Augmented reality and virtual reality are being used in various domains and have many useful applications today, apart from gaming. A few useful open source platforms that help to implement these technologies are listed in this article.
The global market for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) is increasing at an exponential rate. Consumers and enterprises are benefiting, as they can access and experience a remote environment in real-time.
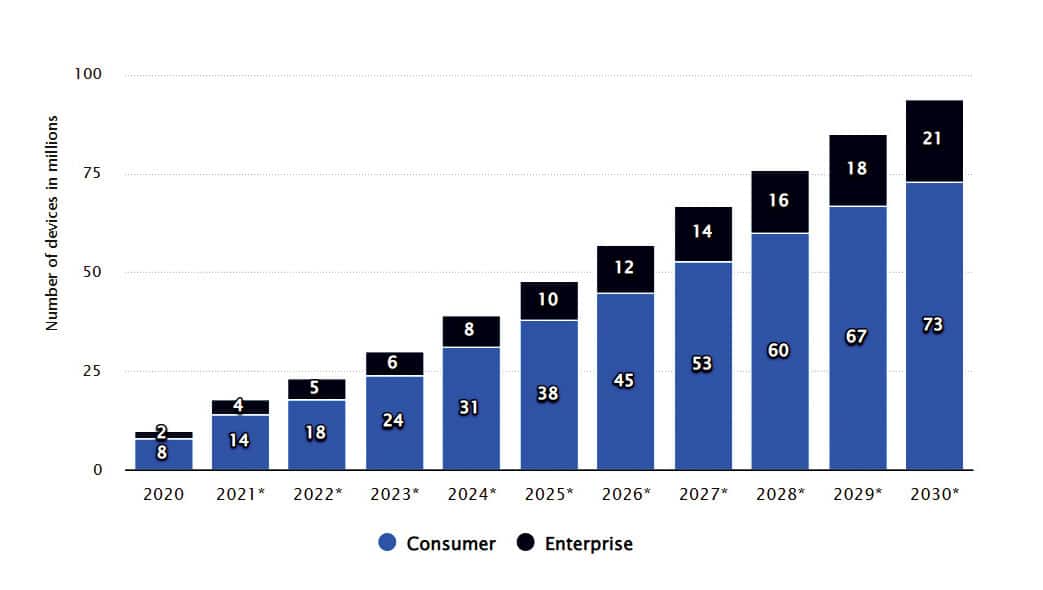
Figure 1 depicts Statista.com’s research analytics with respect to the AR and VR market, both from historical as well as future perspectives.
Virtual and augmented reality complement each other, as they enhance people’s perception of their surroundings by incorporating digital elements that look like natural features. Virtual Fixtures, a system created by the US Air Force’s Armstrong Laboratory in 1992, was the first fully functional AR system that enabled an immersive mixed reality experience for users.
The entertainment and gaming industries were the first to offer commercial augmented reality experiences. Many commercial businesses have adopted AR applications for education, healthcare and entertainment since then. With AR techniques, content can even be accessed by scanning or viewing a picture with a mobile device.
AR provides users with new levels of sensory stimulation. Its usage (e.g., integrating computer vision, putting AR cameras into smartphone applications, and object identification) can help you digitally modify and interact with the surroundings. An example is superimposing additional measured information like electromagnetic radio waves, in precise alignment with where they are in space, to the existing reality. There is a huge potential for AR to be used in the collection and dissemination of tacit knowledge. Real-time and semantic settings that contain environmental factors are frequent when using augmentation techniques. As an example, a live video broadcast of a sporting game can provide both immersive and perceptual information along with additional data like scores. Technologies that use both AR and heads-up display (HUD) technology can be combined in this manner.
AR vs VR
Virtual information permeates the user’s experience of reality in VR. In AR, the user’s view of reality is enriched by including computer-generated information inside the data gathered from the actual world.
Architects, builders and real estate companies can utilise VR to generate a virtual tour of a new building or layout, while AR can help to illustrate the structure and systems of a building superimposed over a real-world scenario.
Key implementation domains in AR and VR
AR and VR have a wide and huge scope in education, e-governance, the corporate sector and many other domains, as listed below:
- Architecture or building plans
- Qualitative analysis in chemistry
- Assembly/disassembly of an electrical engine
- Exploration of human anatomy
- Simulation of circulation of blood in heart
- Simulation of flight/vehicle/space stations
- Building electronic circuits in zero physical defects
- Virtual classrooms for teaching and learning
Myths regarding AR and VR implementations
AR and VR can be implemented using minimum resources as well as very limited infrastructure and hardware. There are a lot of myths associated with AR and VR, some of which are listed below:
- Need for huge resources and costly hardware
- Specialised graphic cards are needed
- Specialised processors are needed
- Integration of GPU/TPU is required
- Need for high performance programming frameworks
None of the above is true.
Key features required for effective use of AR and VR
To reap the maximum benefits of AR and VR, a few key features must be integrated into the devices, including software and hardware infrastructure:
- Drag-and-drop
- Dynamic editing
- Simulation
- Real-world backdrop
- Superimposed objects
- Hardware integration
- SLAM (simultaneous localisation and mapping) support
- Cross-device publishing
- Real-time analytics
- Uploading dynamic content
- 3D object tracking
- Support for smart glasses
- Content creation
- Geolocation tracking
- Cloud storage
A few open source high performance platforms used for implementing AR and VR are listed below.
A-Frame (aframe.io):
- Open source platform for VR with entity component system
- Java based programming functionality for high performance implementations
- No need for any third party application/hardware
- All we need is a Web browser and JavaScript library
OpenIllusionist (https://www.openillusionist.org.uk/home/):
- Dynamic integration of objects
- Real-time user inputs
- Dynamic modelling
- Virtual objects analytics
ApertusVR (http://apertusvr.org/):
- High performance platform for AR, VR and mixed reality (MR)
- HTTP rest API integrated
- Embeddable framework-independent
- Network topology-independent
ARToolkit+ (http://www.arreverie.com/artoolkit.html):
- Modular open source code
- Smart glasses
- Content library
- Mobile focus on secure development
- Android and iOS support
- Content creation
- Simulation
- Superimposed objects
- Drag-and-drop
- Virtual reality integration
Holokit (https://holokit.io/):
- Virtual reality integration
- Real-world backdrop
- Superimposed objects
- Inside-out tracking function
- 3D objects
- Multi-degree diagonal field of view
- Content creation
- Merges the real and virtual
BRIO (https://experience.brioxr.com/):
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Multiple file format support
- Virtual reality integration
- 3D objects
- Content creation
- Cross-device publishing
- Content library
- Real-world backdrop
- Simulation
- Tracking and analytics
- Superimposed objects
Adobe Aero (https://www.adobe.com/in/products/aero.html):
- Dynamic interactive elements
- Content creation
- Set pathways for animations
- Drag-and-drop
- Content library
- Tracking and analytics
- Simulation
- Virtual reality integration
- Cross-device publishing
Vuforia Engine (https://developer.vuforia.com/):
- Unparalleled accuracy
- Dynamic simulation
- Virtual reality integration
- 3D objects
- Creative empowerment
- Superimposed objects
- Content creation
- Maximum reach
- Content library
- Tracking and analytics
- Real-world backdrop
- Advanced vision
- Drag-and-drop
Scope for research and development
AR and VR help in providing a multisensory experience in which real-world items are improved with computer-generated perceptual information, including visual, aural, haptic, somatosensory, and olfactory information. Combining the real and virtual worlds, these technologies allow in-the-moment interaction, and accurately register 3D models of virtual and actual items.

Researchers and practitioners can use open source platforms of AR and VR to provide an interface between real-time experiences and remote infrastructure. There is a huge scope for research as there is no need to move physically to any location and remote points are always accessible.
Scientists, medical practitioners, surgeons, and experts in space exploration missions can use AR, VR and MR (mixed reality) to have a simulated view or remote experience of the actual infrastructure. This can be beneficial for multiple applications.