Networks are prone to viruses and hacking. Internet users need to be aware of what threats and risks they are susceptible to, and what evasive and protective measures they can take to secure themselves. You will get an idea about the different network security techniques, as well as the vulnerabilities and the top open source tools to overcome them, from this article.
Computer security breaches have become common nowadays, with several occurring around the world every day. Some of the breaches are considered minor, with little loss of monetary or data resources, but many of them are major, or even catastrophic. Many of us have heard of the hacking of Sony Pictures’ network in 2014, which the FBI attributed to the government of North Korea. More recently, hackers from Russia have been accused of tampering with the voting systems in the 2016 US presidential elections, and also with the data of Ukrainian businesses and several government agencies. So hackers are continuously looking out for new vulnerabilities to exploit. When our networks are not secure, then the information about individuals, organisations, and even our government, is at the risk of being exposed or leveraged against us.
Many of us use artificial intelligence (AI) and the IoT in one way or the other to make our lives smarter – be it for home automation or industrial automation. Hackers have an eagle eye on the data generated by IoT devices. They try to enter and invade networks through this medium and ultimately steal whole sets of data or infect the complete network. Hence, network security is something that cannot be taken for granted.
According to the US based SANS Institute, network security is the process of adopting different preventive measures to protect the underlying network infrastructure from misuse, unauthorised access, modification, malfunction, destruction or any improper disclosure. Implementation of preventive measures allows users, computers and programs to perform all their permitted critical functions within a secure environment. Network security includes the protection of not just software technologies but also the associated hardware.
Effective network security manages access across the entire network. It targets different types of threats and prevents them from entering or spreading on the network. Network security includes multiple layers of defence at the edge as well as within the network. Each of the network security layers implements its own policies and controls. Only authorised users gain access to the network’s resources and malicious actors are blocked from carrying out any exploits or threats. Network security is implemented for both public and private computer networks that are used for everyday jobs like communicating with colleagues in a business or with government agencies, conducting transactions, etc. There are private networks like those within a company and others which might be open for the public. The most common way of protecting a network resource is by assigning a unique name and a corresponding password for it.
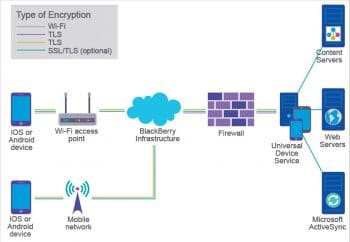
Securing a network also involves a complex combination of various hardware devices, such as firewalls, routers, and anti-malware software applications. Businesses and government agencies employ highly skilled information security analysts to implement various security plans and constantly monitor the efficacy of these plans.
The different ways of ensuring network security are:
1. Access control
2. Use of antivirus and anti-malware software
3. Application security
4. Behavioural analytics
5. Prevention of data loss
6. Email security
7. Implementing firewalls
8. Intrusion prevention systems
9. Network segmentation
10. Security information and event management
Listed below are some top vulnerabilities in a network, and the key techniques to protect networks against them.
USB thumb drives
USB drives are one of the most common ways a network can be infected from inside a firewall. There are a couple of reasons for this – these drives are small, inexpensive, hold a lot of data and can also be used on multiple types of computers. The ubiquity of thumb drives has driven hackers to develop a targeted malware, such as the notorious Conficker worm. This malware automatically executes upon connecting with any live USB port. The worst part is that the default OS configurations allow most programs (including the malicious ones) to run automatically. This is like everyone in your neighbourhood having a key to open their own electric garage door, and being able to use the same key to open the garage doors of everyone else.
Preventive measure
The default auto-run policies of a computer need to be changed.
Wireless access points
Wireless access points provide immediate connectivity to any of the users in the proximity of the network. Wireless attacks by war drivers (the people in vehicles looking for unsecured Wi-Fi networks) are common and have caused significant damage in the recent past. Wireless access points are insecure, regardless of the encryption used. Different protocols like the Wireless Encryption Protocol contain many known vulnerabilities that can be easily compromised with attack frameworks like Aircrack.
Preventive measures
1. WPA2 Enterprise using RADIUS is widely recommended along with an access point that’s capable of performing the required authentication and enforcing all security measures.
2. Strong passwords should be used and be changed on a frequent basis.
Laptops and netbooks
Laptops are portable and include full operating systems. They come with a handy Ethernet port that’s used for tapping directly into a network. A notebook may already have some malicious code running in the background to scour the network and find some additional systems to infect. Apart from the infected laptops compromising our internal network, it is more important to think about the laptops running the malicious code. All of us have some form of sensitive information that cannot leave the perimeter of the office (like home addresses, account details, medical records, phone numbers, etc.). So when the laptop is attacked, all of this is at risk.
Preventive measures
1. Different open source solutions like TrueCrypt can reduce such risks.
2. Implementation of encrypted file systems for all sensitive data.
3. We should have control over the endpoints that enter and leave the internal system.
4. Different sensitive information like DV, VPN and Wi-Fi access passwords should never be stored persistently on devices like laptops or netbooks.
Miscellaneous USB devices
Thumb drives are not the only USB-connected devices that the IT department needs to be wary of. Many other devices are also capable of storing data on some common file system that can be read and written in by using a USB or similar connection. Since this is not the primary function of such devices, they are overlooked as potential threats. But the fact is, if an endpoint can easily read and execute data from the device, then it can really pose as much of a threat as a thumb drive. Such devices include MP3 players, digital cameras, printers, scanners, digital picture frames, etc.
Preventive measures
1. Implement and enforce different asset control policies that keep a check on what devices can enter the environment and, also, when they can enter.
2. There should be frequent reminders about all the policies that deal with these controls.
The Trojan human
Just like the Trojan horse, the Trojan human also enters a business in disguise. The Trojan human could be in business attire or dressed like a repairman (telecom, appliance, HVAC, etc). Such tricksters are known to have penetrated some of the most secure environments (including server rooms).
Preventive measures
1. Continuous reminders should be sent to the employees regarding the best practices to follow when authorising third parties.
2. Sources accessing our system must be properly identified and validated by asking questions, rather than making assumptions.
Optical media
Most people are surprised to learn that even optical media like CDs can be used to infect a network. CDs labelled with the name of popular recording artists are used as a guise. Once the CD is inserted into the system, the classified information can be accessed using authorised credentials, and the secure data present on the system can be easily stored on the CD in encrypted archives. So, recordable media that appears to be legitimate can also be used to piggyback data in and out of networks.
Preventive measures
1. Implement and enforce different asset control policies that keep a check on the devices that can enter the environment and when.
2. There should be frequent reminders about the policy and the kind of controls incorporated.
E-mail
E-mail, too, is often misused. Messages with confidential information can be forwarded to any external target. In addition, the e-mails themselves can let in nasty viruses. One e-mail could phish for the access credentials of an employee and later, these stolen credentials can be leveraged in a second-stage attack.
Preventive measures
1. Always identify the sender of the mail by using technologies such as PGP. Even a simple set of questions before sending any sensitive information will work.
2. Access control should be enforced for broad, alias-based e-mail addresses.
3. Reminders about the security policies should be continuously sent out to employees.
Different open source tools to secure a network
Let’s have a quick look at some of the important open source tools that help us secure a local network.
Nmap: This is a free and open source network scanner tool that is used to discover the various hosts and services present on a computer network by sending different packets and analysing the response for each of them. It offers a couple of important features that play a great role in protecting our network from external infections. It features the powerful NSE scripts that can help detect misconfiguration, vulnerabilities, and security related information about network services. Nmap can easily address network conditions like latency and congestion during a scan.
Features
1. Identifies the host on a network.
2. Scans ports.
3. Can interrogate network services on remote devices to determine the version name.
4. Determines the operating system and hardware characteristics of the network devices.
5. Can interact with the target using a scripting engine.
Open VAS: OpenVAS is an open source vulnerability scanning suite that started from a fork of the Nessus engine. It is also called the open vulnerability assessment system. It is basically a software framework consisting of different services and tools that offers vulnerability scanning and vulnerability management using a Web based dashboard.
Features
1. It can detect various security issues in all types of servers and network devices.
2. It understands and lets users know about what is being exposed on any external facing services.
3. Results obtained after scanning are delivered to our email address for analysis, allowing us to start fixing any kind of risks that our systems may face due to external threats.
OpenSSH: OpenSSH is a suite containing different secure networking utilities that are based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. It provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client-server architecture. It was created by OpenBSD developers as an alternative to SSH. OpenSSH is not just a single computer program, but a set of programs that serves as alternatives to different unencrypted protocols like FTP and Telnet. It is integrated to several operating systems while its portable version is available as a package in a specific system.
Features
1. Uses a bi-directional data-forwarding technique that helps return communication to the client side server.
2. It can set up a secured channel through which all the data sent to local or client-side UNIX domain sockets and client-side TCP ports may be easily forwarded for routing on the server side.
3. It secures all the traffic between two points by tunnelling all insecure protocols through an SSH tunnel.
4. It includes SCP, which provides easy access to copy files securely.
5. It can access internal network services with the help of SSH tunnels using a single point of access.
OSSEC: This is also known as Open Source HIDS Security. It is an open source, host based intrusion detection system widely used to perform log analysis, integrity checks and Windows Registry monitoring. It’s also used for rootkit detection, time based alerting and active response. It supports intrusion detection for most of the operating systems including OpenBSD, Linux, OS X, Solaris, Windows, etc.
Features
1. Easy to set up and configure.
2. OSSEC has a centralised and cross-platform architecture that allows multiple systems to be easily managed and monitored at the same time.
3. It has a log analysis engine that can correlate and analyse different logs from multiple devices and formats.
4. OSSEC is compliant with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard requirements.
5. It has benefits for both the security and operations staff.
Tips for securing a home network
Here are a few common but important tips that can add a lot to the security of a local network.
1. Change the admin user name and password for routers on a continuous basis.
2. Activate encryption.
3. Change the network name on a regular basis.
4. Always turn off the guest networks when not required. This will keep strangers away from being able to randomly hop on.
5. Activate the encryption for all files present on the local network.
6. Double up on firewalls.
7. Always keep the firmware updated on all the devices connected to the local network.