With prolific growth in the number and variety of smartphone applications, which span multiple platforms, it becomes mandatory to increase the speed of app development to stay competitive in the market. Ionic is a promising open source mobile UI framework that makes the hybrid app development process swifter and smoother.
Smartphone apps have become an inevitable part of our day-to-day life. A recent study has found that around 52 per cent of time spent on the digital media is with smartphone apps, which clearly indicates the central role that mobile apps have attained in the recent past. The estimated revenue generated through smartphone apps is a massive US$ 45 billion. The aforementioned statistics loudly proclaim the need to focus more on smartphone application development in terms of speed and cross-platform support. Mobile apps can be categorised into three broad categories:
- Native apps
- Mobile websites
- Hybrid apps
Each of the above categories has its own pros and cons. Native apps are tightly integrated with the platform for which they are built. Obviously, the major issue with native apps is the need for a separate development process for individual platforms like Android, iOS, etc. So native app development requires specialised development teams.
The mobile websites, on the other hand, are completely developed with Web technologies like HTML 5, CSS 3, etc, and run on a smartphone Web browser. They are primarily mobile extensions of the websites. Mobile websites are not able to harness the full potential of the platform and the hardware sensors.
Hybrid apps are built by merging the advantages of both the above categories. These apps enable developers to use the same code base and export it to different platforms, which removes the need for multiple code bases. Hybrid apps are able to harness most device features. Hence, the recent trend in smartphone app development is towards the cross-platform hybrid category.
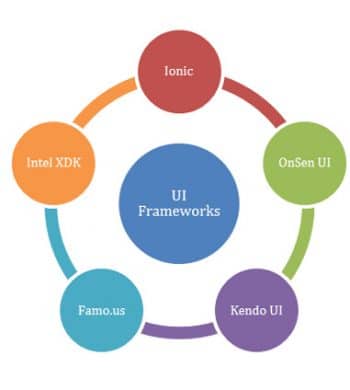
To assist developers in increasing the speed of app development, there are various app development frameworks. Ionic is a specialised UI framework for smartphone app development. The UI frameworks for hybrid smartphone apps are increasing. Figure 1 shows the wide and rich spectrum of UI frameworks currently available.
Each of these frameworks has its own speciality, apart from the common features. For example, Famo.us focuses on graphics rendering and is more suitable for development of smartphone apps loaded with animation. The Onsen UI allows developers to build apps for mobiles and tablets with multiscreen support.
An introduction to Ionic
As stated earlier, Ionic is a UI framework. The point to be noted here is that Ionic is not a replacement for frameworks like PhoneGap, etc. Ionic is a front-end SDK, which primarily aims to achieve a native look and feel for the smartphone apps user interface. The Ionic framework is open source with an MIT licence. It fills that vacuum which lies between creating native looking apps and Web standards.
The Ionic apps can be compiled with Cordova or PhoneGap, and stunning native featured apps can be built. These hybrid apps are not dependent on mobile Web browsers but they use the low-level browser shell like WebView on Android, and UIWebView on iOS. The major advantage of using Ionic is that the developers can leverage their familiarity with existing Web technologies like HTML, CSS and JavaScript.

Installation
The Ionic installation requires certain dependencies. You should have Node.js installed in your system (https://nodejs.org/en/). As Ionic requires the Cordova framework, it needs to be installed, as follows:
npm install -g cordova
If you are inside a proxy server, the proxy settings must be made using the following commands:
npmconfig set proxy http://user_id:password@proxy_ip:port npmconfig set https-proxy http:// user_id:password@proxy_ip:port
Then the Ionic framework must be installed with the following command:
npm install -g ionic
In Linux environments, the sudo prefix should be used with the above commands. The installation of Ionic is a very simple process which can be completed within minutes, provided you have good Internet connectivity.
The Ionic app-building process
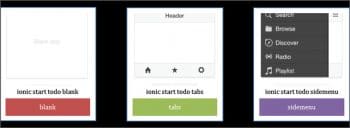
The app-building process in Ionic is very simple. The first step is to start a project and specify an app template type. Ionic has three template types for applications as shown in Figure 2.
To create a blank app, use the following command:
$ ionic start todo blank
In the above command, ’todo’ indicates the app name and the blank indicates the template type. If you are inside the proxy server, then the corresponding proxy settings need to be done before executing the Ionic command. The proxy settings will be done as follows:
set proxy=http://"user_id:password"@proxy_ip:port sethttps_proxy=http://"user_id:password"@proxy_ip:port
The successful execution of the above command will create a folder termed todo, the structure of which is shown in Figure 3.
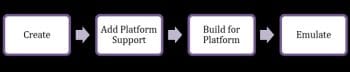
The next step is to add the platform support for iOS, Android, etc. This can be carried out with the following commands:
$ ionic platform add android $ ionic platform add ios
The next steps are to execute the build and emulate platform-specific commands as shown below:
$ ionic build android $ ionic emulate android
These steps are as illustrated in Figure 4.

Ionic app testing methods
The app built using Ionic can be tested using the variations shown in Figure 5.
Desktop browser: This method allows you to test your app in the desktop browser using the following command, in the app directory:
$ ionic serve
This command would trigger the live-reload server for the project, which means that any changes made to the underlying HTML, CSS or JavaScript will be directly reflected in the result.
Simulator test: The corresponding platforms simulator can be utilised to test the app built using the Ionic framework. The build, emulate and cordova prepare commands are employed.
Mobile browser: The app can be directly tested in a mobile browser. The desktop test server running the application can be accessed from a mobile Web browser to test the application. This type of app testing is only suitable for simple apps. When the apps get fairly complex, the behaviour is interrupted by some of the browser features.
Native app testing (device): Another method to test the app is as the native app in the device. The device needs to be plugged in, and the following command should be executed to directly test on the device:
$ ionic run android
A simple app
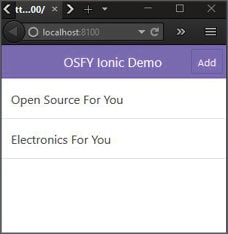
The JavaScript portions of the Ionic app are built using Angular.js. A List app with portions of code in index.html, app.js and controllers.jsare is given below:
<scriptsrc=js/app.js></script>
<scriptsrc=js/controllers.js></script>
</head>
<body ng-app=starter>
<ion-pane>
<ion-header-bar class=bar-royal>
<h1 class=title>OSFY Ionic Demo</h1>
<div class=buttons>
<button class=button ng-click=openModal()>
Add
</button>
</div>
</ion-header-bar>
<ion-content>
<ion-list ng-controller=ToDoListCtrl>
<ion-item ng-repeat=item in toDoListItems>
{{item.task}}
</ion-item>
</ion-list>
</ion-content>
</ion-pane>
</body>
In app.js, type:
angular.module(starter, [ionic, starter.controllers])
In controllers.js, type:
angular.module(starter.controllers, [])
.controller(ToDoListCtrl, function ($scope) {
$scope.toDoListItems = [
{
task: Open Source For You,
status: not done
},
{
task: Electronics For You,
status: not done
}]
});
The output of the above code is shown in Figure 6.
The Ionic Lab
The Ionic Lab enables developers to harness the power of Ionic with the help of a desktop app. It allows developers to perform the following tasks:
- App creation
- App preview
- App building
- App running
- App uploading
- App logging
The Ionic Lab is available for download at http://lab.ionic.io/ .
Ionic Creator
Ionic Creator is more advanced than Ionic Lab. It allows the creation of Ionic apps with a drag and drop graphical user interface. It can be accessed from the browser at https://creator.ionic.io/app/login. Ionic Creator is available for free with limited features. The advanced features are accessible according to their pricing policy.
Ionic Market
Ionic Market facilitates the discovery and sharing of all resources related to Ionic. These resources include community built themes, apps, plugins, etc. The URL for Ionic Market is http://market.ionic.io/. This marketplace allows you to jumpstart your Ionic app development process.
To summarise, the Ionic UI framework makes the process of building hybrid mobile applications faster and enables seamless integration with the native platforms look and feel.
References
[1] http://ionicframework.com/ – The Ionic Homepage
[2] http://ionicframework.com/docs/guide/ – The Ionic Documentation
[3] https://ccoenraets.github.io/ionic-tutorial/index.html – Ionic Tutorials
[4] http://www.business2community.com/infographics/mobile-apps-usage-statistics-trends-infographic-01248837#ZuqXFFJpFSJG9oqy.97 – Smartphone stats