The metaverse, where real life converges with the digital world, has given birth to many new age business models and use cases. Digital twins within the metaverse offer new ways of interacting with the real world. Let’s see how…
One of the key technologies driving the evolution of the metaverse is that of digital twins. Most popular in the retail industry, a digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object or system, offering a comprehensive digital representation that can be used for various purposes. When combined with the metaverse, digital twins can enable new ways of experiencing and interacting with the real world.
Architecture of metaverse-based digital twins
The architecture of a metaverse-based digital twin consists of several layers. At the bottom layer is the physical asset or system that the digital twin is replicating. This could be anything from a building, to a manufacturing plant, to a vehicle. The physical asset is equipped with sensors and other IoT devices that collect data on its operations, condition, and performance. This data is then transmitted to the digital twin, which is hosted in the cloud or on-premises.
The next layer is the data processing layer, which consists of several components that work together to process the data collected from the physical asset. This layer typically includes data ingestion and storage, data processing and analysis, and data visualisation and reporting. Data ingestion and storage involves collecting data from various sources, and storing it in a scalable and secure data store. Data processing and analysis involves applying advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to the collected data to extract insights and identify patterns. Data visualisation and reporting involves presenting the results of the analysis in an easy-to-understand format.
The third layer is the digital twin layer, which is responsible for creating a virtual representation of the physical asset or system. The digital twin layer consists of several components, including the virtualization engine, the digital twin model, and the digital twin APIs. The virtualization engine is responsible for creating and managing the digital twin, while the digital twin model defines the relationships between the physical asset and its virtual counterpart. The digital twin APIs provide an interface for interacting with the digital twin, enabling users to view and manipulate the virtual representation of the physical asset.
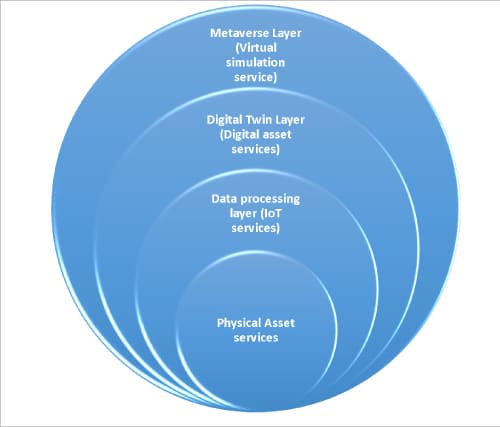
The fourth layer is the metaverse layer, which is where the digital twin is brought to life. The metaverse layer consists of several components, including the immersive environment, the social interaction engine, and the real-time simulation engine. The immersive environment is the virtual space where the digital twin is presented, while the social interaction engine enables users to interact with each other in the virtual world. The real-time simulation engine is responsible for simulating the behaviour of the physical asset in real-time, based on the data collected from the IoT devices.
Components of metaverse-based digital twins
The components of a metaverse-based digital twin can be grouped into several categories. These categories include the physical asset, the data collection and processing components, the digital twin model, the virtualization engine, and the metaverse components.
The physical asset component consists of the physical object or system that the digital twin is replicating. This component includes all the sensors and IoT devices that collect data on the physical asset’s operations, condition, and performance.
The data collection and processing components are responsible for collecting, storing, and analysing the data collected from the physical asset. These components typically include data ingestion and storage, data processing and analysis, and data visualisation and reporting.
The digital twin model component defines the relationships between the physical asset and its virtual counterpart. This component includes the digital twin model, which is a comprehensive representation of the physical asset, and the digital twin APIs, which provide an interface for interacting with the digital twin.
The integration of digital twins with metaverse solutions has proven to be advantageous in several ways. Digital twins offer a virtual replica of physical entities, and metaverse solutions provide a platform to integrate them into a virtual environment. This combination enables businesses to harness the benefits of both technologies to enhance their operations and offerings.
One significant advantage of digital twins with metaverse solutions is improved efficiency. By creating a virtual replica of physical entities, businesses can simulate operations and analyse data to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This process can lead to better resource allocation, reduced downtime, and optimised operations. For example, in the manufacturing industry, digital twins with metaverse solutions can be used to simulate production processes and identify areas for optimisation, leading to increased production rates and reduced waste.
Another advantage of this solution is improved customer experience. By creating virtual environments that allow customers to interact with digital twins, businesses can offer a more immersive and engaging experience. For instance, in the retail industry, customers can virtually try on clothes or see how furniture would look in their homes before making a purchase.
Digital twins with metaverse solutions also offer improved remote collaboration. By creating virtual workspaces, businesses can allow employees to collaborate on projects, regardless of their physical location. This approach can reduce the need for travel and increase productivity.
Furthermore, digital twins with metaverse solutions offer improved safety and risk management. By simulating scenarios and predicting potential risks, businesses can identify and mitigate safety hazards before they occur. For example, in the oil and gas industry, digital twins with metaverse solutions can be used to simulate drilling operations and identify potential risks.
The integration of digital twins with metaverse solutions offers several advantages, including improved efficiency, enhanced customer experience, improved remote collaboration, and improved safety and risk management. As these technologies continue to evolve, the potential for innovative applications and new advantages will continue to emerge.
Industrial applications of metaverse-based digital twins
Metaverse technology with digital twins is rapidly evolving and transforming various industrial sectors by enhancing customer experiences, optimising business operations, and improving overall efficiency. This technology has the potential to revolutionise how industries operate.
Retail industry: In the retail sector, digital twins within the metaverse help create an immersive shopping experience. Virtual stores set up with digital twins technology enable customers to experience products in a 3D environment. Customers can view products, interact with them, and get an accurate representation of how these look and feel. This technology can also help retailers in optimising inventory management and supply chain management.
Healthcare industry: Metaverse with digital twins can enable healthcare professionals to monitor patients remotely and provide more personalised treatments. The technology can help doctors simulate patient conditions, analyse treatment options, and improve patient outcomes. It can also aid in creating realistic surgical simulations that can help train surgeons.
Manufacturing industry: In the manufacturing sector, digital twins within the metaverse help create a digital thread for products. This allows manufacturers to track products throughout their life cycle from design to production, delivery, and even end-of-life disposal.
Digital twins technology can also aid in optimising production processes by simulating different scenarios and analysing the results to identify the most efficient process.
Telecom industry: In the telecom sector, metaverse and digital twins enable the creation of a virtual network. Digital twins technology can help in creating a virtual representation of the entire network, including all devices and connections. This virtual network can help telecom companies to improve network performance and identify potential network issues.
Automotive industry: In the automotive sector, metaverse and digital twins can enable a more personalised driving experience. Digital twins technology can help to create a virtual representation of the car, including all its components, systems, and software. This representation can help in optimising the car’s performance, identifying potential issues, and providing a more personalised driving experience.
Common challenges of developing digital twins with the metaverse
Developing digital twins with the metaverse can present various challenges due to the complexity and emerging nature of these technologies. Here are some common problems that developers may encounter.
Data integration and interoperability: Integrating real-time data from physical objects or systems into digital twins within the metaverse can be challenging. Ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different data formats, protocols, and devices can pose technical hurdles. Developing robust data pipelines and standardisation methods is crucial to ensure seamless data integration.
Scalability and performance: Building digital twins that can handle a large number of concurrent users and complex interactions within the metaverse can strain system resources. Scaling the infrastructure to support a growing user base and maintaining optimal performance, such as low latency and high responsiveness, can be demanding tasks.
Security and privacy: Digital twins often involve sensitive data, such as information about physical assets or personal user data. Ensuring the security and privacy of this data throughout the digital twin-metaverse ecosystem is critical. Implementing robust security measures including authentication, encryption, and access controls is essential to protect against unauthorised access, data breaches, and privacy violations.
Realism and immersion: Achieving a high level of realism and immersion within the metaverse can be a significant challenge. Creating realistic and detailed virtual environments that accurately represent the physical counterparts of digital twins requires advanced rendering techniques, physics simulations, and detailed asset modelling. Striving for a seamless integration of the physical and virtual worlds is essential for an immersive experience.
User experience and interaction: Designing intuitive and engaging user experiences within the metaverse is crucial for user adoption. Ensuring smooth and natural interactions between users and their digital twins, as well as with other users, requires thoughtful interface design, haptic feedback, natural language processing, and gesture recognition. Balancing usability, functionality, and immersion is a key consideration.
Standardisation and interoperability: With multiple platforms and technologies emerging in the space, lack of standardisation and interoperability can be a challenge. Ensuring compatibility and seamless integration between different digital twin platforms, metaverse environments, and devices is essential for a cohesive and connected ecosystem. The development of industry-wide standards and protocols can help address this challenge.
Cost and infrastructure requirements: Developing and maintaining digital twins with the metaverse can involve significant costs. Creating high-fidelity virtual environments, managing real-time data streams, and ensuring robust infrastructure can require substantial investments. Managing the cost-effectiveness of development and deployment, while providing a quality user experience, can be a delicate balance.
Ethical considerations: As digital twins become more prevalent and interconnected within the metaverse, ethical considerations arise. Issues such as data ownership, data privacy, algorithmic bias, and potential misuse of digital twins need to be addressed. Establishing ethical guidelines and frameworks to govern the development and use of digital twins within the metaverse is important.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including developers, researchers, industry experts, and policymakers. As technology advances and the field matures, solutions and best practices will continue to evolve to overcome these obstacles.
Popular platforms and solutions for digital twins within the metaverse
Unity3D: This is a widely used game development platform that has expanded its capabilities to support the creation of virtual and augmented reality experiences. It provides tools and features for building immersive environments and integrating digital twins with the metaverse.
Unreal Engine: Developed by Epic Games, this is another popular game engine that offers robust capabilities for creating interactive and realistic virtual worlds. It can be utilised to develop metaverse experiences and integrate digital twins into these environments.
NVIDIA Omniverse: NVIDIA Omniverse is a platform that aims to connect virtual worlds, simulations, and collaborative environments. It provides a framework for creating digital twins, and enables real-time rendering and interaction within the metaverse.
Microsoft Azure Digital Twins: This cloud-based platform is designed for building comprehensive digital representations of physical environments. It allows users to model, simulate, and analyse real-world systems, and can be integrated with metaverse applications to create immersive experiences.
Siemens MindSphere: Siemens MindSphere is an industrial IoT platform that supports the development of digital twins. It enables the integration of real-time data from physical assets with virtual representations, and can be combined with metaverse technologies to create immersive industrial simulations and analytics.
Autodesk Forge: This cloud-based development platform provides tools for creating and managing digital twins. It offers capabilities for visualising and interacting with digital representations of physical assets, which can be leveraged in the context of the metaverse.
IBM Maximo: IBM Maximo is an enterprise asset management platform that includes digital twin functionality. It enables the creation and management of digital twins for assets and infrastructure, and can be integrated with metaverse solutions to provide a holistic view of assets and environments.
PTC ThingWorx: This industrial IoT platform supports the development of digital twins and the integration of real-time data from sensors and devices. It can be used to create digital twins that can interact with the metaverse and provide real-time insights.
What the future holds
Digital twins and the metaverse are two emerging technologies that are expected to shape the future of our digital world. When combined, they can bring about significant advancements and transformative experiences. Here are some potential future trends.
Enhanced virtual collaboration: Digital twins in the metaverse can enable immersive and collaborative experiences. Users will be able to interact with each other and their digital representations in a shared virtual environment. This can revolutionise remote collaboration, allowing teams from around the world to work together seamlessly.
Real-time data integration: Digital twins can collect real-time data from physical objects or systems and integrate it into the metaverse. This will provide a dynamic and up-to-date representation of the physical world, enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and simulations.
For example, a digital twin of a smart city could incorporate live data on traffic, energy usage, and weather conditions.
Personalised virtual spaces: With the metaverse, individuals can have their own customisable virtual spaces. These spaces can be connected to their digital twins, allowing them to personalise their virtual environment based on their preferences, needs, and interests. Users can also interact with their digital twins within these spaces, creating a personalised and immersive experience.
IoT integration: Internet of Things (IoT) devices can be connected to digital twins within the metaverse, enabling enhanced functionality and control. For instance, a smart home digital twin could integrate with IoT devices such as thermostats, cameras, and appliances, allowing users to remotely monitor and control their physical environment from the metaverse.
AI-driven simulations and predictions: The combination of digital twins and the metaverse can facilitate advanced simulations and predictions powered by artificial intelligence. By leveraging historical data and machine learning algorithms, digital twins can simulate scenarios, predict outcomes, and optimise performance in various domains such as manufacturing, healthcare, and urban planning.
Virtual commerce and experiences: The metaverse can serve as a platform for virtual commerce, where users can engage in virtual shopping experiences, try out products before purchasing, and interact with virtual representations of real-world stores. Digital twins can enhance these experiences by providing accurate and realistic representations of products and environments.
Cross-platform interoperability: As the metaverse evolves, interoperability between different platforms and systems will become crucial. Digital twins can act as a bridge between various virtual worlds and environments, enabling seamless transfer of data and experiences across different platforms and applications.
Digital twin economies: The metaverse can give rise to new economic models centred around digital twins. Users could create, own, and trade digital twins representing physical assets, virtual goods, or even intellectual property. This could lead to the emergence of digital twin marketplaces and economies, where individuals and businesses can monetise their digital assets.
These trends demonstrate the potential of combining digital twins with the metaverse to create immersive, interconnected, and intelligent digital experiences. However, it’s important to note that these trends are speculative, and the actual implementation and adoption of these technologies may vary as they continue to develop.
In conclusion, the metaverse with digital twins has the potential to revolutionise different industrial sectors but we need to keep in mind certain roadblocks like infrastructure cost, security challenges, compliance issues, and so on.