The fourth industrial revolution, commonly referred to as Industry 4.0, is all about making businesses smarter. It is focused on deepening the impact of digital technologies by making machines more autonomous and enabling them to communicate with one another. These machines can now manage enormous amounts of data in ways that humans simply cannot handle. This article introduces you to Embedded Internet of Things (EIoT) and Industry 4.0.
The third industrial revolution was focused on converting mechanical and analogue processes to digital ones to be ready for advanced automation. Similar to the transition from steam to electricity in the second industrial revolution, the advent of Industry 4.0 technology marks a major transformation in how companies conduct their operations.
The effects of Industry 4.0 on production are extensive. It is being used to increase operational effectiveness, improve demand forecasting, eliminate data silos, engage in predictive maintenance, provide virtual training to employees, and more. Industry 4.0 encompasses manufacturing from planning to delivery as part of a larger concept known as digital transformation. It includes solutions for deep analytics, shop floor data sensors, smart warehouses, simulated modifications, as well as product and asset tracking.
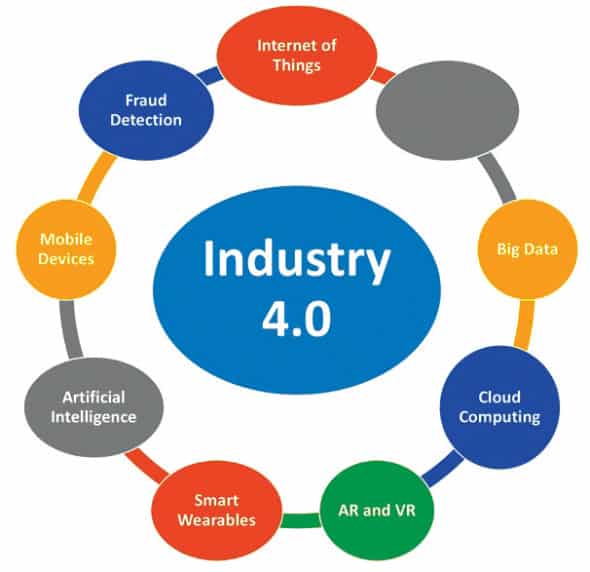
Industry 4.0 technologies assist manufacturers in bridging the gap between previously distinct processes and a more transparent, viewable perspective across the entire business with a wealth of useful insights. The emergence of digital solutions and cutting-edge technology, which are frequently linked to Industry 4.0, have made this convergence possible.
Some of the key technologies associated with Industry 4.0 are:
- Industrial Internet of Things
- Smart wearable gadgets
- Smart cities and advanced monitoring
- Advanced robotics
- Digital twins
- Big Data analytics
- E-governance
- Additive manufacturing (AM)
- Cloud computing
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)
- Quantum computing based systems
- Simulation platforms and suites
By integrating formerly disjointed systems and processes with interconnected computer systems across the value and supply chain, these technologies are assisting in the digital transformation of manufacturing.
Adopting Industry 4.0, digital manufacturing, and the associated interconnectivity enables businesses to reap a variety of benefits, including improved operational performance and increased agility.
Embedded Internet of Things (EIoT) and Industry 4.0
Embedded Internet of Things (EIoT) refers to the integration of embedded devices (including sensors and open source hardware) with IoT based platforms and communication channels to enable real-time communication for varied applications. EIoT with Industry 4.0 is a technology shift of traditional engineering and governance to smart deployments. The three technical themes (connectivity, intelligence, and flexible automation) driving this transformation are collectively referred to as Industry 4.0, or the fourth industrial revolution with embedded devices.
The fourth industrial revolution represents breakthroughs in technologies, such as robots, intelligent systems, nanotechnology, quantum computing, microbiology, the Internet of Things, 3D printing, and autonomous cars.
In order to build a cyber-physical environment, Industry 4.0 combines OT (operational technology) and IT. A number of software platforms and libraries can be used for the simulation of EIoT and Industry 4.0 applications (Table 1).
| Platform/Software suite | URL |
| Cloud MQTT | cloudmqtt.com |
| Mosquitto MQTT Broker | mosquitto.org |
| FlowHub | flowhub.io |
| Sumo | eclipse.org/sumo |
| NoFloJS | noflowjs.org |
| PraxisLive | praxislive.org |
| Netron | github.com/lutzroeder/netron |
| Ryven | gentle-sand-0114c7110.azurestaticapps.net/ |
| PyFlow | wonderworks-software.github.io/PyFlow/ |
| Wyliodrin | wyliodrin.com |
| Flutter Wireless | flutterwireless.com |
| SiteWhere | sitewhere.io |
| DSA | iot-dsa.org |
| Zetta | zettajs.org |
| Node Red | nodered.org |
| IoTivity | iotivity.org |
| Open IoT | openiot.eu |
Table 1: Platforms and software suites for simulation of Industry 4.0 applications
Some use cases
In Industry 4.0 and EIoT simulations, there is a need to integrate lightweight protocols so that low-powered and smart gadgets can communicate effectively. MQTT is a key protocol that is used in Industry 4.0 and IoT based deployments.
There are primarily two types of objects in IoT communication — publisher and subscriber. Publishing refers to the transmission of data signals — the process of moving data from a computer to an external device. The receiver system is referred to as the subscriber in IoT communication.
Publisher and subscriber are terms used to describe the source and recipient of a data signal, respectively. The MQTT broker, also known as an IoT server, serves as the focal point and regulates communication between publishers and subscribers. It manages the data that publishers broadcast for the other devices known as subscribers. For instance, information may be sent from a temperature sensor to a farmer’s mobile phone. In this instance, the temperature sensor (publisher) is the source of the data signals, and the farmer’s gadget is the receiver (subscriber).
These MQTT broker applications can be installed on a variety of specialised hardware, including Raspberry Pi, Arduino, laptops, servers, and many others.
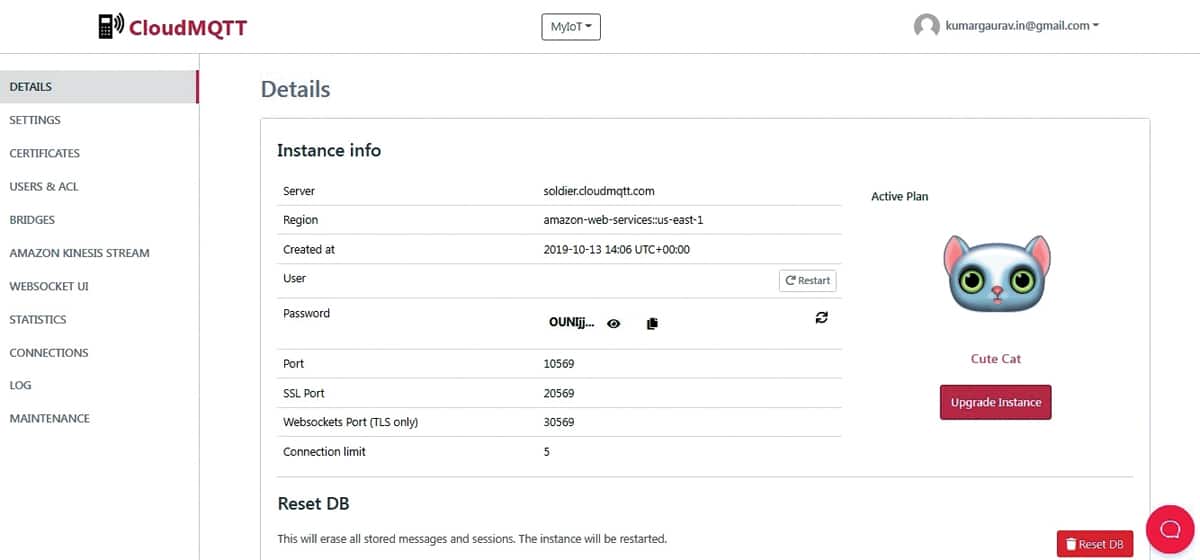
Cloud based MQTT
URL: cloudmqtt.com
CloudMQTT, one of the most widely used MQTT brokers, can be used for device communication and implementation of Industry 4.0 based scenarios. It can be used to implement IoT scenarios for a variety of applications including smart toll plaza, smart cities, smart homes, and smart offices.
For researchers and academicians, CloudMQTT offers a free package called ‘Cute Cat’ that allows five users or connections for IoT devices. Using an active Google account, free instances can be built on the CloudMQTT network.
The features integrated in Cloud MQTT include:
- Open source message broker that implements the MQTT protocol
- 24×7 availability of MQTT broker
- Cloud compatibility
- Lightweight and high performance; integrates with low power single boards like
- Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP8266 as well as computers and servers
- Integration of lightweight methods for messaging using a publish and subscribe message queueing model
- Fully managed Mosquitto servers in the cloud
To establish a real-time connection between CloudMQTT and a device, IoT hardware or smartphones can use authentication information from CloudMQTT.
Traffic simulation using Eclipse SUMO
URL: eclipse.org/sumo
Smart vehicular communication in smart cities and e-governance are key application areas of Industry 4.0. Eclipse SUMO (Simulation of Urban MObility) is very effective in simulating a traffic scenario. It integrates a range of features to simulate smart vehicular environment, and can work with multiple vehicles of different types in different environmental conditions.
SUMO is free and open source. Since its introduction in 2001, it has enabled the modelling of multi-mode traffic networks, which include pedestrians, public transportation, and private vehicles. Numerous auxiliary tools, such as network import, route calculations, visualisation, and emission calculation, are included with SUMO and automate fundamental processes for the development, execution, and evaluation of traffic simulations. Custom models can be added to SUMO, and it offers a number of APIs for controlling the simulation from a distance.
The key features of SUMO are:
- Free and open source
- Automated driving
- Vehicle communication
- Traffic management
- Multimodal traffic
- Microscopic simulation
- Online interactions
- Traffic lights
- Network import
- Demand generation
- Performance
- Portability
The manufacturing sector is experiencing exciting times right now as new digital technologies emerge. Industry 4.0 is also making it easier for humans and robots to collaborate, enabling firms to gain more knowledge, lower the possibility of error, and make wiser decisions. The only way for manufacturers to stay ahead of the curve in this new digital era is by embracing Industry 4.0.
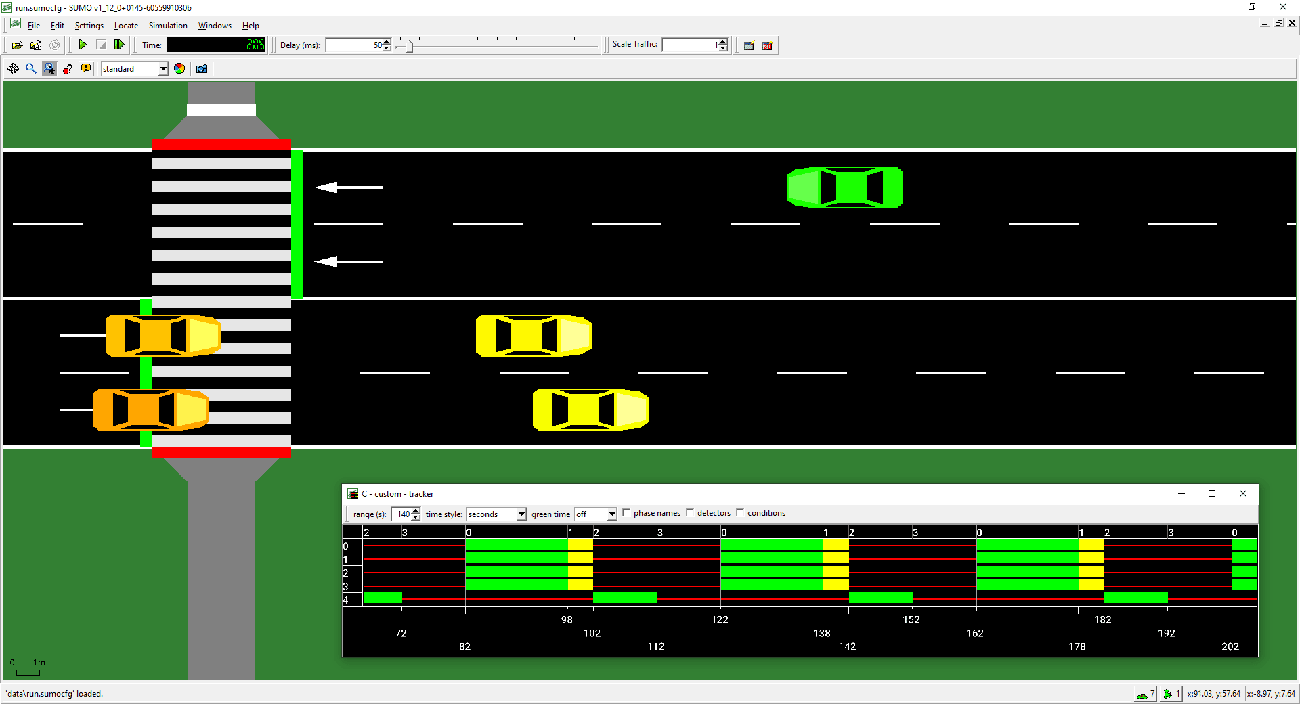
Researchers and practitioners of Industry 4.0 can use free and open source platforms to simulate and experiment with its real world applications. Such simulation sessions will help analyse the outcome in real-time before actual deployment.

























































![Industry-4,-Cloud-computing,-physical-systems,-IoT,-cognitive-computing-industry_132815174-[Converted] Industry-4,-Cloud-computing,-physical-systems,-IoT,-cognitive-computing-industry_132815174-[Converted]](https://www.opensourceforu.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Industry-4-Cloud-computing-physical-systems-IoT-cognitive-computing-industry_132815174-Converted-696x486.jpg)