Databases are playing a crucial role in improving the functioning and efficiency of blockchain environments, helping store and manage data related to blockchain transactions and smart contracts. There are quite a few free and open source databases that are doing a good job in this domain.
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary power in various industries, bringing about transformative changes to traditional systems and opening new avenues. Through its decentralised and transparent nature, blockchain presents a wide range of practical applications that can reshape existing processes and foster innovative solutions.
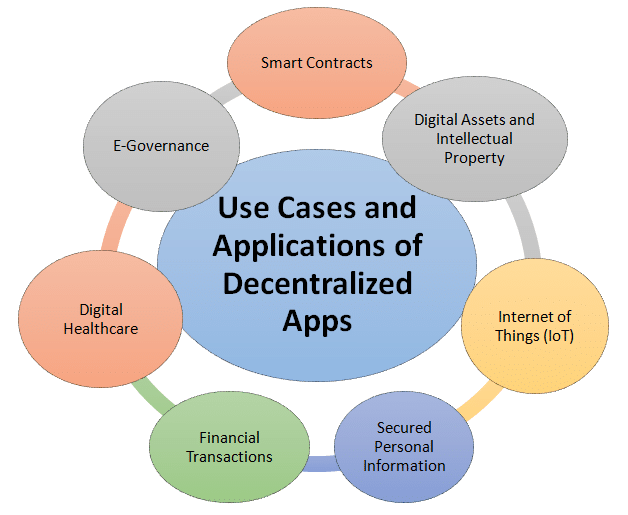
Rreal world use cases of blockchain
One of the notable examples of blockchain utility is found in the financial sector. By leveraging blockchain technology, secure and efficient peer-to-peer transactions can be conducted without the need for intermediaries such as banks.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have become popular as digital currencies operating on blockchain networks, facilitating direct and trustless transactions across borders. Additionally, blockchain has the potential to revolutionise remittances by enabling faster and more cost-effective cross-border money transfers, particularly benefiting underserved populations.
Blockchain technology has demonstrated significant potential in revolutionising supply chain management. Through its ability to record and track transactions and the movement of goods on a distributed ledger, blockchain enhances transparency and traceability. This capability proves particularly valuable in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where ensuring the safety and authenticity of products is crucial. By leveraging blockchain, issues such as counterfeit goods can be mitigated, ensuring consumers receive genuine and high-quality products.
The healthcare sector has also seen the application of blockchain technology. Blockchain enables the secure storage and sharing of medical records on a decentralised network, ensuring data integrity, privacy, and accessibility. This approach reduces the risk of data breaches and allows healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history, even across different healthcare systems. Additionally, blockchain facilitates the secure sharing of clinical trial data, promoting collaboration and accelerating medical research.
In the real estate industry, blockchain is driving transformation through the use of smart contracts. These contracts automate and execute agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs. Property ownership records can be stored on a blockchain, preventing fraud and streamlining the process of transferring property titles. Blockchain-powered platforms are also emerging, enabling fractional ownership of real estate and expanding investment opportunities to a broader audience.
The energy sector is also benefiting from blockchain technology. By leveraging blockchain, decentralised energy trading platforms can be established, allowing peer-to-peer energy transactions and promoting the use of renewable energy sources. Blockchain-based systems can track energy production and consumption, facilitating efficient energy management and ensuring a reliable supply.
These examples illustrate the real-world applications of blockchain technology. From finance, supply chain management, and healthcare to real estate and energy, blockchain’s decentralised and transparent nature opens up vast possibilities for innovation. As the technology continues to evolve and mature, it is expected to find even more diverse applications, transforming various industries and driving positive change in how we interact and conduct business.
The role of databases in the blockchain environment
Databases play a crucial role in supporting the functioning and efficiency of blockchain environments. They provide a means to store and manage data related to blockchain transactions, smart contracts, and other associated information.
One important use of databases in a blockchain environment is to store off-chain data. Blockchain networks typically prioritise on-chain data storage to maintain the integrity and immutability of transaction records. However, there are instances where it may not be practical or efficient to store certain data, such as large files, multimedia content, or extensive metadata, directly on the blockchain. In such cases, databases are used to store this off-chain data while referencing it through cryptographic hashes or pointers on the blockchain. For example, IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) is a distributed database that is often used in conjunction with blockchain to store and retrieve large files, ensuring efficient storage and retrieval of data while maintaining a link to the blockchain.
Another important role of databases in blockchain environments is to provide indexing and querying capabilities. Blockchain networks are designed for secure and decentralised transaction storage, but they are not optimised for complex data retrieval and querying. Databases can be used to create indexes and data structures that allow for efficient search and retrieval of specific information from the blockchain. By using databases in conjunction with blockchain, developers and users can leverage the benefits of both technologies. For instance, Ethereum, a popular blockchain platform, uses a database called LevelDB to index and query its transaction data, enabling faster and more efficient data retrieval.
These databases are used to store and manage the state of smart contracts in blockchain environments. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that reside on the blockchain and automatically enforce the terms and conditions defined within them. As smart contracts can contain complex logic and state variables, databases provide a way to store and update the current state of these contracts. For example, in Ethereum, the state of smart contracts is stored in a database called the ‘state trie’, which allows for efficient contract execution and retrieval of contract states.
Databases are also employed in blockchain environments to support scalability and performance. While blockchain networks aim to achieve decentralised consensus and immutability, they often face challenges in terms of transaction throughput and latency. By using databases that are designed for high-performance data storage and retrieval, blockchain systems can offload certain operations to the database layer, enabling faster transaction processing and improved scalability. For example, some blockchain platforms employ databases like RocksDB or Cassandra to handle the storage and retrieval of transaction data, enhancing overall network performance.
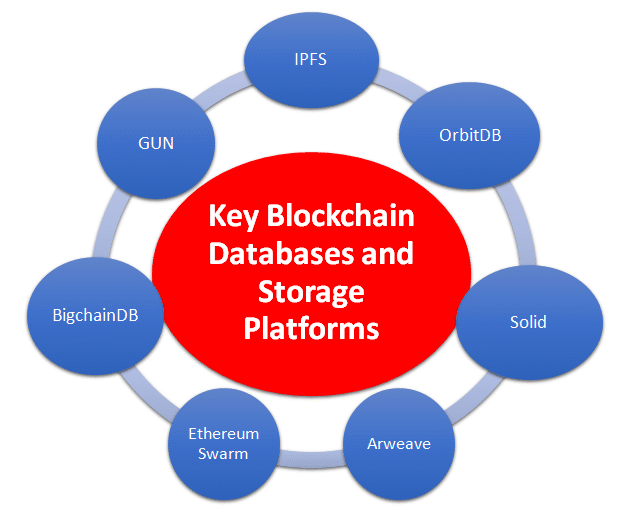
Free and open source databases and storage platforms for blockchain development
When it comes to developing decentralised applications (dApps), databases play a crucial role in storing and managing data in a decentralised manner. Here are some notable databases suitable for decentralised app development, along with their URLs and descriptions.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) –https://ipfs.io/
IPFS is a distributed file system that provides decentralised storage and retrieval of files. It uses content-addressing to uniquely identify files and leverages a network of nodes to store and distribute data. IPFS is often used in conjunction with blockchain technology to store large files, multimedia content, or extensive metadata in a decentralised and censorship-resistant manner.
OrbitDB –https://orbitdb.org/
OrbitDB is a distributed peer-to-peer database built on top of IPFS. It offers a simple API for creating and managing databases that can be shared and synchronised across multiple nodes. OrbitDB supports different database types such as key-value stores, document stores, and event logs, making it suitable for various decentralised app use cases.
Ethereum Swarm –https://swarm.ethereum.org/
Ethereum Swarm is a decentralised storage and content distribution platform that is part of the Ethereum ecosystem. It allows developers to store and retrieve data in a decentralised manner using a distributed network of nodes. Swarm integrates seamlessly with Ethereum smart contracts, enabling dApp developers to store and access data securely and efficiently.
GUN (graph database) –https://gun.eco/
GUN is a decentralised graph database that enables real-time data synchronisation across peers. It provides a distributed, offline-first data storage and synchronisation mechanism, making it ideal for building decentralised applications that require real-time collaboration and data consistency. GUN’s data synchronisation capabilities make it suitable for applications like messaging, collaborative editing, and social networks.
Holochain –https://holochain.org/
Holochain is a framework for building decentralised applications that can be run on peer-to-peer networks. It provides a distributed hash table (DHT) that allows developers to store and retrieve data in a decentralised manner. Holochain focuses on agent-centric development, where each user has their own chain of data that they control, enhancing privacy and scalability in dApp development.
Arweave –https://www.arweave.org/
Arweave is a permanent and decentralised storage network that provides immutable and censorship-resistant data storage. It utilises a blockchain-like structure called the ‘blockweave’ to store data and ensures its availability over a long period of time. Arweave is often used for decentralised app development, particularly for applications that require permanent storage of critical data or content.
BigchainDB –https://www.bigchaindb.com/
BigchainDB combines the benefits of distributed databases and blockchain technology to provide a scalable and decentralised data storage solution. It offers high throughput and low latency, making it suitable for decentralised applications that require fast and efficient data management. BigchainDB allows developers to store, retrieve, and query large amounts of data in a decentralised and tamper-proof manner.
Solid –https://solidproject.org/
Solid is a decentralised data storage and identity protocol developed by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web. It enables individuals to store and manage their own data in personal online data stores (PODs) while controlling access and permissions. Solid provides a standardised way to decentralise data storage and allows for interoperability between decentralised applications.
Storj –https://storj.io/
Storj is a decentralised cloud storage platform that leverages blockchain and peer-to-peer technology. It enables developers to store files in a distributed manner across a network of nodes, ensuring data redundancy and privacy. Storj uses cryptographic techniques to secure data, and offers an efficient and cost-effective alternative to centralised cloud storage providers.
Sia –https://sia.tech/
Sia is a decentralised storage platform that utilises blockchain technology to create a secure and distributed network for storing and retrieving data. It allows developers to store files in a decentralised manner across a network of nodes while maintaining data integrity and confidentiality. Sia’s decentralised architecture makes it resistant to censorship and provides a cost-effective storage solution for decentralised applications.
Whisper –https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/Whisper
Whisper is a messaging protocol and decentralised database developed by the Ethereum project. It enables secure and private communication between nodes in a decentralised network. Whisper allows developers to build applications that require peer-to-peer messaging and data synchronisation in a trustless and decentralised manner.
Whether it’s storing files, managing data, or enabling real-time collaboration, these databases provide the necessary infrastructure for building robust and scalable decentralised applications. By leveraging their features and capabilities, developers can create innovative and resilient dApps that operate in a decentralised and trustless manner. The provided URLs can be explored for further information, documentation, and resources related to each database.
The research in this domain
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, there are several areas where research and development efforts are focused to enhance the capabilities of databases and storage solutions within the blockchain ecosystem. Some key areas of exploration include:
Scalability: Blockchain databases face scalability challenges due to the distributed nature of the technology. Research is being conducted to improve the scalability of blockchain databases, enabling them to handle a larger number of transactions and store more data without compromising decentralisation and security. Techniques such as sharding, off-chain storage solutions, and layer 2 protocols are being explored to enhance scalability.
Performance optimisation: Efforts are underway to optimise the performance of blockchain databases and storage applications. This includes research into improving transaction processing speeds, reducing latency, and enhancing the overall efficiency of data storage and retrieval mechanisms. Techniques such as consensus algorithm improvements, caching mechanisms, and advanced indexing methods are being explored to achieve better performance.
Privacy and confidentiality: Privacy and confidentiality are important considerations in blockchain databases and storage applications. Research is focused on enhancing privacy features, such as zero-knowledge proofs, confidential transactions, and privacy-preserving smart contracts. Additionally, efforts are being made to explore methods for efficient and secure data encryption, ensuring sensitive data remains protected within the blockchain ecosystem.
Interoperability and standards: Interoperability between different blockchain networks and storage applications is a critical area of research. Efforts are being made to develop standardised protocols, data formats, and APIs that enable seamless integration and data exchange between diverse blockchain databases and storage solutions. Interoperability research aims to create an interconnected and collaborative blockchain ecosystem.
Security and trust: Blockchain databases and storage applications require robust security measures. Research is focused on improving security mechanisms, such as advanced cryptographic techniques, consensus algorithm enhancements, and protection against various attacks. Additionally, efforts are being made to enhance data integrity, immutability, and trust within blockchain databases.
Integration with emerging technologies: Blockchain databases and storage applications are being explored in combination with other emerging technologies to unlock new possibilities. Research is being conducted on integrating blockchain with technologies such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing, and decentralised machine learning. This integration can enable innovative applications and enhance the functionality of blockchain databases.