Lets developers add LLM-powered intelligence to software with a single line of code eliminating manual prompt engineering and speeding up AI-enabled application development.
A new open-source programming framework is redefining how developers embed AI into software, enabling large language models to plug into existing codebases without any hand-crafted prompts. Presented at a major programming languages conference in Singapore and published in a leading academic journal, the approach called a “meaning-typed programming” paradigm promises to remove one of the biggest bottlenecks in real-world AI integration: prompt engineering.
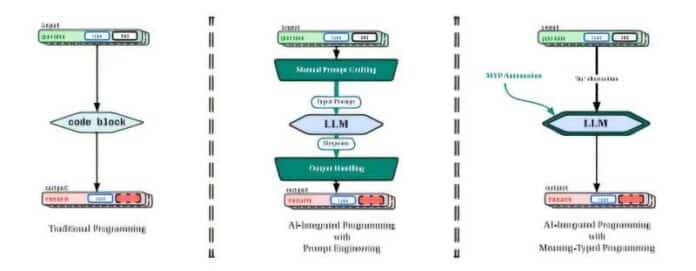
Traditionally, software and AI models operate on fundamentally different assumptions. Conventional programs rely on deterministic operations over well-defined data structures. LLMs, meanwhile, expect loosely structured natural-language text. Bridging those worlds forces developers to manually assemble textual prompts that encode context, intent and variable values often requiring hundreds of lines of carefully tuned template code. This manual process is not only slow and error-prone but also difficult to scale across large projects.
The new framework introduces a single operator that allows developers to invoke LLM reasoning as easily as calling a function. Behind that single line of code sits a compiler built on a meaning-typed intermediate representation that analyzes the semantics of the surrounding program. A runtime engine then uses that semantic map to automatically generate focused, context-aware prompts for the LLM. The system effectively “understands” what the programmer intends and produces the necessary instructions for the AI model, eliminating the need for manual prompt crafting.
Evaluations show notable gains: higher accuracy, lower latency and stronger robustness compared to existing prompt-automation solutions such as DSPy. In a user study, developers completed tasks more than three times faster and wrote nearly half the lines of code typically required for AI-augmented features. By collapsing the gap between traditional programming and model-driven inference, the framework significantly reduces engineering overhead in workflows where rapid experimentation and precise outputs matter.
The open-source release has already attracted thousands of downloads, with early adopters exploring use cases in domains that increasingly rely on hybrid software-AI systemsfinance, customer support, education, health services and research tooling. By enabling LLM integration without prompt engineering expertise, the framework lowers the barrier to AI-driven development and could accelerate the creation of personalized applications, intelligent agents and domain-specific automation tools. For developers and teams under pressure to ship AI-enhanced features, the ability to add LLM reasoning through a single line of code signals a shift toward more accessible, intent-aware software design.