Open source metaverse platforms hold the key to a future world of infinite possibilities. These platforms are inclusive, easily accessible, community driven and encourage innovation. We take a quick look at some of them.
The concept of a metaverse, a virtual shared space where users can interact with a computer-generated environment and other participants, has captivated the imagination of both technology enthusiasts and creative minds. Metaverse platforms represent a vision of a virtual reality space where individuals can interact, create, and explore together. Open source metaverse platforms leverage the power of collaboration, transparency, and community engagement to create a shared virtual environment that fosters creativity, innovation, and inclusivity.
An open source metaverse platform takes the metaverse experience a step further, offering a collaborative, customisable, and accessible virtual reality experience. In this article, we explore the concept of an open source metaverse platform, its benefits, and its potential impact on various industries and communities.
Importance of open source in metaverse development
Metaverse is an immersive virtual space that transcends traditional boundaries, allowing users to navigate and interact with a computer-generated environment using avatars or virtual representations of themselves. It combines elements of augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality, enabling social connections, exploration, and creation in a digital realm.
Open source metaverse platforms have gained traction due to their collaborative and inclusive nature. These platforms, built on open source technologies, allow developers and communities to contribute, modify, and extend the platform’s capabilities, fostering a sense of ownership and creativity among users.
Benefits of open source for metaverse platforms
Open source metaverse platforms face certain challenges, such as ensuring data privacy, addressing security concerns, and maintaining user safety within the virtual environment. Balancing customisation and standardisation, fostering community engagement, and managing diverse contributions require effective governance and moderation. However, they do come with a few benefits.
Collaboration and customisation: Open source metaverse platforms empower users to collaborate in building and shaping the virtual environment. Developers and users can contribute code, assets, and features, enabling customisation and personalisation. This collective effort fosters a diverse and dynamic metaverse that reflects the interests and needs of its users.
Accessibility and inclusivity: Such platforms prioritise accessibility, ensuring that the virtual reality experience is available to a wider audience. They can run on various devices and operating systems, enabling users to participate regardless of their hardware limitations. Furthermore, open source communities often emphasise inclusivity, addressing accessibility challenges and promoting diverse user experiences.
Innovation and community engagement: The open source nature of metaverse platforms encourages innovation and experimentation. Developers can build upon existing features, introduce new functionalities, and integrate emerging technologies such as AI, blockchain, and spatial computing. Community engagement plays a vital role in shaping the direction and evolution of the platform, creating a vibrant ecosystem of creators and users.
Community-driven development and collaboration: Open source metaverse platforms embody the spirit of collaboration, customisation, and inclusivity in the virtual reality landscape. These platforms offer a transformative experience that transcends geographical boundaries, fostering creativity, innovation, and social connections. As technology progresses and communities continue to contribute, the open source metaverse will unlock new possibilities, shaping the future of immersive experiences, education, entertainment, commerce, and healthcare.
Community-driven development and collaboration are key aspects of open source metaverse platforms. These platforms rely on the active participation and contributions of a diverse community of developers, users, and creators. Open source metaverse platforms encourage transparency in development by making the source code accessible to the community. This transparency allows developers to understand the platform’s underlying architecture, contribute improvements, and identify and fix bugs.
An open source metaverse platform encourages users to actively participate, share their ideas, and provide feedback on existing features and functionalities. This feedback loop ensures that the platform evolves according to the needs and preferences of the user community. Developers and users can propose new features, suggest improvements, and contribute code to enhance the platform’s capabilities.
Open source metaverse platforms empower users to create and contribute their own content. Users can design and share 3D models, textures, animations, and scripts, expanding the possibilities of the virtual environment. The platform provides tools and resources for content creation, allowing community members to showcase their creativity and contribute to the shared experience. To maintain a healthy and productive community environment, open source metaverse platforms often implement community moderation and governance mechanisms. Community members can participate in decision-making processes, such as defining rules and guidelines, establishing code of conduct, and ensuring compliance with ethical and legal standards. These mechanisms foster a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members, ensuring the platform’s long-term sustainability.
Open source metaverse platforms provide collaboration tools and communication channels to facilitate interaction and coordination among community members. These tools may include forums, mailing lists, chat platforms, and version control systems. They enable community members to exchange ideas, seek help, coordinate development efforts, and collaborate on specific projects or features.
These platforms prioritise documentation and knowledge sharing to support community-driven development. Documentation resources, including guides, tutorials, and API references, are made readily available to help users understand the platform’s functionalities and contribute effectively. Community members actively share their expertise, providing support and guidance to newcomers.
Community-driven development in open source metaverse platforms follows an iterative and continuous improvement process. Through the collaboration and feedback loop, the platform undergoes regular updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
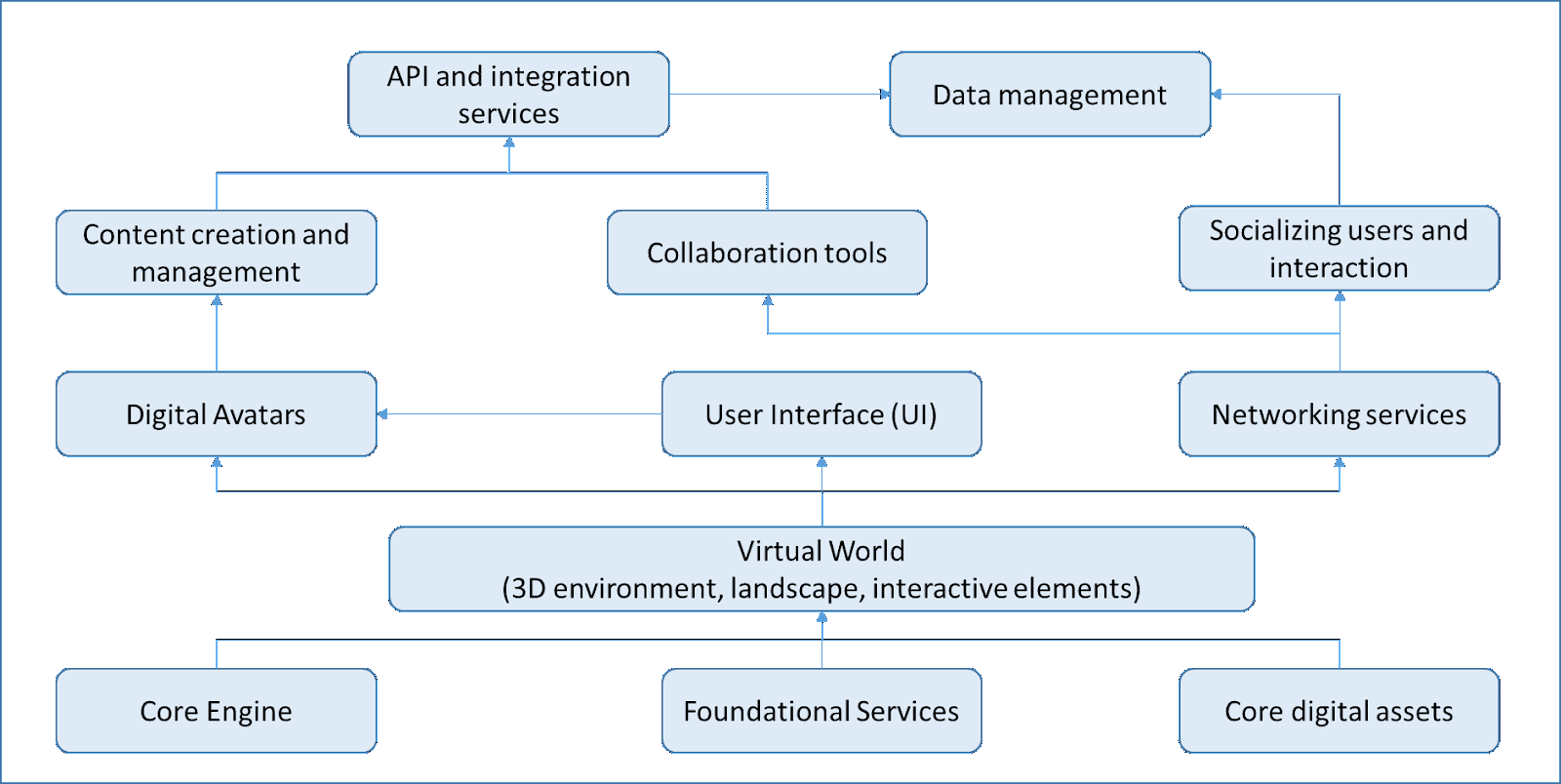
Key components of an open source metaverse platform
An open source metaverse platform typically consists of several key components that work together to create an immersive and interactive virtual reality experience for its users.
Core engine: The core engine forms the foundation of the open source metaverse platform. It includes the core functionalities and services responsible for rendering the virtual environment, managing user interactions, and handling network communication. It is the backbone of the platform, which ensures seamless navigation and interaction within the metaverse.
Virtual world: The virtual world is the digital representation of the metaverse where users can explore, interact with objects and other users, and engage in various activities. It encompasses 3D environments, landscapes, structures, and interactive elements that make up the virtual space.
Avatars: Avatars are the virtual representations of users within the metaverse. They allow users to customise their appearances and movements, enabling a more personalised and social experience. Avatars serve as the means through which users can communicate and interact with each other in the virtual environment.
User interface (UI): The user interface provides the means for users to interact with the metaverse. It includes menus, control panels, and HUDs (heads-up display) that allow users to access settings, communicate with others, and navigate the virtual world easily.
Networking and communication: Networking and communication components enable real-time interactions between users within the metaverse. They handle the transmission of data, such as avatar movements, chat messages, and collaborative activities, ensuring a seamless and responsive virtual experience.
Content creation and management: The content creation and management component provides tools and interfaces for users and developers to create and manage content within the metaverse. This includes creating 3D models, textures, animations, and scripts, as well as managing user-generated content.
Collaboration tools
Collaboration tools foster community engagement and teamwork within the metaverse. They include features such as shared workspaces, project collaboration tools, and content sharing platforms that enable users to work together on creative projects and shared experiences.
Social interaction: Social interaction components facilitate communication and socialisation among users. This may include text chat, voice chat, and emotes, allowing users to connect and interact with each other, making the metaverse a social and collaborative space.
API and integration: API (application programming interface) and integration components allow developers to extend the functionalities of the open source metaverse platform. They enable integration with external services, plugins, and third-party applications, fostering innovation and flexibility within the platform.
Data management: Data management to handle digital assets, templates for virtual platforms, data protection against user data and customised user experience related data are handled with these services to facilitate efficient data-driven user experience design.

Advantages of open source metaverse platforms
Open source metaverse platforms offer several advantages that contribute to their popularity and potential.
Flexibility and customisation: These platforms allow users to modify and customise the software according to their specific needs and preferences. This flexibility enables developers and creators to build unique virtual experiences tailored to their target audience.
Community collaboration: By making the metaverse platform open source, developers from around the world can contribute to its development, identify and fix bugs, and add new features. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and accelerates the platform’s growth.
Lower costs: Open source metaverse platforms eliminate the need for expensive licensing fees. Individuals and organisations can use and modify the software without incurring significant costs, making it more accessible to a wider range of users. This affordability factor promotes inclusivity and encourages diverse participation.
Enhanced security and privacy: With open source platforms, the source code is openly available for inspection and review by a global community. This transparent approach can enhance security by allowing experts to identify and fix vulnerabilities promptly. Open source projects also tend to prioritise privacy and data protection, giving users greater control over their virtual identities and personal information.
Interoperability and standards: Open source metaverse platforms often focus on interoperability, enabling users to seamlessly move between different virtual environments. Standardisation efforts within the open source community facilitate the integration of various components, tools, and technologies, creating a more interconnected metaverse experience.
Avoiding vendor lock-in: These platforms provide users with independence from a single vendor or company. By avoiding vendor lock-in, users have the freedom to switch between different platforms or even create their own versions, reducing dependence on a specific provider and promoting healthy competition.
Educational and research opportunities: Open source metaverse platforms offer valuable educational and research opportunities. Students, researchers, and developers can study the code base, experiment with new ideas, and contribute to the advancement of virtual reality technologies.
Innovation and experimentation: Open source metaverse platforms often act as incubators for innovation and experimentation. The accessibility of the code base encourages developers to push boundaries, create new features, and explore novel use cases. This vibrant ecosystem drives rapid innovation and evolution within the metaverse space.
It’s important to note that open source metaverse platforms also come with challenges, such as the need for technical expertise and potential fragmentation.
OpenSimulator
OpenSimulator (http://opensimulator.org/wiki/Main_Page), also termed as ‘OpenSim’, is an open source metaverse platform that allows individuals and organisations to create and deploy their own virtual worlds. It serves as a framework for building 3D virtual environments, offering a rich set of features for user interaction, content creation, and collaborative experiences.
At its core, OpenSimulator enables users to design and customise their virtual worlds, constructing landscapes, buildings, and objects. Users can create and customise avatars, defining their appearance, clothing, and animations, fostering personal expression and individuality within the virtual environment. One of OpenSimulator’s strengths lies in its support for real-time collaboration, enabling multiple users to interact and communicate with each other within the virtual space. It facilitates social interaction, teamwork, and the organisation of virtual events. OpenSimulator incorporates a scripting language called OSSL (OpenSimulator Scripting Language), enabling users to create interactive objects and automate behaviours within the virtual world. The platform includes a physics engine that simulates realistic physics interactions, such as gravity, collisions, and object dynamics, and enhances the realism and immersion of the virtual environment.
OpenSimulator supports the creation of multiple regions or simulators that can be interconnected to form a larger virtual world. Another notable feature is the hypergrid connectivity, which allows users to teleport and explore other OpenSimulator-powered virtual worlds. It also supports content import and export, enabling users to import external assets, such as 3D models and textures, into their virtual worlds. There is an active community of users, developers, and content creators who contribute to the platform’s development and provide support.
The key features of OpenSimulator are:
- Supports 3D virtual spaces of dynamic sizes
- Full support for multi-user cum online 3D environment
- Support for multiple clients and protocols
- Real-time physics simulation and supports inworld scripting using LSL/OSSL
JanusVR
Janus VR is an immersive web browsing platform that allows users to explore and interact with virtual reality (VR) environments. It combines the power of virtual reality with the accessibility of the web, providing a unique and immersive browsing experience.
It offers users seamless connectivity, allowing them to browse the web, interact with content, collaborate with others, and personalise their virtual spaces.
Virtual reality browsing: Janus VR enables users to browse the web in a fully immersive VR environment. Users can navigate websites, interact with content, and explore virtual spaces, all within the context of VR.
Navigation and teleportation: Users can move around virtual environments through various navigation options, including walking, flying, or teleportation. This feature allows for seamless exploration and interaction within the VR space.
Multiuser collaboration: Janus VR supports multiuser collaboration, enabling users to interact with others in real time. Users can meet and communicate with people from around the world, enhancing the social aspect of the VR experience.
Web content integration: It integrates web content seamlessly into virtual environments. Users can view websites, watch videos, access web applications, and interact with traditional web content, transforming the browsing experience into a spatial and immersive one.
Customisation and personalisation: Users can personalise their virtual spaces within Janus VR. They can customise the appearance of their virtual surroundings, create virtual objects, and manipulate the environment to suit their preferences and needs.
For developers, JanusVR provides a range of tools and features to create interactive VR experiences. With support for WebVR integration, scripting capabilities, and collaboration tools, developers can unleash their creativity.
WebVR integration: Janus VR supports WebVR, a JavaScript API that enables the creation of VR experiences on the web. Developers can build VR-enabled websites and applications that seamlessly integrate with Janus VR, expanding the possibilities of immersive web content.
Janus markup language (JML): JML is Janus VR’s scripting language, specifically designed for creating interactive VR environments. Developers can use JML to define and manipulate objects, add interactivity, and create immersive experiences within Janus VR.
Collaboration tools: Janus VR provides developers with tools for creating multiuser experiences. Developers can build virtual spaces where multiple users can interact, collaborate, and communicate in real time, fostering social engagement and shared experiences.
Custom 3D models and environments: Developers can create and import custom 3D models and environments into Janus VR. This feature allows for the creation of unique and visually appealing virtual spaces, enhancing the immersive experience for users.
Interactivity and animation: Janus VR supports interactivity and animation through its scripting capabilities. Developers can use JavaScript to create dynamic and interactive elements within the VR environment, adding life and engagement to virtual experiences.
Cross-platform compatibility: The platform is compatible with various VR platforms, including headsets such as Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and Windows Mixed Reality. This cross-platform compatibility allows developers to reach a broader audience and ensures that their VR experiences can be accessed by users on different devices.
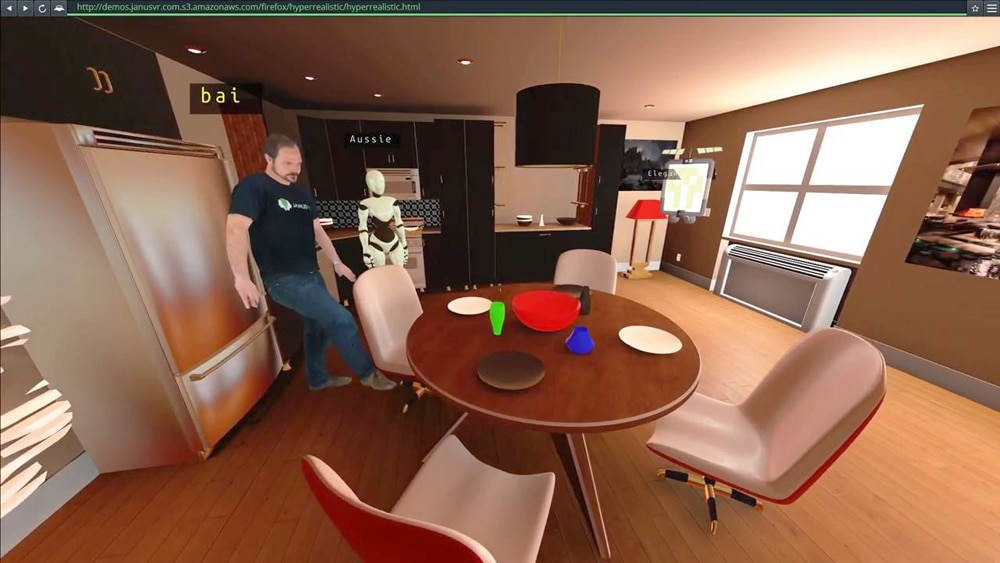
Mozilla Hubs
Mozilla Hubs (https://hubs.mozilla.com/) is an innovative social virtual reality (VR) platform developed by Mozilla. It enables users to connect and interact with each other in virtual environments, fostering collaboration, communication, and creativity.
At its core, Mozilla Hubs is a web-based VR platform, utilising WebVR and WebXR technologies. It allows users to access and experience virtual environments directly through web browsers, without the need for additional software installations or downloads. The web-based nature of Mozilla Hubs makes it easily accessible to a wide range of users, as it can be accessed on various devices, including VR headsets, desktop computers, and even mobile devices.
One of the key features of Mozilla Hubs is its ability to create and customise virtual spaces. Users can design and build their own immersive environments, complete with interactive objects, spatial audio, and ambient lighting. The platform supports 3D model import, enabling users to integrate their own custom objects and elements into their virtual spaces. This customisation aspect allows for endless creativity and personalisation, making each virtual environment unique and tailored to specific needs.
Mozilla Hubs facilitates real-time communication and collaboration between users. Users can interact and engage with each other using voice chat, spatial audio, and text-based messaging. This feature fosters social interaction, teamwork, and the ability to collaborate on projects or activities within the virtual environment.
Furthermore, users can create personalised avatars, customising their appearance, clothing, and accessories. This adds a sense of identity and presence within the virtual world, enhancing social interactions and self-expression.
The platform also supports multimedia sharing, enabling users to share images, videos, and documents within the virtual environment. This feature promotes collaboration and information sharing, allowing users to present and discuss various media assets in real time.
Privacy and security are significant considerations for Mozilla Hubs. The platform follows strong privacy practices, and user conversations within the virtual environment are end-to-end encrypted, ensuring that communication remains secure and private. Mozilla is committed to user data protection and upholds strict data privacy standards.
Being an open source project, the platform encourages community contributions, innovation, and the development of compatible tools and extensions. This fosters a collaborative ecosystem where developers can build upon and customise Mozilla Hubs to suit their specific needs.
Other open source metaverse platforms
Apart from JanusVR, there are several other open source metaverse platforms available in 2023 that provide diverse and immersive virtual reality experiences. These platforms offer unique features, innovative technologies, and decentralised environments, allowing users and developers to explore and create in the metaverse. Here are the top options.
Webaverse: Webaverse is a decentralised VR platform with top technical features. It utilises blockchain technology for asset ownership and secure transactions, allowing users to create, buy, sell, and trade virtual goods using cryptocurrencies and NFTs. Webaverse emphasises decentralisation, hosting virtual worlds on distributed peer-to-peer networks. Users can explore interactive virtual environments, engage in multiplayer games, and collaborate on creative projects. The platform supports user-generated content and embraces an open source approach, encouraging community participation and innovation within the Webaverse ecosystem.
Hypercube: Hypercube is a virtual reality (VR) platform that offers immersive and interactive experiences. It enables users to navigate and interact with virtual environments using advanced VR technologies. With its spatial computing capabilities, Hypercube allows users to move freely within virtual spaces, providing a sense of presence and realism. The platform supports various input methods, including hand gestures and motion controllers, enhancing user engagement. Hypercube’s aim is to provide a seamless and immersive VR experience that blurs the line between the physical and virtual worlds.
Somnium Space: Somnium Space is a virtual reality (VR) platform that offers users a persistent, immersive, and user-generated metaverse. Users can explore and interact with a vast virtual world filled with unique landscapes, buildings, and user-created content. Somnium Space emphasises blockchain technology, enabling true ownership of virtual land and assets through non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Users can socialise, attend events, trade virtual goods, and even build and monetise their own experiences.
XREngine: XREngine is a cutting-edge game engine designed for creating immersive virtual reality (VR) experiences. Built from the ground up for VR, XREngine offers advanced features and optimisations specifically tailored to the unique demands of VR development. It supports high-performance rendering, physics simulations, and spatial audio, providing a realistic and immersive environment. XREngine also includes tools and frameworks for creating interactive gameplay mechanics and immersive storytelling. Its goal is to empower developers to create captivating VR experiences with seamless performance and visual fidelity.
WebXR Device API: The WebXR Device API is a web standard that provides a unified and consistent way to access and interact with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) devices through web browsers. It allows developers to create immersive and interactive XR experiences that can be accessed directly from a browser, without the need for additional plugins or applications. The API provides capabilities such as tracking the user’s head and hand movements, rendering VR and AR content, and integrating with input devices like controllers. It aims to democratise XR development and make XR experiences easily accessible on the web.
Open source platforms allow users and developers to shape the metaverse according to their needs and preferences, leading to a diverse and dynamic virtual reality landscape. As the technology progresses and more platforms emerge, the metaverse is poised to revolutionise various industries, including education, entertainment, commerce, and healthcare.