Explore how GraphRAG addresses the core limitations of vector-based retrieval and is a significant step forward in the evolution of intelligent applications.
As large language models (LLMs) continue to revolutionise how we build intelligent applications, the need to enhance their factual accuracy, reasoning capabilities, and real-world grounding has never been more urgent. Traditional retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) frameworks have helped overcome some limitations of LLMs by allowing them to fetch relevant context before generating responses. However, these approaches often fall short in preserving relational context and enabling deeper reasoning.
Enter GraphRAG—a paradigm that brings the power of knowledge graphs to the world of LLMs, enabling more structured, context-aware, and semantically rich responses.
The problem with traditional RAG
RAG pipelines typically rely on vector databases to perform similarity searches on document chunks. This method enables retrieval of semantically relevant information based on embeddings, making it effective for unstructured data. However, this approach often suffers from several pitfalls.
Loss of relational structure
Entities and their relationships get flattened into chunk-based representations, limiting the model’s ability to reason across connections.
Redundant or irrelevant retrieval
Without understanding relationships, the retriever may pull in text that’s semantically similar but contextually irrelevant.
Limited explainability
Vector-only methods provide little transparency into why a particular document was retrieved or how entities are connected.
What is GraphRAG?
GraphRAG enhances the RAG architecture by introducing a knowledge graph as the retrieval backbone. A knowledge graph represents real-world entities and their relationships in a structured form (nodes and edges), enabling machines to reason across connected concepts.
In a GraphRAG setup, unstructured content (like documents or transcripts) is first parsed to extract entities and relations. These are then used to construct a knowledge graph, representing domain knowledge as an interconnected network. LLM queries are enriched by retrieving relevant subgraphs instead of mere document chunks. The retrieved context offers relational grounding, leading to more accurate and interpretable answers.
This fusion of symbolic reasoning (via graphs) and generative capabilities (via LLMs) allows for more reliable outputs, especially in enterprise and high stakes use cases.
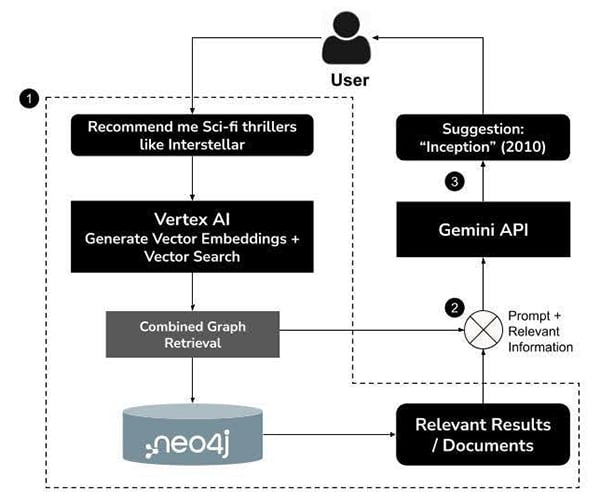
Use cases in action
The potential of GraphRAG is far-reaching. Consider applications in:
- Technical support systems, where understanding relationships between APIs, modules, and error codes is critical.
- Healthcare, where the interplay between symptoms, treatments, and patient history can be modelled as a graph for more accurate diagnostics.
- Legal tech, where the web of laws, cases, and precedents demands nuanced retrieval that simple semantic similarity cannot provide.
In each case, GraphRAG empowers LLMs to navigate complex domains by tapping into structured domain knowledge.
From vector search to hybrid intelligence
One of the unique aspects of GraphRAG is its hybrid retrieval model. Rather than discarding vector-based similarity, it combines it with graph-based traversal. This allows developers to:
- Use vector search for broad context or semantic matching.
- Apply graph queries (e.g., Cypher) to retrieve precise subgraphs.
- Combine both signals for a more refined retrieval pipeline.
This dual-mode approach ensures flexibility and performance, especially in use cases where both semantic richness and structural precision are essential.
Looking ahead: The rise of agentic GraphRAG
As developers increasingly move from simple Q&A bots to agent-based architectures, GraphRAG lays the foundation for agentic GraphRAG—a model where LLMs act as reasoning agents that navigate the knowledge graph autonomously.
In agentic GraphRAG:
- The LLM can generate and execute graph queries on its own.
- It can chain multiple hops to explore complex relationships.
- It may integrate with tools or APIs to act on its findings—booking a meeting, fetching reports, or synthesising insights.
This represents a shift from static retrieval to dynamic reasoning, positioning knowledge graphs not just as passive stores of information, but as interactive environments for intelligent agents.
GraphRAG is more than an architectural upgrade—it represents a philosophical shift in how we think about information retrieval in the age of generative AI. By combining the semantic depth of LLMs with the structural intelligence of knowledge graphs, we can unlock new levels of precision, explainability, and trust in AI applications.
As we look to the future, agentic GraphRAG offers a glimpse of what’s possible when machines don’t just retrieve knowledge but interact with it meaningfully. The fusion of symbolic and statistical AI may well be the bridge to the next wave of open, interpretable, and intelligent systems.