The blockchain first came into existence in October 2008, on the foundation of a proposal for Bitcoin, with the objective to create a decentralised, peer-to-peer money network without the involvement of any bank or government. With blockchain technology gaining popularity, there are new job requirements in the field. This article lists the roles, skills, certifications and industries that can be looked at to build a career based on blockchain.
A blockchain can be defined as “a time-stamped series of immutable records of data that is managed by a cluster of computers not owned by any single entity.” Every block of data is secured and linked to each other using a cryptographic mechanism, i.e., a chain. In layman terms, blockchain is termed as an encoded, dispersed database that records data similar to a computerised record of exchanges, transactions, contracts, etc. The chief highlight of blockchain is that its automated record is widely available over a large number of PCs, which means the blockchain system is accessible across a wide network of computers in a distributed fashion. In the real-world, blockchain has already started a revolution in the finance and IT sectors with Bitcoins, smart contracts, Hyperledger and other applications.
Blockchain plays a strong role in building trust across business networks, and it does so using the following five attributes.
Distributed: Blockchain works in a distributed ledger, which is shared and updated with every single transaction happening across the nodes connected to it. Every transaction happens in real-time without any involvement of the central server.
Secure: The entire blockchain network is cryptographically secured using SHA-256 bit, restricting any sort of unauthorised user access.
Transparent: Every node or participant has the entire copy of blockchain data, so all the transactions can be seen by all the parties connected to the blockchain.
Consensus-based: All the participants must agree that a transaction when it happens is valid, and this is done using consensus algorithms.
Flexible: Smart contracts are executed based on conditions written onto platforms.
In recent years, blockchain has become a trend similar to the way cloud computing was in the mid- 2000s and providing professionals, developers and R&D professionals with strong opportunities across various sectors. According to Upwork’s skills index, blockchain is the fastest growing skill in the IT sector. As per Burning Glass Technologies, there will be more than 6000+ job openings in this field over the next 5-13 months. So, building a career in blockchain is a good decision in the present scenario. Blockchain technology is transforming companies into more efficient and trustworthy organisations. As it is a new technology, there is a huge shortage of skilled professionals, and big industries and enterprises are leaving no stone unturned to find blockchain experts and giving them a jumpstart in positions and salaries. So, if you are looking for good opportunities in blockchain technology, this article will provide must-needed information with regard to career roles and positions, certifications, technical skills, and even the requirements in the industry.
Career roles and positions in blockchain technology
Like any other technology stack, blockchain needs roles that vary from architects and developers to consultants and testers. However, there are some basic differences as this is an emerging technology where there is good scope for a lot of research related roles. Table 1 lists a few popular roles in blockchain based application development.
There are other intermediary roles depending on the size, volume and complexity of application development, which may also crossover to other disciplinary roles such as AI engineer to implement machine learning based verification mechanism in a blockchain platform, Big Data architect who helps to design complex data design in blockchain application design, and cloud architect who helps to design the Infrastructure-as-a-Service design of a cloud based blockchain platform (e.g., Azure, AWS, GCP based blockchain services).
| Role | Role description |
| Technical analyst | Handles technical research with respect to platform suitability. |
| Platform architect | Overall SPOC for blockchain application design and infrastructure design. |
| Business analyst/Functional consultant | Helps in understanding the functional and non-functional requirements, and oversees use case development, test case development, test data preparation. |
| Frontend designer | Prepares the user experience/journey for UI design. |
| Blockchain engineer (including DevOps role) | Implements the blockchain application and DevOps pipeline activities. |
| Security consultant | Helps to design the platform security, application security, data security and network/communication security involved in the application design. |
| Test engineer | Works on test preparation and execution. |
| Data engineer | Works on data modelling (conceptual, logical and physical), and data driven design related activities. |
| Design architect | Prepares the solution design along with the platform architect and security consultant for shaping up the components and interfacing activities. |
| Table 1: Popular roles in blockchain based application development | |
Certifications in blockchain
Some common and popular certifications help you build your career in blockchain technology. The most popular are listed here. There is no recommendation or endorsement of any of these courses. They are merely listed here to show how to walk the path to building a career in blockchain.
University of Nicosia
The University of Nicosia offers multiple blockchain courses and certifications.
Blockchain Developer certification: Intended for developers to understand blockchain basics, cryptocurrency programming and security frameworks.
Blockchain Business Analyst certification: Intended for consultants to understand regulatory frameworks in cryptocurrencies, and business considerations for design and development of a blockchain platform.
Blockchain Analyst certification: Intended for functional and technical analysts to understand open financial systems, digital payment transactions, and application of blockchain platforms in digital payment platforms.
This university is also the first in the world to offer an M.Sc in Digital Currency, which covers blockchain and distributed ledger technology.
Blockchain Institute of Technology (BIT)
BIT offers professional certifications like Certified Blockchain Professional (CBCP) and Certified Senior Blockchain Professional (CSBCP). CBCP is intended for technical architects who understand blockchain platforms, Bitcoin, business applications of blockchain, cryptocurrency and its usage, development of smart contracts, and design/development of decentralised applications.
CSBCP is advanced professional certification intended to cover the security aspects of the blockchain platform, accounting and smart ledger/distributed ledger management, regulatory and compliance frameworks across different geo/industry standards, advanced smart contract topics, and financial instrument topics.
BIT also offers various online courses on blockchain, Bitcoin, Ethereum and cryptocurrency.
Blockgeeks certification
Blockgeeks offers various short-term courses coupled with certifications on Ethereum platform topics, blockchain for business professionals (functional and non-technical topics), smart contract security aspects, Hyperledger platform and its tools, and the blockchain regulatory framework programme. These certifications help you to earn a blockchain certified developer title in specific topics like Bitcoin, Hyperledger, Ethereum, and regulatory frameworks.
Blockchain Training Alliance (BTA)
BTA offers professional certifications like:
- BTA Certified Blockchain Business Foundation (CBBF) to cover the basics of blockchain fundamentals as well as business topics in blockchain applications.
- BTA Certified Blockchain Solution Architect (CBSA) to cover solution design and development of blockchain platforms and applications.
- BTA Certified Blockchain Developer Ethereum (CBDE) to develop Ethereum platform based blockchain applications, including programming constructs and practical experience.
- Certified Blockchain Developer Hyperledger Fabric (CBDH) to develop Hyperledger framework and Hyperledger Fabric based applications, including design and development in the platform.
- Certified Blockchain Security Professional (CBSP) to cover advanced security topics like regulatory frameworks, platform security, application security, and data security around various compliance standards.
Exams for these courses are conducted in Pearson VUE centres like for any other professional certification.
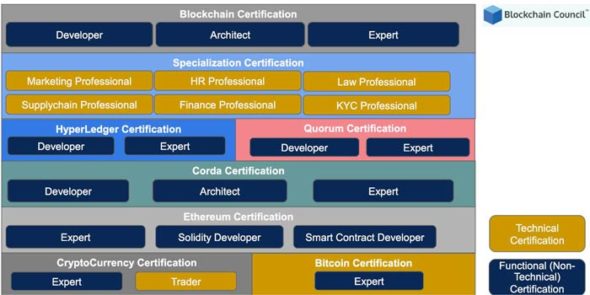
Blockchain Council certifications
Blockchain Council offers domain-centric certifications for blockchain professionals like blockchain certified developer, blockchain certified expert, blockchain marketing professional, blockchain HR professional, blockchain certified architect and blockchain finance professional. It also provides specialisation certifications in Corda, Hyperledger, Bitcoin, cryptocurrency and Ethereum (Figure 1).
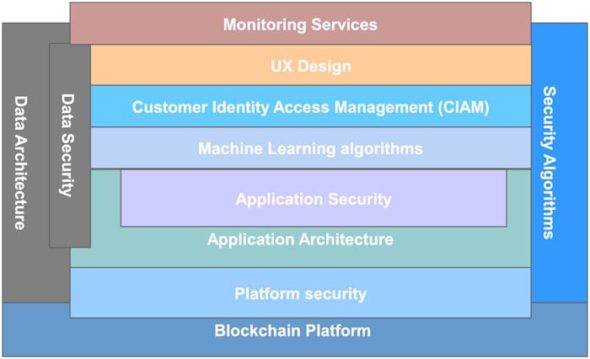
Technical skills that professionals in blockchain technology need
To take up a blockchain technology based role, it is important to understand various technical aspects and technology frameworks. For instance, one must understand platform security as any failure on this front can cause the entire blockchain based implementation to collapse.
Other blockchain fundamentals that must be understood include basic technical terms such as cryptocurrency, decentralised networks, nodes, mining algorithms, tokens, hash, initial coin offering (ICO), and forks, to name a few. This is important to understand the differences between various blockchain platforms, and choose the right platform and right architecture for implementing the solution for a given problem.
Technical design of a blockchain platform
A blockchain platform includes the following.
Programming constructs like Java, Python and Ruby, which are required to program the consensus and other decentralised applications in the blockchain platform. Some popular platforms like Hyperledger support a number of programming constructs other than Java and Ruby, such as GoLang, C#, JavaScript, to name a few.
Platform security is fundamental to a blockchain, where one has to understand how to implement an unbreakable architecture to make it reliable for consumers by using various standards like CryptoCurrency Security Standards (CCSS).
Data architecture designs the data model, data flow and data structures to be handled in the transaction to make the entire process efficient, cost-effective, and easy to use for customers.
Application security is designing the security considerations required for various components in the application, including interservice communication and messaging, as well as monitoring and measuring the accessibility to the application.
Security algorithms are the work engines of any blockchain platform, and help to strengthen its computational activities.
Customer Identity Access Management (CIAM) platforms can be any third party integration services like PingIdentity, Akamai, and ForgeRock, to name a few. These services help to transform the customer experience, and handle single sign-on and digital identity for the entire platform.
Machine learning algorithms are a set of algorithms that build a predictive learning model to protect the system from potential attacks.
UX design helps to design a better user experience, making the platform easy to use with a higher return on investment by attracting customers. This is fundamentally a business-engineering concept, used for developing an intuitive and easy to use application design.
Data security and integrity help to handle data models with the highest security features in both data at motion (when it is transformed in any transaction handling) and data at rest (when it is stored in the data store), so that there is no tampering of data.
Monitoring services ensure the entire system is working properly as expected, including alerts and event management. These also manage health-checks of the entire system in all the layers like infrastructure, applications and data.
The industries in which blockchain will act as a disruptive technology
Here is a list of the sectors blockchain technology promises to disrupt in the near future.
Blockchain in the banking and financial sectors: The banking and finance sectors are using blockchain extensively for transactions using digital cryptocurrencies. As the technology is decentralised, one can use any cryptocurrency variant to transfer money without the involvement of a third entity. With millions of transactions happening every day in the banking sector, the blockchain has a secure system for maintaining records.
Blockchain in real estate: The real estate industry is plagued by complex procedures and time-consuming paper work. The entire traditional system of documentation can now be replaced with blockchain technology. All documents can be stored safely with less effort and cost, and smart contracts created between buyers and sellers, while funding can be done with consensus algorithms.
Blockchain technology also eliminates third parties by enabling direct communication between two parties.
Blockchain in the gaming industry: Blockchain has the power to unlock amazing benefits for gaming entrepreneurs and developers by preventing fraudulent activities and providing a secure environment for designing, launching and testing games. It even assists game developer companies to buy and sell games. Popular gaming platforms like Microsoft’s Xbox and the Sony PlayStation are also using cryptocurrencies in a safe manner. Players who win at various competitions in gaming conferences can be rewarded with Bitcoins. With a blockchain based solution players can buy gaming accessories without going through a bank to process the transactions. Country barriers are non-existent, too.
Blockchain in healthcare: The healthcare industry has highly sensitive information and blockchain can be used to reduce the risks of data leakage. Blockchain is highly helpful in transforming medical data and storing records in a convenient manner, avoiding the misuse of data. In addition, it offers authorisation and people identification services.
Blockchain in the legal industry: The legal industry has multi-dimensional and variable data, and the blockchain can play a key role in storing and verifying transactions securely and with transparency. With blockchain, records can be stored, easily verified and authenticated. Blockchain can revolutionise operations in the industry using smart contracts for IPRs, financial transactions, etc.
Blockchain in transportation: In the transportation industry, strong document coordination on shared distributed ledgers helps to eliminate useless paper work. With the help of smart contracts, customs clearance at several checkpoints can be done quickly and efficiently, reducing processing time and effort.
Blockchain helps the transport industry to promote faster delivery by helping to resolve disputes for payments. The processing and administration costs involved in transportation are reduced, as blockchain avoids reliance on paper transactions.
Blockchain in government: Blockchain technologies can help reduce and eliminate bureaucratic red tape and corruption in government agencies. For example, welfare, disability, veterans’ and unemployment benefits could be more easily verified and distributed, eliminating fraud and waste. Smart contracts could ensure that government funds are released only when certain conditions are met. Security, efficiency, and transparency in government functions could be increased across the board.
Blockchain in education: As the power of online and distance learning grows, so does the need for an independent way of verifying students’ transcripts and educational records. A blockchain based system could serve almost as a notary for educational records, creating a way for educational institutions to access secure records and transcripts. In fact, it could also help universities and other large institutions collaborate. No longer would a student have to wait for the course s/he wants offered at Harvard if Oxford is offering it online; her/his grades and records would also be easily and instantly transferable.
As new technologies evolve, it is important to make sure that industries stay updated with them to keep ahead of the competition. Blockchain technology will impact several industries in the years to come. Security of data is something every business is looking for, and there is no safer option than blockchain when it comes to recording and transferring data. In the near future, the demand for blockchain professionals will rise tenfold and create opportunities for a host of new business ventures.