on a range of devices. In short, it brings all mobile app lifecycle related operations together in one solution for ease of management.
Recommendation: Different MADPs support different approaches, standards and tools for achieving the different lifecycle processes. The enterprise must match its existing tools and processes to the MADPs in consideration before taking the final call.
Easy integration with cloud services and third party tools
This feature addresses the dual challenges of enterprise data access and security. An enterprise may be leveraging certain cloud services and its data may reside on the cloud for a certain category of ecosystem components. Further, it may leverage third party tools of mobility management like Airwatch, MobileIron, etc. The enterprise mobile app must integrate well with these heterogeneous sources of data and the management tools.
Many MADPs consider this crucial need and provide good support for easy integration with these third party services.
Recommendation: The enterprise needs to understand its existing ecosystem and processes, together with its needs relating to third party tools integration with respect to MADP, before taking the final call.





