This brief tutorial will help you to install and configure Grafana for your organisation.
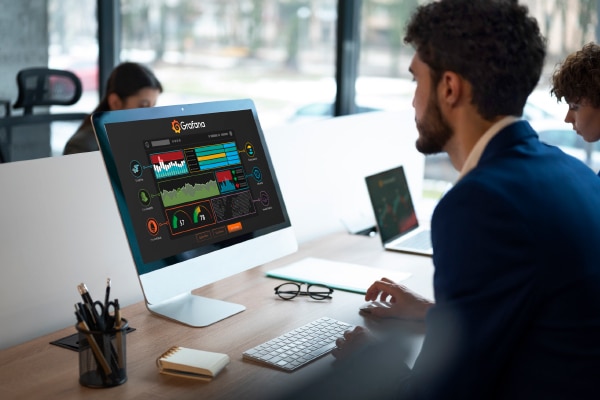
Grafana is an open source platform designed for monitoring and observability. It enables you to query, visualise, alert on, and comprehend your metrics regardless of their storage location. Its open source adaptability and cost efficiency are significant, with great emphasis on security. Grafana’s integration with the DevSecOps toolchain includes correlating security events with performance metrics and integrating security dashboards. The compliance dimension (audit logs, access restrictions) is important for organisations.
The advantages of using Grafana
Intuitive
Grafana is crafted with the user as a primary consideration. Its user-friendly design renders it accessible for novices, while maintaining sufficient power for experienced professionals.
Versatile data sources
Grafana can interface with an array of data sources, including Prometheus and MySQL. This adaptability allows for the visualisation of nearly any data type.
Configurable dashboards
You can design dashboards according to your requirements. The customisation choices are virtually limitless due to the variety of panels and widgets available.
Real-time monitoring
Grafana facilitates the real-time observation of data, essential for promptly addressing faults or alterations.
Community and support
With a robust community and abundant resources, you are never isolated in your Grafana experience. Assistance is perpetually available, along with articles to provide guidance.
Visualisations
Rapid and adaptable client-side graphs pose a plethora of possibilities. Panel plugins provide many methods for visualising metrics and logs.
Installing Grafana
To install Grafana on Windows/Linux/macOS, download the installer from https://grafana.com/grafana/download. Run the .msi file and follow the prompts.
For Linux (Debian/Ubuntu), use the following code:
sudo apt-get install -y adduser libfontconfig1 wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana_10.2.3_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i grafana_10.2.3_amd64.deb sudo systemctl start grafana-server sudo systemctl enable grafana-server
For macOS (using Homebrew), the code is:
brew install grafana brew services start Grafana
To access the Grafana dashboard, open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000. The default username and password are both admin and can be changed after the first login.
Adding data sources
Grafana supports multiple data sources (e.g., Prometheus, InfluxDB, MySQL, Loki).
Here’s an example. Connect Prometheus, click on Configuration (gear icon) > Data Sources > Add data source.
Select Prometheus and configure http://localhost:9090 (default Prometheus address).
Click on Save & Test to verify the connection.
Creating dashboards
For manual creation, click on Create (plus icon) > Dashboard > Add new panel. Write queries (e.g., PromQL for Prometheus) and visualise data (graphs, gauges, tables). Save the dashboard.
You can also import pre-built official/community dashboards from Grafana Dashboards. Click on Import and paste the dashboard ID (e.g., 1860 for Node Exporter).
Setting up alerts
To create alert rules, edit a panel and go to Alert > Create Alert. Define conditions (e.g., CPU usage > 90%). Configure notification channels by going to email/Slack/PagerDuty and clicking on Alerting > Notification channels. Add contact points (e.g., Slack webhook).
Securing Grafana
Change the default password by clicking on Admin > Profile > Change Password.
Enable HTTPS. Edit Grafana config file (/etc/grafana/grafana.ini) as follows:
ini [server] protocol = https cert_file = /path/to/cert.pem cert_key = /path/to/key.pem Restart Grafana: sudo systemctl restart grafana-server
Grafana enables comprehensive visualisation and monitoring of data in real-time. Users can set up data sources, design dashboards, and configure alerts through the web interface. Moreover, the guided walkthrough from installation to integration and dashboard setup facilitates the monitoring of system metrics, business KPIs, and other time-series data.
Unified observability across complex IT infrastructures is made possible with Grafana due to its broad support of data sources, which include Prometheus, InfluxDB, MySQL, and Elasticsearch. Furthermore, its agile and strong plugin ecosystem enhances the capability to be tailored to an array of use cases in DevOps, IoT, analytics, and business intelligence.
Properly configuring a Grafana environment greatly enhances operational and system insights, facilitating better decision-making while boosting the reliability of the system. This underlines its critical importance in contemporary monitoring and observability frameworks.