The integration of the metaverse with blockchain technology has opened exciting possibilities for managing digital assets in virtual environments. As virtual worlds become increasingly immersive and interconnected, the need for secure and efficient asset management solutions has never been greater.
Metaverse integrates a collective virtual space composed of interconnected digital environments, typically accessed through immersive technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). These virtual worlds offer users the ability to interact with each other and digital objects in real-time, blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms.
Within the metaverse, digital assets encompass a wide range of virtual objects, including virtual currencies, virtual real estate, digital art, virtual clothing, and more. These assets hold intrinsic value to users and can be traded, bought, and sold within virtual environments. However, managing ownership, provenance, and authenticity of these assets presents unique challenges in the digital realm.
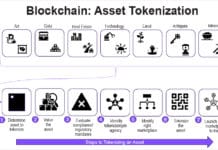
By leveraging blockchain, digital assets in the metaverse can be securely tokenised, represented as unique cryptographic tokens, and managed on a distributed ledger. This ensures transparent ownership records and eliminates the risk of fraudulent transactions.
The integration of blockchain technology into the metaverse brings several benefits.
- Secure ownership: Blockchain enables verifiable ownership of digital assets through cryptographic signatures, reducing the risk of theft or unauthorised duplication.
- Interoperability: Blockchain standards such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) allow for seamless interoperability between different virtual worlds, fostering a unified digital economy.
- Provenance tracking: The transparent and immutable nature of blockchain facilitates the tracking of digital asset provenance, ensuring authenticity and protecting against counterfeit items.
- Monetisation opportunities: Blockchain-powered marketplaces within the metaverse enable creators to monetise their digital creations directly, without the need for intermediaries.
- Decentralised governance: Blockchain-based metaverse platforms can operate without central authorities, giving users greater control over the virtual environment and its economy.
Metaverse real estate and digital assets with virtual reality
‘Metaverse real estate’ refers to virtual parcels of land or properties within interconnected digital realms. These spaces, often built using blockchain technology for secure ownership and transactions, mirror the dynamics of real-world real estate markets. Users can buy, sell, lease, and develop virtual properties, with their values determined by factors such as location, accessibility, and desirability.
Digital assets within the metaverse encompass a wide array of virtual goods and commodities, ranging from virtual artworks and collectibles to in-game items and virtual currencies. These assets hold intrinsic value within their respective digital ecosystems and can be traded, exchanged, or utilised for various purposes, much like their physical counterparts in the real world.
VR technology serves as the gateway to this immersive metaverse experience, allowing users to interact with virtual environments in a lifelike manner. Through VR headsets and peripherals, individuals can explore virtual properties, attend virtual events, and engage with other users in shared digital spaces, fostering social interaction and collaboration on a global scale.
The implications of metaverse real estate and digital assets are far-reaching. For one, they offer new avenues for investment and speculation, as individuals seek to capitalise on the burgeoning virtual economy. Moreover, they present opportunities for creativity and expression, enabling users to build and customise their virtual properties according to their preferences and imagination.
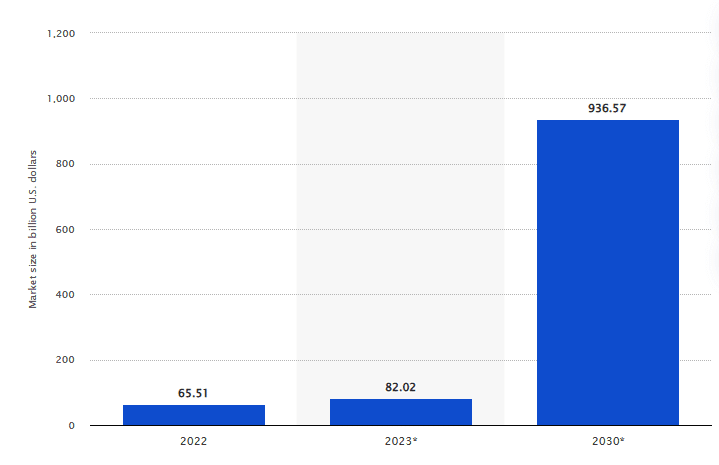
However, some challenges such as governance, security and interoperability do exist in metaverse real estate. Establishing robust frameworks for property rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring data privacy are essential for fostering trust and legitimacy within virtual environments. Promoting compatibility and seamless integration between different virtual platforms can enhance user experiences and facilitate broader adoption.
A few metaverse real estate projects and use cases
Decentraland
https://decentraland.org
Decentraland is a virtual world where users can buy, sell, and develop virtual real estate using the platform’s native cryptocurrency, MANA. Users can build and monetise experiences on their land, creating a vibrant virtual economy.
The Sandbox
https://www.sandbox.game
The Sandbox is a virtual world where players can create, own, and monetise their gaming experiences and virtual real estate. Users can purchase LAND, the digital real estate in The Sandbox, and develop games, experiences, and social hubs on their parcels. Sandbox integrates a gaming platform where players can create, own, and monetise voxel assets using blockchain technology.
CryptoVoxels
https://www.cryptovoxels.com
CryptoVoxels is a virtual world powered by the Ethereum blockchain where users can buy, sell, and build on parcels of virtual land. It’s designed to be a decentralised platform for creative expression and social interaction. Cryptovoxels is powered by blockchain focused on user-generated content and virtual land ownership.
Somnium Space
https://somniumspace.com
Somnium Space is an open, social, and persistent VR world where users can buy, sell, and develop virtual real estate with key technologies of the virtual blockchain world (VBW). It features a decentralised economy and supports various forms of content creation and interaction.
Blockchain and metaverse integration
Blockchain, renowned for its decentralised and immutable ledger system, and the metaverse, an expansive virtual environment where users interact and engage in diverse activities, together offer a novel framework for innovation and advancement.
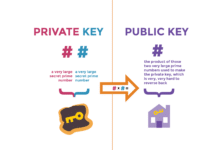
At its core, blockchain brings enhanced security, transparency, and trust to the metaverse ecosystem. By leveraging distributed ledger technology, transactions within the metaverse can be securely recorded and verified, fostering a reliable environment for digital asset ownership, trading, and exchange. Smart contracts, a hallmark feature of blockchain, further streamline interactions by automating agreements and transactions, thus enhancing efficiency and reducing the need for intermediaries.
Blockchain integration addresses critical challenges within the metaverse, such as digital identity and asset interoperability. Through blockchain-based identity solutions, users can securely manage their digital identities across different virtual platforms, ensuring privacy and control over personal data. Additionally, blockchain facilitates the seamless transfer and interoperability of virtual assets between various metaverse environments, enabling users to retain ownership and value across diverse virtual experiences.
The combination of blockchain and the metaverse opens new avenues for decentralised governance and community-driven initiatives. Decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs), enabled by blockchain technology, empower users within the metaverse to collectively govern virtual spaces, make decisions, and allocate resources.
In the realm of digital economies, blockchain integration enables the creation of robust, interoperable marketplaces where users can buy, sell, and trade virtual assets with confidence. Digital assets within the metaverse can be represented as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or fungible tokens, unlocking new possibilities for monetisation, asset ownership, and value creation. Additionally, blockchain-based incentive mechanisms, such as token rewards and staking, incentivise user participation and contribution to the metaverse ecosystem.
Know your customer (KYC) using metaverse and blockchain
Know your customer (KYC) processes are vital in financial scenarios, particularly in banking. With the emergence of the metaverse and blockchain, KYC processes are undergoing significant transformations, offering more efficient and secure methods for identity verification and compliance.
In the context of banking, the integration of the metaverse and blockchain technologies can revolutionise KYC processes by providing a decentralised and transparent framework for identity verification. Blockchain ensures that customer data is securely stored and easily accessible, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraudulent activities. Using smart contracts, KYC procedures can be automated, streamlining the onboarding process for customers while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Metaverse offers a virtual environment where users can create digital identities that are tied to their real-world credentials through blockchain technology. This enables banks to conduct KYC checks in the virtual space, enhancing accessibility and convenience for customers while maintaining the integrity of the verification process. Customers can interact with banking services seamlessly within the metaverse, eliminating geographical barriers and providing a more immersive banking experience.
The combination of the metaverse and blockchain can enhance the security of KYC processes by leveraging advanced authentication methods such as biometrics and decentralised identifiers (DIDs). These technologies enable customers to have greater control over their personal data, reducing the reliance on centralised authorities for identity verification. Additionally, the use of zero-knowledge proofs allows for the verification of customer information without exposing sensitive data, preserving privacy while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.

E-governance and financial applications of metaverse blockchain
One of the foremost applications of metaverse-blockchain integration lies in enhancing the transparency and efficiency of governmental processes. Using blockchain technology, governments can establish immutable and transparent ledgers for various activities such as voting, public procurement, and identity management within the metaverse. By recording transactions on a decentralised ledger, the integrity of data is upheld, reducing the risk of fraud and corruption. Citizens can engage in e-voting securely from anywhere in the metaverse, ensuring greater accessibility and participation in democratic processes.
Moreover, financial transactions within the metaverse can be revolutionised through blockchain-based systems. Cryptocurrencies and digital assets can be seamlessly exchanged within virtual environments, enabling frictionless cross-border transactions and fostering economic activity within the metaverse. Smart contracts can automate financial processes such as payments, lending, and asset tokenisation, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
The metaverse can serve as a playground for innovative financial instruments and decentralised applications (dApps). Decentralised finance (DeFi) platforms can offer a wide array of financial services, including lending, borrowing, and trading, accessible to users within the metaverse. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), unique digital assets representing ownership of virtual or real-world items, can enable new forms of digital ownership and commerce within virtual environments.
The integration of e-governance and financial applications within the metaverse also poses challenges. Concerns regarding privacy, security, and regulatory compliance require careful consideration to ensure the trust and confidence of users. Additionally, issues of digital inclusion and accessibility must be addressed to prevent the exacerbation of existing socioeconomic disparities within virtual societies.
To reiterate, the combination of metaverse technology and blockchain holds immense potential for revolutionising digital asset management in virtual environments. By providing secure ownership, interoperability, and monetisation opportunities, blockchain-powered metaverse platforms empower users to fully immerse themselves in a vibrant and decentralised digital economy. As the metaverse continues to evolve, leveraging blockchain will be crucial in unlocking its full potential for creators, investors, and users alike.
The research conducted in this area underscores the transformative potential of blockchain-based e-governance solutions within virtual environments. By leveraging decentralised ledgers, governments can establish trust and transparency in electoral processes, public procurement, and identity management within the metaverse. Moreover, the implementation of blockchain technology in financial applications within virtual environments offers a paradigm shift in how individuals engage in economic activities, enabling frictionless transactions, automated contracts, and novel financial instruments.
Ethical, legal, and societal implications must be thoroughly examined to ensure the responsible development and deployment of these technologies. Questions regarding privacy, security, digital inclusion, and regulatory compliance demand careful consideration to mitigate potential risks and ensure the equitable participation of all users within virtual environments.
The research on the integration of blockchain, the metaverse, and digital assets is multidisciplinary and dynamic, spanning technical, ethical, and socioeconomic dimensions. As this field continues to evolve, researchers have a unique opportunity to contribute to the development of frameworks, policies, and technologies that harness the full potential of these transformative innovations while addressing the challenges and complexities inherent in their adoption.