Smartphone users generally keep their data and personal information on the cloud and access it through different apps. This poses a threat to the security of personal data, especially when a smartphone app seems to have suspicious code. This article covers a couple of tools for fingerprinting and forensic analysis of Android apps.
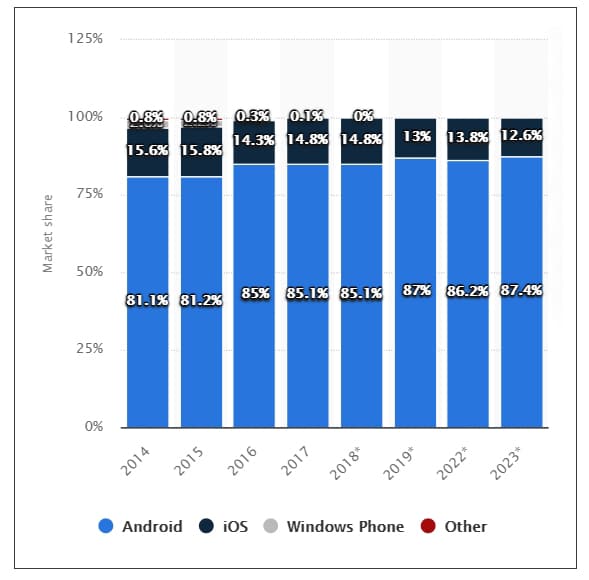
All of us use smartphone apps for personal and official work or for accessing social networks. Research reports indicate that many apps are dangerous and could lead to data leakage. Android is a popular smartphone platform that is used for thousands of apps. A Statista.com report indicates that there are 3.5 billion smartphone users in the world. Of these, 87 per cent have Android smartphones.
Cases of sniffing attempts in Android apps
Companies working rigorously on security and privacy spend huge amounts of money so that secure anti-malware can be released for Internet users. As per a report by CPO Magazine, cyber-attacks will cost around US$ 6 trillion in 2021. The loss was valued at US$ 2 trillion in 2019.
Washington based Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) reports that the following cyber-attacks took place in recent months.
February 2021
- In a unit of Oxford University working on the Covid-19 vaccine, there was an incident of unauthorised access to information
- North Korea based hackers extorted billions of cryptocurrencies
March 2021
- A group of hackers used Facebook to broadcast malicious and suspicious links to capture information
- Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) of India received evidence of Chinese hackers spying in sensitive sectors
Tools and libraries for fingerprinting Android apps
Before covering the tools and libraries, we should first be clear about the backend or base of any Android app. An Android package (APK) file is the base installation file of a classical Android App. The hackers or sniffers try to corrupt this file, and then send it via special URLs or links so that the receivers download and install it on their Android smartphones.
Before installation of any Android App, its fingerprinting and analysis is necessary. There a number of sources and repositories where such APK files are available for download.
Figure 2 gives a few cloud repositories where thousands of Android apps are available. These should be analysed first before direct installation in a phone.
Many smartphone users download games and apps from the cloud without checking whether they are secure or not.
A number of tools and libraries are available for the fingerprinting and forensic evaluation of Android apps and the associated APK files. Google Play store also uses a number of utilities and forensic tools to check apps regularly, and keeps users informed about suspicious apps. While it updates the apps whenever required, it also bans or blacklists suspicious apps, and notifies users about the same.
Two utilities that can be used to verify the different parameters and security aspects of Android apps, before they are installed, are briefly described below.
AAPT tool (https://androidaapt.com/)
This free and open source library is available to check an Android app before actual installation. It is also used for reverse engineering and fingerprinting of coding done at the backend of the Android app.
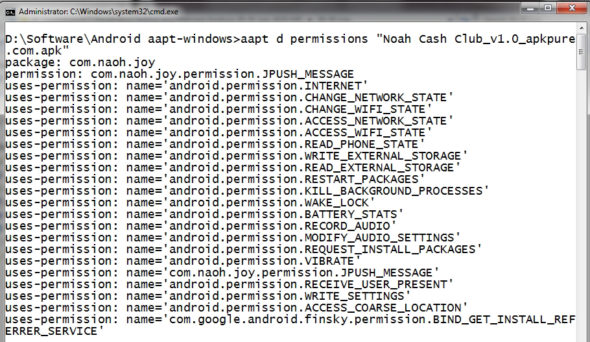
With a single instruction, the permissions of an APK file can be generated and then the user can see whether these are secure or not.
Figure 4 displays all the associated permissions of the APK. It is clear from the figure that many permissions are very sensitive, and a decision can be taken whether to install this app or not.
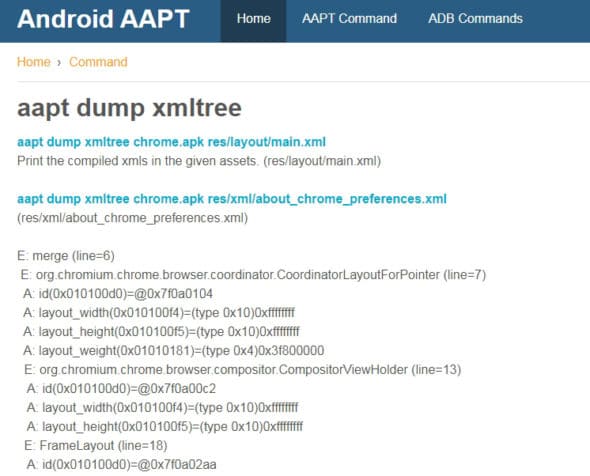
The complete XML tree of the Android code is also available with the xmltree keyword in the instruction. In this way, the backend code can be analysed and forensic evaluation of the app can be done.
DexDump utility (https://github.com/benbenmushi/dexdumpWindows)
In addition to the AAPT tool, the DexDump utility can be used to see the backend script and code of an Android app. Here, DEX refers to Dalvik Executable, which ensures the successful execution of the Android app. DEX is the executable file with the compiled code of the Android app.
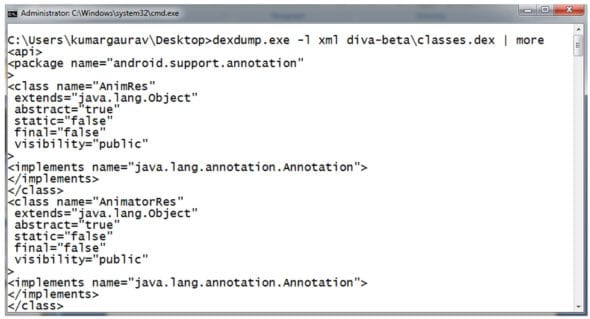
With every Android app, the DEX file can be generated by unzipping (extracting) the APK file. Using the DexDump utility, the .dex file is scanned and then fingerprinting of the code is done. The DexDump utility is used to view different perspectives of the code to find out if there is any malware or suspicious instruction in the Android app.