In today’s world, there is a proliferation of data. So much so that the one who controls data today, holds the key to wealth creation. Let’s take a long look at what Big Data means and what it can do for us.
Big Data has undoubtedly gained much attention within academia and the IT industry. In the current digital and computing world, information is generated and collected at an alarming rate that is rapidly exceeding storage capabilities. About 4 billion people across the globe are connected to the Internet, and over 5 billion individuals own mobile phones, out of which more than 3.39 billion users use the mobile Internet. Several social networking platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc, have a big hand in the indiscriminate increase in the production of data.
Apart from the social media giants, there is a large amount of data being generated by different devices such as sensors, actuators, etc, which are used as part of the IoT and in robots as well.
By 2020, it is expected that more than 50 billion devices will be connected to the Internet. At this juncture, predicted data production will be almost 44 times greater than that in 2010. As a result of the tech advances, all these millions of people are actually generating tremendous amounts of data through the increased use of smart devices. Remote sensors, in particular, continuously produce an even greater volume of heterogeneous data that can be either structured or unstructured. All such data is referred to as Big Data.
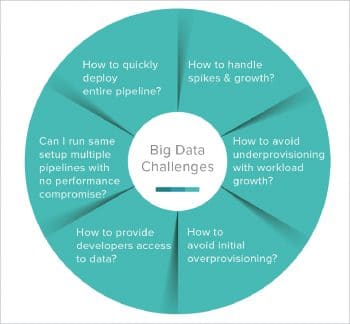
We all know that this high volume of data is shared and transferred at great speed on different optical fibres. However, the fast growth rate of such huge data volumes generates challenges in the following areas:
- In searching, sharing and transferring data
- Analysis and capturing of data
- Data curation
- Storing, updating and querying data
- Information privacy
Big Data is broadly identified by three aspects:
1. The data is of very high volume.
2. It is generated, stored and processed very quickly.
3. The data cannot be categorised into regular relational databases.
Big Data has a lot of potential in business applications. It plays a role in the manufacture of healthcare machines, social media, banking transactions and satellite imaging. Traditionally, the data is stored in a structured format in order to be easily retrieved and analysed. However, present data volumes comprise both unstructured as well as semi-structured data. Hence, end-to-end processing can be impeded during the translation between the structured data in a relational database management system and the unstructured data for analytics. Among the problems linked to the staggering volumes of data being generated is the transfer speed of data, the diversity of data, and security issues. There have been several advances in data storage and mining technologies, which enable the preservation of such increased amounts of data. Also, during this preservation process, the nature of the original data generated by organisations is modified.
Some big sources of Big Data
Let’s have a quick look at some of the main sources of data along with some statistics (Data source: http://microfocus.com).
1. Social media: There are around 1,209,600 (1.2 million) new data producing social media users every day.
2. Twitter: There are approximately 656 million tweets per day!
3. YouTube: There are more than 4 million hours of content uploaded to YouTube every day, with all its users watching around 5.97 billion hours of YouTube videos each day.
4. Instagram: There are approximately 67,305,600 (67.30 million) Instagram posts uploaded each day.
5. Facebook: There have been more than 2 billion monthly active Facebook users in 2017 so far, compared to 1.44 billion at the start of 2015 and around 1.65 billion at the start of 2016. On an average, there are approximately 1.32 billion daily active users as of June 2017. Every day, 4.3 billion Facebook messages get posted. There are around 5.75 billion Facebook likes every day.
6. Mobile text messages: There are almost 22 billion text messages sent every day (for personal and commercial purposes).
7. Google: On an average, in 2017, more than 5.2 billion daily Google searches get initiated.
8. IoT devices: Devices are a huge source of the 2.5 quintillion bytes of data that we create every day – this not only includes mobile devices, but smart TVs, airplanes, cars, etc. Hence, the Internet of Things is producing an increasing amount of data.

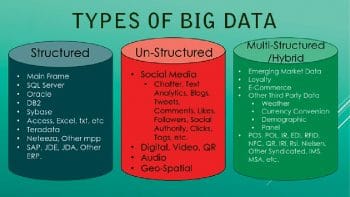
Characteristics of Big Data
There are several characteristics of Big Data as listed below.
Volume: This refers to the quantity of generated and stored data sets. The size of the data helps in determining the value and potential insights into it; hence, it helps us to know if a specific set of data can actually be considered as Big Data or not.
Variety: This property deals with the different types and nature of the data. This actually helps people who analyse the large data sets to effectively use the resulting insights obtained after analysis. If a specific set of data contains different varieties of data, then we can consider it as Big Data.
Velocity: The speed of data generation also plays a big role when we classify something as Big Data. The speed data is generated and further processed at to arrive at results that can be analysed for further use is one of the major properties of Big Data.
Variability: When we talk about Big Data, there is always some inconsistency associated with it. We consider the data set as inconsistent if it does not have a specific pattern or structure. This can hamper the different processes required to handle and manage the data.
Veracity: The quality of the captured data can also vary a lot, which affects the accurate analysis of the large data sets. If the captured data’s quality is not good enough to be analysed then it needs to be processed before analysis.
How is Big Data analysed?
We all know that we cannot analyse Big Data manually, as it’s a highly challenging and tedious task. In order to make this task easier, there are several techniques that help us to analyse the large sets of data very easily. Let us look at some of the famous techniques being used for data analysis.
1. Association rule learning: This is a rule-based Big Data analysis technique which is used to discover the interesting relations between different variables present in large databases. It is intended to identify the strong rules that are discovered in the databases using different measures of what is considered ‘interesting’. It makes use of a set of techniques for discovering several interesting relationships, also called ‘association rules’, among all the different variables present in the large databases.
All such techniques use a variety of algorithms in order to generate and then test different possible rules. One of its most common applications is the market basket analysis. This helps a retailer to determine the several products frequently bought together and use that information for more focused marketing (like the discovery that most of the supermarket shoppers who buy diapers also go to buy beer, etc). Association rules are widely being used nowadays in continuous production, Web usage mining, bioinformatics and intrusion detection. These rules do not take into consideration the order of different items either within the same transaction or across different transactions.
2. A/B testing: This is a technique that compares the two different versions of an application to determine which one performs better. It is also called split testing or bucket testing. It actually refers to a specific type of the randomised experiment under which a set of users are presented with two variations of the same product (advertisements, emails, Web pages, etc) – let’s call them Variation A and Variation B. All the users exposed to Variation A are often referred to as the control group, since its performance is considered as the baseline against which any improvement in performance observed from presenting the Variation B is measured. Also, at times, Variation A itself acts as the original version of the product which is being tested against what existed before the test. All the users in the group exposed to Variation B are referred to as the treatment group. This technique is used to optimise a conversion rate by measuring the performance of the treatment against that of the control using some mathematical calculations.
This testing methodology removes the possible uesswork from the website optimisation process, and hence enables various data-informed decisions which shift the business conversations from what ‘we think’ to what ‘we know’. We can make sure that each change produces positive results just by measuring the impact that various changes have on our metrics.
3. Natural language processing: This area of computational linguistics is linked to the interactions between different computers and human languages. In particular, it is concerned with programming several computers to process large natural language corpora. The different challenges in natural language processing are natural language generation, natural language understanding, connecting the machine and language perception or some combinations thereof. Natural language processing research has mostly relied on machine learning. Initially, there were many language-processing tasks which involved direct hand coding of rules. Nowadays, different machine learning pattern calls are being used instead of the statistical inference to automatically learn various rules by analysing large sets of data from real-life examples. Many different classes of machine learning algorithms have been used for NLP tasks. These algorithms utilise large sets of ‘features’ as inputs. These features are developed from the input data set. Recent research has focused more on statistical models, which take probabilistic decisions based on attaching the real-valued weights to each input feature. Such models really have the edge because they can easily express the relative certainty for more than one different possible answer rather than only one, therefore producing more reliable results, compared to when such a model is included as only one of the many components of a larger system.
How can Big Data benefit your business?
Big Data may seem to be out of reach for different non-profit and government agencies that do not have the funds to buy into this new trend. We all have an impression that ‘big’ usually means expensive, but Big Data is not really about using more resources; rather, it’s about the effective usage of the resources at hand. Hence, organisations with limited financial resources can also stay competitive and grow. For that, we need to understand where we can find this data and what we can do with it.
Let us see how Big Data can really help different organisations in their business
1. Targeted marketing: There are several small businesses which cannot compete with the huge advertising budgets that large organisations have at their disposal. In order to remain in the game, they have to spend less, yet reach qualified buyers. This is where the need for analysis and measurement of data comes in, in order to target the person most likely to turn into a customer. There is a huge amount of data that is freely accessible through different tools like Google Insights, etc. Organisations can find exactly what different people are looking for, when they are really looking for it and also find out their locations. For instance, the CDC (Centre for Disease Control, USA) uses the Big Data provided by Google to analyse a large number of searches relating to the flu. With the obtained data, researchers are able to focus their efforts where there is a greater need for flu vaccines. The same technique can be applied for other products as well.
2. Actionable insights: Big Data can really become like drinking from a fire hose if we do not know how to turn different facts and figures into useable information. But as soon as an organisation learns how to master different analytical tools, which turn its metrics into readable reports, graphs and charts, it can make decisions that are more proactive and targeted. And that’s when it will gain a clear understanding of the ‘big problems’ affecting the business.
3. Social eavesdropping: A large chunk of the information in Big Data is obtained from social chatter on several social networking sites like Twitter and Facebook. By keeping an eagle eye on what is being said in different social channels, organisations can really understand how the public perceives them and what to do if they need to improve their reputation. For example, the Twitter mood predicts the stock market. Johan Bollen once tracked how the collective mood from large sets of Twitter feeds correlated with the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The algorithm which was used by Bollen and his group actually predicted market changes with 87.6 per cent accuracy.

Applications of Big Data
There is a huge demand for Big Data nowadays, and there are numerous areas where it is already being implemented. Let’s have a look at some of them.
1. Big Data is used in different government sectors for different tasks like power theft investigation, deceit recognition and ecological fortification. Big Data is also used to examine different food based infections by the FDA.
2. It is widely used in the healthcare industry by physicians and doctors to keep track of their patients’ history.
3. Big Data is also used in the education sector by implementing different techniques such as adaptive learning, problem control, etc, to reform different educational courses.
4. Big Data is used in fraud detection in the banking sector.
5. It is used by different search engines to provide the best search results.
6. Different price comparison websites make use of Big Data to come up with the best options for their users.
7. Big Data is also used for analysing and processing the data obtained from different sensors and actuators connected to IoT.
8. Different speech recognition products such as Google Voice and Siri also make use of Big Data to recognise the speech patterns of the user.
9. Big Data and data science have taken the gaming experience to new heights. Different games are now designed using various Big Data and machine learning algorithms, which have the self-improving capability when a player jumps to a higher level.
10. Big Data is of great help for the recommender and suggestion tool which prompts us about similar products to purchase on different online shopping platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, etc.







































































We offer a genuine money to people who are sincerely and honestly in need of some money for some personal and business purposes. We are glad to be able to fulfill your dreams in offering you the exact amount of money you need. we do not charge for processing/origination cost. Our money is secured and safe and it will be delivered into your bank account within 48 hours of application. contact us now with your interest Email: urbansuccessfundings@gmail.com