In these days of traffic congestion and autonomous driving, software that connects pedestrians and vehicles with governing bodies is the need of the hour. Open source simulation platforms for the Internet of Vehicles are enabling just that.
The Internet of Vehicles (IoV), a sub-segment of the Internet of Things (IoT), enables smart vehicular networks, smart urban infrastructure, wireless integrated smart ambulances, and more. Smart vehicular networks are today used for traffic law enforcement, as a part of e-governance and smart citizen services. IoV helps vehicles to communicate with each other with respect to the status of the traffic, keeping roads clear and safe. This wireless technology is particularly useful for autonomous driving.
Smart cities are about keeping us safe, helping our planet, and making life a lot more fun. Vehicles in smart cities and smart vehicular networks send information to each other using special communication called vehicle-to-everything (V2X). V2X helps vehicles communicate with each other, sends signals to traffic lights, and even provides information to people walking around. It helps car drivers be aware of what’s happening around them. It can make driving safer by giving a warning of any danger ahead and can help ambulances get through traffic really fast.
Simulation tools and scenarios are being used for research and development in the fields of smart cities and vehicular networks. These provide a controlled, cost-effective environment to model, analyse, and optimise complex urban transportation systems before real world implementation. They analyse complex scenarios to mitigate risks and ensure roads are safe for everyone.
Figure 1: Smart city and wireless connected vehicles
A few important free and open source platforms for IoV simulation for research are described briefly here.
SUMO (Simulation of Urban MObility)
URL: https://eclipse.dev/sumo/
SUMO is powerful and multi-functional open source software supporting microscopic traffic simulation. It is used for the simulation of IoV-based scenarios in smart cities. It can simulate smart traffic forecasting, evaluation of traffic lights, automated driving, vehicle communication, and urban mobility planning and analysis. It combines with artificial intelligence and data science for multi-dimensional data evaluation and predictions.
Eclipse SUMO supports automated driving and vehicle communication simulations so that smart IoV scenarios can be investigated effectively with the use of emerging technologies. Intermodal traffic systems including road vehicles, public transport, and pedestrians can be integrated in simulation scenarios. It offers traffic management capabilities with video detectors and induction loops, and provides online interaction through its Traffic Control Interface (TraCI).

CupCarbon
URL: https://www.cupcarbon.com/
CupCarbon is an open source simulator supporting multiple programming languages so that IoT integrated vehicular networks can be analysed and controlled. The features that enable it to simulate vehicular communication include:
- Wireless simulator for simulation of smart cities
- Smart vehicular network
- Advanced wireless protocols with IoT integration
OMNeT++
URL: https://omnetpp.org/
OMNeT++ is a modular, component-based C++ simulation library and framework. It simulates communication networks, internet protocols, performance modelling of network systems, and wireless ad-hoc networks. It has extensible and modular architecture for building network simulators, and supports wired and wireless communication networks. Integration of on-chip networks and the INET framework helps simulate communication networks.
PTV VISSIM
URL: https://www.ptvgroup.com/en/products/ptv-vissim
This microscopic, multimodal traffic flow simulation software helps with:
- Public transport and urban planning
- Evaluation and optimisation of transport infrastructure performance
- Traffic engineering and transportation planning
- Evaluation of traffic signal operations
- Traffic patterns of all road users on a microscopic scale
It analyses traffic congestion, emissions, and road space distribution.
MATSim (Multi-Agent Transport Simulation Toolkit)
URL: https://matsim.org/
- This open source project for agent-based transport simulations features:
- Large-scale transport simulations
- Modules for demand modelling
- Toolbox for large-scale agent-based transport simulations
- Agent-based mobility studies
- Modules for re-planning the road network
- Transportation demand modelling
- Modules for mobility simulation
It allows iterative simulation runs and output analysis.
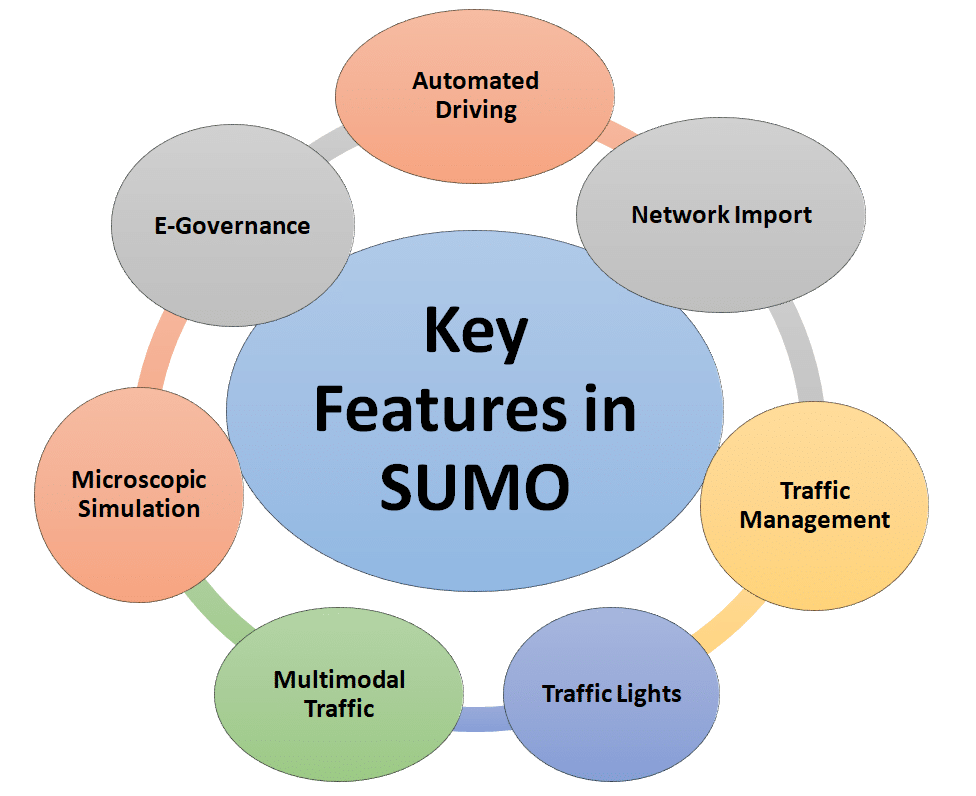
Working with the SUMO simulator
SUMO is free and open source, highly portable, microscopic, and offers a continuous road traffic simulation package designed to handle large road networks. It is widely used for modelling and analysing traffic scenarios in smart city and vehicular network research.
SUMO can be downloaded from the official website. Use the link https://sumo.dlr.de/docs/Downloads.html. Its key components are:
Netedit: This graphical user interface (GUI)-based network editor is used to create and modify road networks and vehicular communications. Multiple vehicles of different types can be created.
sumogui: This is a GUI-based working panel for running and visualising the simulations associated with urban mobility and vehicular communications.
netconvert: netconvert is used to import the road networks from various sources for a real-time look at the implementation scenarios.
od2trips: od2trips is used to import the origin-destination traffic along with zone information. It helps analyse the simulation from multiple perspectives.
Here’s how you can create a simulation scenario using SUMO.
- Open netedit to design a road network with vehicular information.
- The network scenario can be created from the interface available at osmWebWizard.
- Traffic demand is implemented with a route xml file that specifies the types of vehicles, multiple routes, departure time and related information.
- The GUI of Sumo is launched by loading the sumocfg file to visualise the simulation.
The Open Street Map is used with osmWebWizard so that a real-time map of the city or specific location can be accessed. SUMO modules integrate random traffic with real-time roads so that simulations using various algorithms can be done effectively.
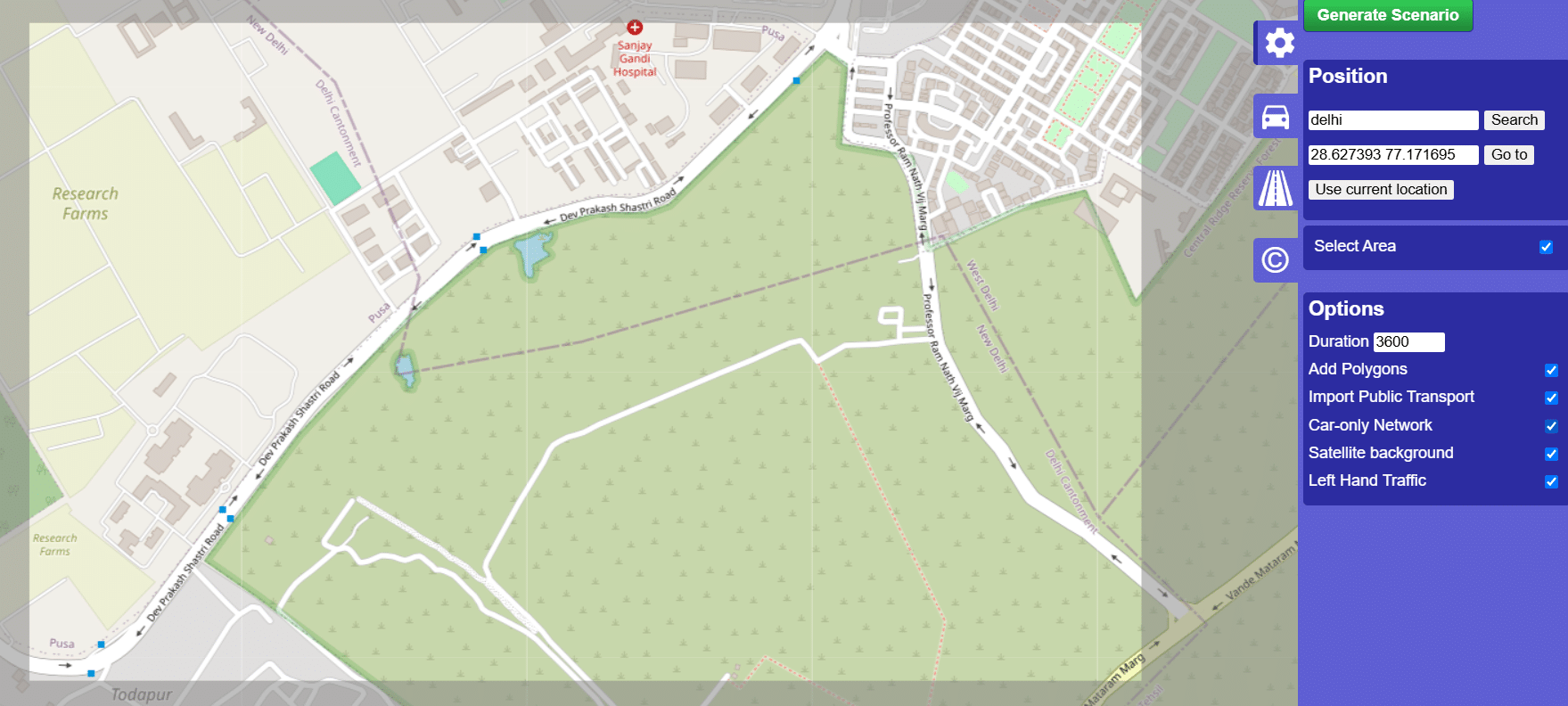
Once the scenario is created on SUMO, there are multiple options to simulate the designed network on different types of interfaces.
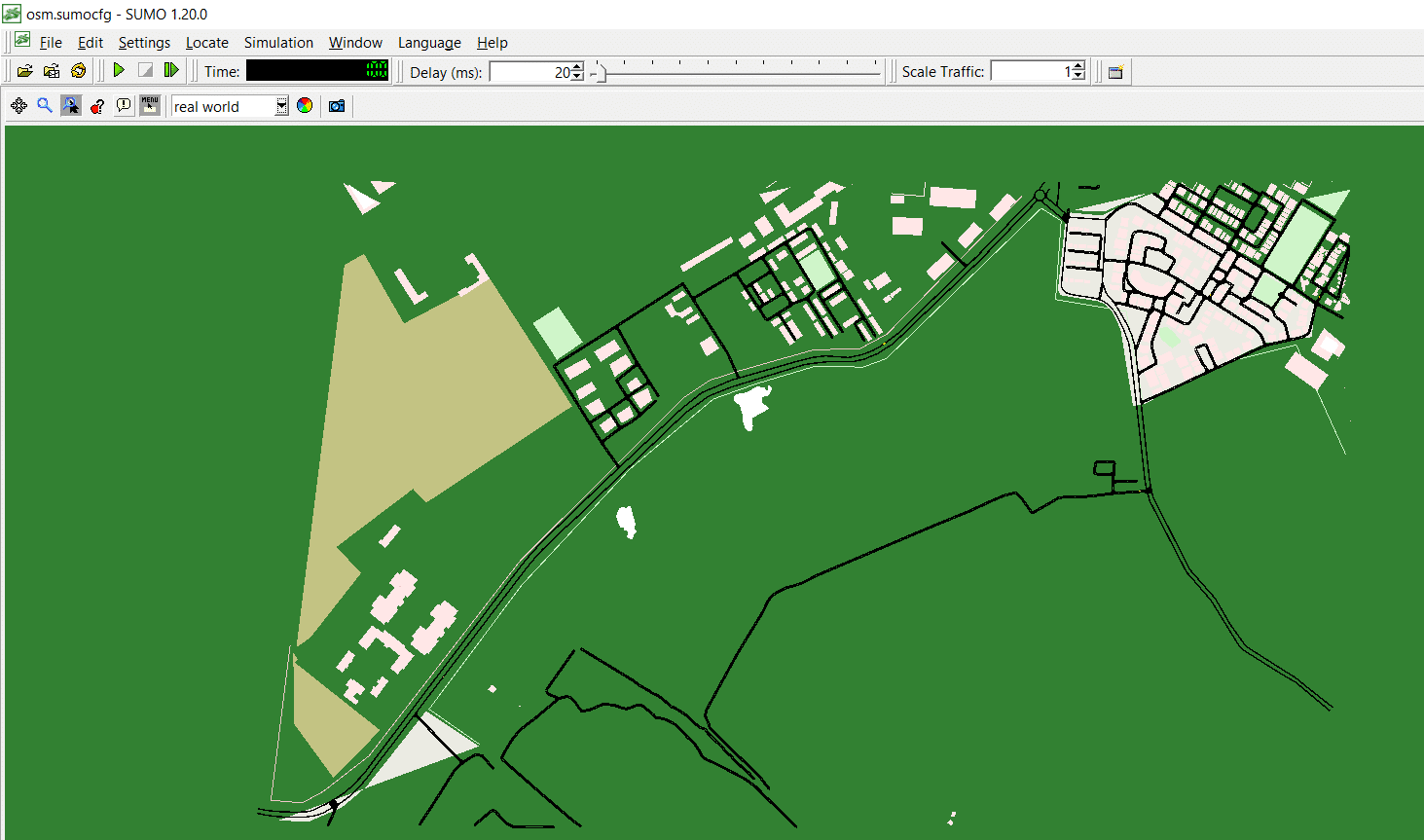
Researchers continue to experiment with the simulation of smart cities and smart vehicular networks on a wide range of parameters so that the status of the traffic can be evaluated. The key domains of current research include vehicle to grid (V2G) communication, edge and cloud computing for IoV, and vehicle to everything (V2X) communication. Vehicle to pedestrian (V2P), vehicle to vehicle (V2V), vehicle to infrastructure (V2I), and vehicle to network (V2N) communication are further areas of research.