This comprehensive overview of the Microsoft Agentic Framework focuses on its latest features, practical implementation, real-world use cases, and the strategic benefits it brings to modern solution architecture.
The Microsoft Agentic Framework is rapidly emerging as a cornerstone for developers, architects, and technology leaders seeking to build dynamic, intelligent systems powered by multiple collaborating agents. In an era where automation, distributed intelligence, and adaptive software are increasingly vital, this framework offers robust tools and features to accelerate the design and deployment of agent-based solutions.
What is the Microsoft Agentic Framework?
The Microsoft Agentic Framework (MAF) is an SDK and governance model for building systems composed of cooperating software agents. Each agent perceives context, plans action, invokes tools, and exchanges messages with peers to complete tasks. At its core, the Microsoft Agentic Framework is a set of libraries, APIs, and runtime components designed to simplify the creation and orchestration of software agents. These agents are autonomous entities capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and cooperating with other agents to achieve complex objectives. The framework abstracts much of the complexity involved in communication, state management, and coordination, enabling developers to focus on business logic and system goals.
Its key concepts are:
- Agent: A bounded unit with role, capabilities, memory, and objectives.
- Capability (Tool): A callable function or external service an agent can use.
- Message: Typed payload with headers for identity, causality, and policy decisions.
- Policy: Declarative rules that allow, transform, redact, or block actions.
- Plan: A structured decomposition of a goal into steps with dependencies.
- Memory: Context cache (short-term) and knowledge retrieval (long-term).
- Orchestration: Assignment, routing, and synchronisation across agents.
- Evaluation: Offline tests and online telemetry used to score quality, safety, and cost.
New features of the Microsoft Agentic Framework
The latest release of the Microsoft Agentic Framework introduces several enhancements aimed at improving scalability, intelligence, and developer productivity. Here are the most notable new features.
Enhanced multi-agent communication protocols
The framework now supports advanced messaging standards, allowing agents to communicate using secure, asynchronous channels. This improvement facilitates both real-time collaboration and reliable message delivery, even in distributed environments.
Plug-and-play agent modules
Developers can now integrate pre-built agent modules or create reusable components that can be plugged into existing solutions. This modular approach accelerates development and encourages best practices in code reuse.
Adaptive learning capabilities
Agents can be equipped with machine learning models that enable them to adapt their behaviours based on historical data and environmental feedback. These adaptive agents can refine their strategies over time, leading to smarter, more effective systems.
Visual orchestration designer
A new graphical interface allows architects to design, configure, and monitor agent workflows visually, reducing the learning curve and improving transparency in complex solutions.
Robust monitoring and diagnostics
The framework includes comprehensive tools for logging, real-time monitoring, and diagnostics, making it easier to identify bottlenecks, troubleshoot issues, and ensure system reliability.
Step-by-step guide: Utilising the new features of MAF for multi-agent development
Step 1: Setting up the framework
Install the Microsoft Agentic Framework via NuGet or the preferred package manager:
dotnet add package Microsoft.AgenticFramework
Step 2: Defining agents and capabilities
Create a basic agent by inheriting from the AgentBase class and implementing the desired behaviours:
public class WeatherAgent : AgentBase
{
public override Task OnMessageAsync(MessageContext context)
{
if (context.Message.Type == “GetWeather”)
{
var weatherInfo = FetchWeather(context.Message.Payload);
return context.RespondAsync(new Message(“WeatherResponse”, weatherInfo));
}
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
This agent responds to weather queries and demonstrates how agents can process messages asynchronously.
Step 3: Orchestrating agents visually
Launch the visual orchestration designer provided with the framework. Drag and drop agent modules, define message flows, and set up triggers. This step allows you to design complex agent interactions without deep coding.
Step 4: Enabling adaptive learning
Integrate machine learning capabilities using the framework’s built-in support:
public class AdaptiveAgent : AgentBase
{
private readonly ILearningModule _learningModule;
public AdaptiveAgent(ILearningModule learningModule)
{
_learningModule = learningModule;
}
public override async Task OnMessageAsync(MessageContext context)
{
var prediction = await _learningModule.PredictAsync(context.Message.Payload);
await context.RespondAsync(new Message(“PredictionResult”, prediction));
}
}
This approach allows agents to make data-driven decisions and evolve their responses over time.
Step 5: Monitoring and diagnostics
Leverage the built-in monitoring dashboard to track agent health, message throughput, and system performance. Set up alerts for anomalies and review diagnostic logs for troubleshooting.
This architecture is helpful in the following aspects.
- Agility: The framework’s modular architecture and visual tools allow rapid prototyping and iteration, enabling teams to adapt solutions swiftly to changing requirements.
- Extensibility: With plug-and-play modules and support for third-party integrations, the framework accommodates evolving business needs without necessitating extensive rewrites.
- Reliability: Robust monitoring, diagnostics, and secure communication protocols ensure that agentic solutions are dependable and resilient to failures.
- Cost-effectiveness: By promoting code reuse, streamlining development, and reducing maintenance overhead, the framework helps organisations control costs while delivering sophisticated, scalable solutions.
Common use cases for the Microsoft Agentic Framework
The Microsoft Agentic Framework (MAF) supports diverse real-world scenarios where distributed intelligence, autonomy, and collaboration drive measurable business outcomes. Its modularity, interoperability with Azure AI, and built-in orchestration features make it suitable for multiple verticals.
Enterprise knowledge automation
Agents can manage and synthesise knowledge from multiple data silos—SharePoint, Teams, Outlook, or Dynamics 365—enabling organisational intelligence through context-aware responses. A ‘Retriever-Reasoner-Critic’ agent chain can produce consistent, auditable outputs that comply with enterprise policies.
Sustainability and smart cities
Multi-agent systems coordinate environmental sensors, transportation units, and energy grids. Agents use telemetry data to balance power demand, optimise traffic flow, and minimise carbon footprint. Integration with Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins accelerates predictive simulations of urban dynamics.
Cybersecurity operations and threat intelligence
Security analysts can deploy detector, correlator, and responder agents for real-time intrusion detection. Agents collaborate through MAF’s secure message bus, automatically escalating anomalies to SOC teams. Reinforcement learning improves incident classification accuracy over time.
Manufacturing and industrial IoT
Edge-deployed agents monitor machines, predict maintenance needs, and autonomously schedule service tasks. Each agent aligns with an OPC-UA data model and feeds telemetry to Azure Monitor. The framework ensures deterministic communication and resilient failover in harsh environments.
Education and personalised learning systems
Tutor, evaluator, and recommender agents provide adaptive learning paths for students. They analyse learner profiles, performance metrics, and behavioural cues to customise lesson delivery—aligned with ethical AI guidelines and student privacy regulations.
Healthcare decision support and telemedicine
Diagnostic agents analyse patient records and imaging data; scheduler agents coordinate care between physicians and patients. MAF’s compliance with HIPAA and ISO/IEC 23894 standards ensures responsible data handling and explainable AI recommendations.
Finance and algorithmic governance
Autonomous trading, fraud detection, and credit-risk analysis benefit from cooperative agent networks. MAF’s deterministic orchestration guarantees model transparency and traceability—essential for auditability under regulatory scrutiny such as GDPR and DPDP 2023.
How MAF’s features help in solution design
| Feature | Description | Usefulness in solution design |
| Multi-agent communication protocols | Secure, asynchronous messaging between agents | Facilitate real-time collaboration, support distributed architectures |
| Plug-and-play modules | Reusable, interchangeable agent components | Accelerate development, promote modular design |
| Adaptive learning | Integrates machine learning for agent adaptation | Enables intelligent, evolving behaviours |
| Visual orchestration designer | Graphical workflow editor for agent coordination | Reduces complexity, enhances solution transparency |
| Monitoring and diagnostics | Real-time performance tracking and troubleshooting | Improve reliability and operational insight |
Advantages of the Microsoft Agentic Framework
The Microsoft Agentic Framework delivers enterprise-grade reliability and governance across the agentic lifecycle—from design to deployment—making it a strategic foundation for AI-driven organisations.
Scalability and performance engineering
The framework’s asynchronous message bus and lightweight runtime enable horizontal scaling across Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) or hybrid on-premises clusters. Developers can instrument p95 latency, message throughput, and recovery time objectives (RTO) as explicit non-functional metrics.
Composable architecture and interoperability
Agents communicate through well-defined contracts and shared schemas, ensuring modular substitution without code rewrites. Integration layers link seamlessly with Azure OpenAI Service, Cognitive Search, Fabric Dataflows, and Power Platform connectors.
Adaptive intelligence and lifelong learning
Agents embed learning modules that continuously refine strategies via reinforcement or supervised updates. This allows self-optimisation, enabling autonomous adaptation to changing datasets, environments, and objectives.
Governance, compliance, and security
Built-in policy engines enforce compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Access tokens and message-level encryption safeguard sensitive data flows. The audit subsystem maintains cryptographically signed logs for accountability and model lineage tracking.
Observability and diagnostics
MAF’s telemetry stack integrates with Azure Monitor Application Insights to visualise message paths, error rates, and agent health. This observability supports root-cause analysis, performance tuning, and compliance verification.
Developer productivity and reusability
The SDK’s declarative configuration model, template agents, and CI/CD integration reduce time-to-market. Teams can deploy reproducible experiments and enforce coding standards through automated quality gates in Azure DevOps pipelines.
Resilience and fault tolerance
Support for checkpointing, replay queues, and dead-letter handling ensures recovery from partial failures. Multi-agent consensus mechanisms increase overall system robustness against node loss or message duplication.
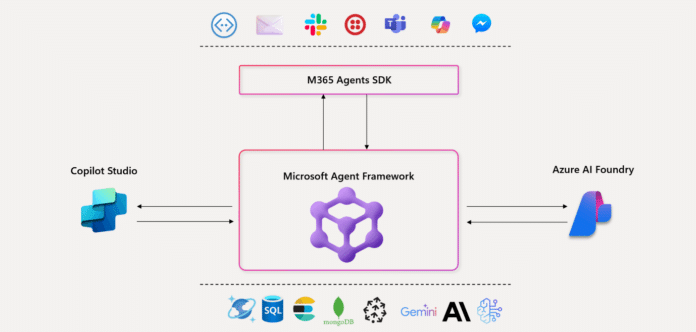
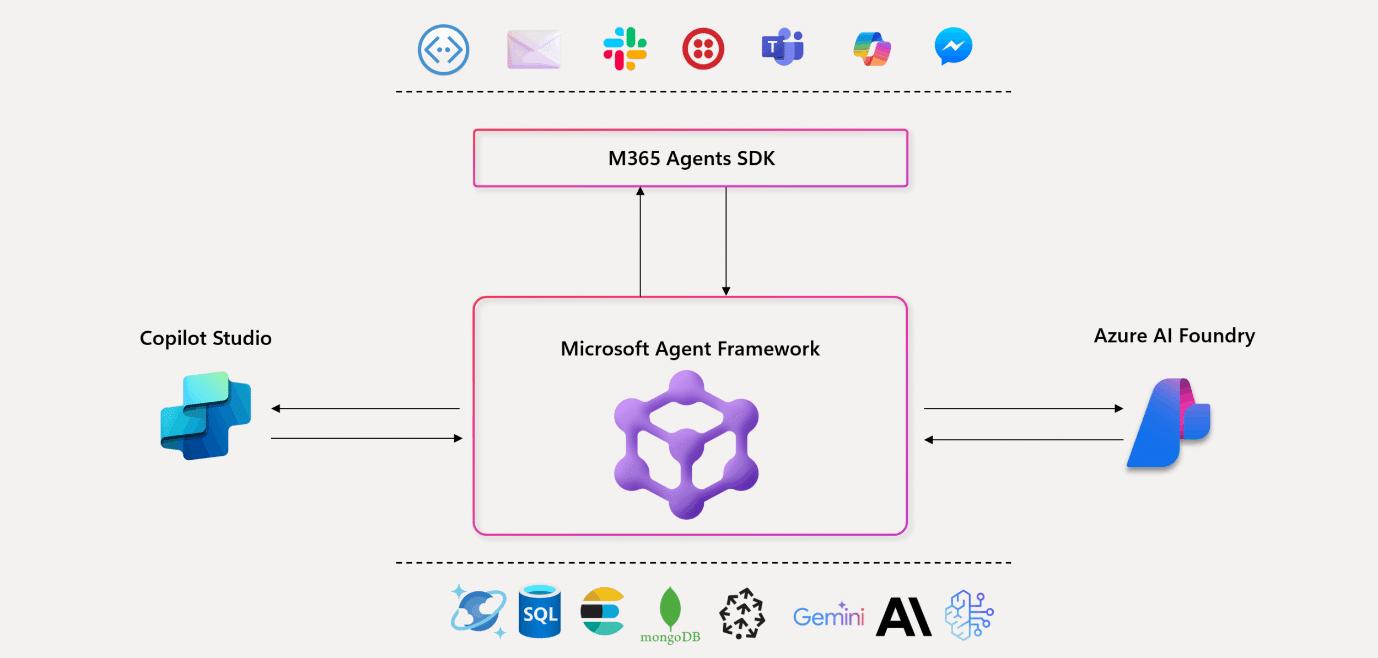
Features of the Microsoft Agentic Framework SDK
The Microsoft Agentic Framework SDK is a powerful open source toolkit designed for developers to build, deploy, and manage sophisticated multi-agent AI applications. It provides a developer-first approach to creating AI agents and workflows, with support for both .NET and Python. Here are some of its key features.
Agent and multi-agent workflow creation
The framework allows for the creation of individual AI agents and the orchestration of complex workflows involving multiple agents. This enables the development of sophisticated applications, where different agents can collaborate to achieve a common goal.
State and storage management
This feature provides capabilities to build an agent ‘container’ that includes state management and storage. This allows agents to maintain context and memory across interactions, which is crucial for more complex and long-running tasks.
Event and activity management
The SDK includes features for managing activities and events, enabling agents to react to and process real-time information and triggers. This is essential for building dynamic and responsive AI applications.
Support for .NET and Python
The framework is designed to be accessible to a wide range of developers by providing support for two of the most popular programming languages — .NET and Python.
Microsoft’s Agent Framework is built with the developer in mind, offering a modern and intuitive experience for building agents. It supports key APIs and languages, making it easier to integrate with existing development practices. As an open source SDK, the framework encourages collaboration and community contributions. This allows for greater transparency, flexibility, and the potential for rapid innovation.
While there is a specific ‘Microsoft 365 Agents SDK’, the broader agent framework is designed to work within the Microsoft ecosystem, enabling integrations with services like Microsoft 365. This allows developers to create agents that can interact with and leverage data from Microsoft’s productivity suite.
The framework is also designed to work seamlessly with Microsoft Azure, providing a scalable and robust platform for deploying and managing agent-based applications in the cloud.
The Microsoft Agentic Framework stands at the forefront of multi-agent software development, empowering teams to build intelligent, collaborative, and adaptive systems with unprecedented ease. Its latest features make it a compelling choice for modern solution design. By embracing this framework, organisations can unlock new levels of agility, extensibility, reliability, and cost efficiency, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.