A security flaw in Kafdrop, an open-source interface for distributed event streaming platform Apache Kafka, has exposed data of undisclosed number of companies at risk, according to a Spectral research.
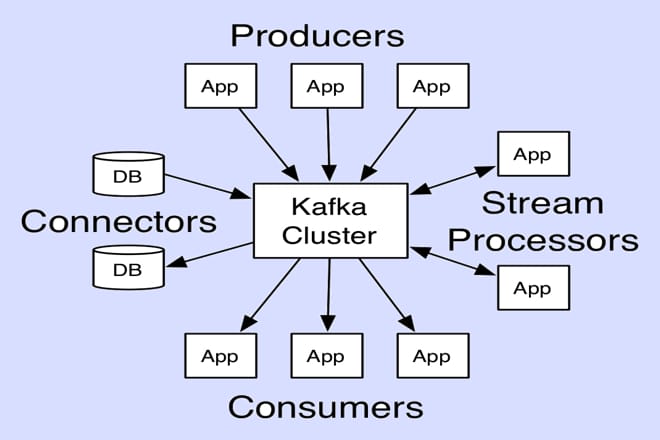
Through DeepConfig research, the team had found large amounts of misconfigured apps. In this case, it was complete Kafka clusters exposed internet-wide because of Kafdrop.
These clusters expose customer data, transactions, medical records, and internal system traffic: providing an inside look into the complete nervous system, all public.
We found exposed clusters from companies across a multitude of industries, including insurance, healthcare, IoT, media, and social networks.
Also exposed was real-time traffic revealing secrets, authentication tokens, and other access details that allow hackers to infiltrate the companies’ cloud activities on AWS, IBM, Oracle and others.
“We can’t name any of the companies whose clusters we discovered, as we don’t want to give threat actors the edge, but these flaws are exceptionally widespread,” said Dotan Nahum, CEO at Spectral. “Furthermore, since Kafka serves as a central data hub, threat actors with assistance from a flawed Kafdrop, can infiltrate and exfiltrate data and manage the cluster as they see fit. They can connect as a Kafka subscriber to cause further havoc across the entire network.”
Misconfiguration Risk
Since Kafka serves as a data hub and central processing system for mission-critical data, an exposed cluster risks every facet of the organisation.
An exposed cluster through Kafdrop can also be managed, which means hackers can also create damage beyond exfiltrating data, such as dropping a cluster, deleting topics, and more.
By understanding the topology of a cluster, a hacker can efficiently connect and impersonate a legitimate consumer, injecting or pulling data at will, says the report.
Data breaches continue to be a top security concern for organisations of all sizes. Such breaches regularly result in non-compliance or the leakage of trade secrets. The researchers have identified five types of data leaks – in managing Kafka topics, internal traffic, email traffic, medical and fintech or secrets configuration.
Upon discovery of the flaw, Spectral immediately contributed an authentication code addition back into Kafdrop.
To act quickly, either take down Kafdrop UIs or redeploy them behind an app server like Ngnix with an active and configured authentication module. Spectral recommends specific mitigation practices to prevent vulnerabilities for the long-run.