The adoption of digital technologies has been slow in the oil and gas (O&G) industry, leading to trillions of dollars in losses. The industry, which is heavily impacted by geopolitical crises and increasing competition from renewable energy, needs to fully embrace IT solutions to address its critical pain points. Open source tools and platforms can be an integral part of these solutions.
The oil and gas (O&G) industry is divided into three categories depending upon the area of operations in the value chain, namely, upstream, midstream, and downstream.
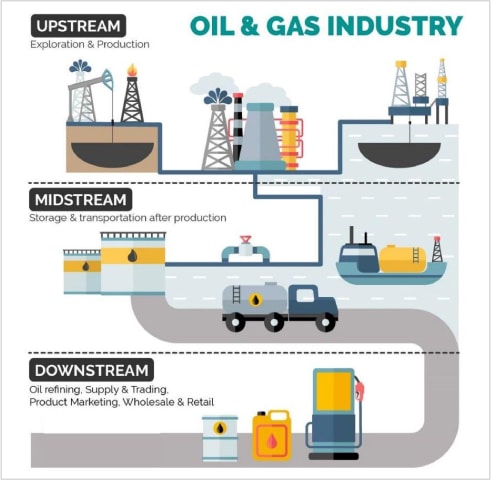
Upstream operations
These operations include:
- Identifying areas where oil/gas can be extracted (exploration)
- Drilling and bringing the oil/gas to the surface (production)
Pain points in upstream operations
- High exploration and drilling costs: Exploration and drilling of oil wells incur millions of dollars in workforce, equipment, material, and logistics.
- Equipment downtime: Without regular and effective maintenance, equipment is prone to failure, leading to downtime in production and significant monetary loss. Figure 2 lists the main causes of unwanted downtime.
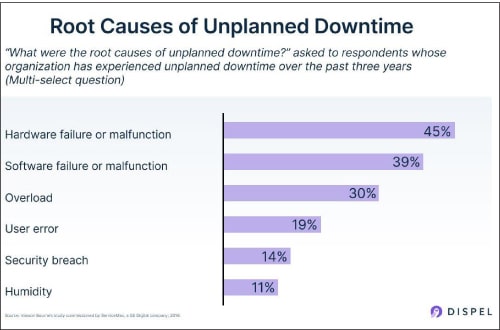
Figure 2: Root causes of unplanned downtime (Source: Vanson Bourne’s study commissioned by ServiceMax, a GE Digital company, 2016) - Sustainability concern: Upstream operations have a heavy carbon footprint.
- Safety risk: The nature of the work poses physical, chemical, and biological occupational hazards to the individuals working in upstream operations.
- Ineffective data management: Numerous sensors generate humongous data. Without effective management and analysis, this data is of little use.
Midstream operations
Midstream operations include:
- Transportation of oil/gas (from production site to refining site)
- Storage of oil/gas
Pain points in midstream operations
- Cyber security risk: The IT and communications infrastructure used in transportation and storage operations is vulnerable to cyber attacks. In 2021, Colonial Pipeline, an American oil pipeline system, suffered a ransomware cyber attack that impacted computerised equipment managing the pipeline.
- Extracting value from data: Harnessing midstream data and extracting value from it remains a huge challenge.
- ESG (environmental, social, and governance) scrutiny: Investment in midstream operations depends on the ESG scrutiny of the company. A low ESG score could stymie the investments leading to higher energy prices, supply disruptions, increased environmental risk, reduced innovation and competition.
- Safety risk: Ageing pipelines, human intervention, corrosion/cracks in storage tanks, and natural calamities pose safety risks.
- Inefficient inventory management: Lack of a robust predictive framework leads to inefficient inventory management and higher costs.
Downstream operations
Downstream operations include:
- Processing of petrochemicals (refining operations)
- Marketing and distribution/sale of refined products (retail and wholesale)
Pain points in downstream operations
- Personnel safety: Hazardous gas leakage is a major safety concern.
- Inventory issues: Inaccurate demand prediction impacts fulfilment rates leading to missed revenue targets owing to stockouts.
- Cyber security risk: These are similar to the risks in midstream operations, but also include refinery IT infrastructure.
- Waste treatment: Without effective treatment, toxic residues can pose serious environmental hazards.
- Data management issues: Ineffective management and analysis of unstructured data generated by sensors and other sources is a major pain point.
Open source is shaping many solutions for O&G industry challenges
Many major oil and gas companies are beginning to see the value of engaging with open source software and are starting to participate in open source projects and communities (Figure 3).

- Shell has joined the Linux Foundation Energy (LF Energy) and intends to play a role in further enhancement of the Open Subsurface Data Universe (OSDU) platform’s utilisation of data from renewable and other energy sources. The code for the data ingestion element of Shell’s Sensor Intelligence Platform will be made open source under the name Real Time Data Ingestion Platform (RTDIP) via LF Energy.
- Chevron is a contributing member of the Eclipse Foundation. The latter provides individuals and organisations with a mature, scalable, and business-friendly environment for open source software collaboration and innovation.
- British Petroleum (BP) is also dabbling with open source. It has a public GitHub account with 13 repositories.
Oil and gas companies are increasingly adopting open source software to save costs, improve collaboration and innovation, and to modify the software to match their specific needs.
The technologies solving the challenges faced by the oil and gas (O&G) industry can be grouped into the following major categories:
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
- Big Data
- Digital twins
- Augmented reality (AR)
- Robotic process automation (RPA)
- Cloud computing
- Blockchain
- Quantum computing
Open source software, tools, and platforms shape these technologies in myriad ways. Here are some examples.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The O&G industry uses a lot of sensors to collect data throughout the value chain. These sensors, along with edge computing and cloud computing infrastructure, form the backbone of Internet of Things (IoT). With the extensive use of IoT, O&G companies can solve many challenges plaguing the industry.
Like most innovative technologies, IoT also relies heavily on open source tools and platforms. Some of them are listed below:
- OpenRemote is an open source IoT platform to control devices, visualise data, and create customised applications.
- Flutter is a UI (user interface) SDK (software development kit) by Google for cross-platform app development.
- ThingsBoard is an open source IoT platform for device management, data collection, processing, and visualisation.
- SiteWhere is an industrial strength open source platform for IoT app development.
- Eclipse IoT is an open source IoT platform with components for managing IoT devices, data, and services.
- Node-RED is an open source visual programming tool for IoT solution development.
Kaa is an open source IoT platform providing a framework for developing and deploying IoT solutions.
5G technology can enhance IoT capabilities through faster speeds, lower latencies, and larger network capacity than previous mobile networks. This makes 5G well-suited for IoT devices, allowing for greater connectivity, more devices and handling of more data traffic.
There are several open source projects that are focused on the development of 5G technology and its applications. A few are listed below.
- O-RAN (open radio access network) is focused on the development of open, interoperable radio access networks for 5G and beyond.
- OpenAirInterface is focused on the development of software for 5G and other wireless communication systems.
- OAI-CN is focused on the development of a core network infrastructure for 5G and beyond.
Research for 6G, the next iteration of 5G, is under way. It promises faster speeds and lower latency than 5G. 6G is expected to become available in the 2030s and will merge the digital and physical world, providing new IoT use cases relevant to the O&G industry.
AI and ML
Open source has enhanced collaboration and innovation in AI/ML by providing a platform for sharing code and ideas. This has created a community of developers working together to advance the field.
There are many open source software, tools, and platforms that are commonly used in AI/ML. Some examples include:
- MindsDB, an open source AI layer for databases
- PyTorch, an open source ML framework
- Keras, an open source deep learning framework
- Apache MXNet, an open source deep learning framework
- OpenAI Gym, an open source platform for reinforcement learning algorithms
Big Data
Open source tools for ML and data visualisation are commonly used for Big Data solutions, providing a flexible platform for building and running data intensive apps.
Open source tools that are commonly used in the field of Big Data are:
- Apache Flink, an open source Big Data processing platform
- Apache Kafka, an open source distributed streaming platform
- Elasticsearch, a distributed, open source search and analytics engine
- Druid, an open source, column-store, real-time OLAP (online analytical processing) data store
- Kylin, an open source distributed analytics engine
Digital twins
Digital twins are digital representations of physical systems or processes that can be used to model, simulate, and analyse their behaviour. Open source technologies and tools can be used to develop and manage digital twin systems.
Open source platforms like Eclipse Hono, Eclipse Ditto, Apache Kafka, Influx DB, and Grafana can collectively enable digital twin capabilities, including IoT real-time data acquisition, virtual representation and management, real-time analytics, and visualisation.
- Eclipse Hono provides remote service interfaces for connecting large numbers of IoT devices and interacting with them in a uniform way, regardless of the device communication protocol.
- Eclipse Ditto is a framework that supports IoT digital twins’ software pattern implementation.
- Apache Kafka enables the building of data pipelines for real-time streaming applications.
- Influx DB is a simple-to-set up, real-time series database that can easily scale.
- Grafana is an analytics and monitoring solution that provides plugin data source models and support for many of the most popular time series databases, such as Graphite, Prometheus, Elasticsearch, and Influx DB.
The combination of these five open source platforms can provide a universal architecture for digital twins.
Augmented reality (AR)
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies can help in alleviating many pain points in the O&G industry like downtime, safety, productivity, costs, etc. Open source software and platforms can implement these technologies. Some of them are listed below.
ARToolKit+ is a collection of software tools to help solve some of the fundamental problems in AR, including geometric and photometric registration.
- mixARE (mix Augmented Reality Engine) is an open source AR browser, published under the GPLv3.
- HoloKit is a low cost open source mixed reality (MR) experience, which includes the HeadKit cardboard headset and TrackKit software.
- Aframe.io is an open source web framework for building 3D/AR/VR experiences.
- ApertusVR is an embeddable, open source, framework-independent, platform-independent, network-topology-independent, distributed, AR/VR/MR engine.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA refers to the use of software to automate business processes typically performed by humans. It is possible to use open source software in the development of RPA systems, as many open source tools and libraries are available for automating several types of processes.
Some examples of open source tools that can be used in the development of RPA systems are listed below.
- Apache Camel is an open source integration framework that can be used to automate the routing and processing of data between different systems.
- Robot Framework is an open source test automation framework for acceptance testing and acceptance test-driven development (ATDD).
- AutoIt is an open source automation language and platform for creating custom scripts and automation programs.
- Ansible is an open source platform for automating the deployment, management, and scaling of applications and infrastructure.
- OpenCV is an open source computer vision library for building applications that process and analyse visual data.
These are just a few examples of the many open source tools, software, and platforms that are available for use in RPA development. It is important to carefully research and evaluate the options for best suitability.
Cloud computing
Here are some open source tools, software, and platforms that can be used in cloud computing.
- Apache CloudStack is an open source cloud computing platform for building and managing Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) clouds.
- OpenStack is an open source platform for building and managing private and public clouds.
- OpenNebula is an open source platform for building and managing private, public, and hybrid clouds.
- Terraform is an open source tool for building, changing, and versioning infrastructure safely and efficiently.
- OpenShift is an open source platform for building and deploying container-based applications.
- Cloud Foundry is an open source platform for building and deploying cloud-native applications.
Blockchain
Open source and blockchain can work together in many ways, with many blockchain platforms being open source, and open source tools used to build apps being on blockchain platforms, leveraging their security and decentralisation.
The following open source tools and platforms can be used in the blockchain space.
- Hyperledger Fabric is an open source blockchain platform that is designed for building enterprise-grade applications.
- EOS is an open source blockchain platform that is designed for high-performance and scalable applications.
- Ethereum is an open source, decentralised platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralised applications (dApps).
- Cosmos is an open source, decentralised network of independent blockchains that are built on the Tendermint consensus algorithm.
Hedera distributed ledger technology
Hedera Hashgraph is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) platform that uses a novel consensus algorithm called the hashgraph algorithm, which is based on the concept of a directed acyclic graph (DAG). In contrast, most blockchain technologies use a consensus algorithm called proof of work (PoW) or proof of stake (PoS).
Hedera Hashgraph claims advantages over traditional blockchains (speed, low fees, advanced security) but is new and untested in production. This hashgraph technology can be explored for many blockchain use cases in the O&G industry.
Quantum computing
Quantum computing is a new and rapidly evolving field that uses quantum mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. It has the potential to solve certain problems much faster than classical computers, which use bits to store and process information.
There are several open source quantum computing projects that provide access to quantum computing software, libraries, and tools, and allow users to contribute to the development of the project. Some of them are given below.
- Qiskit is an open source framework for working with quantum computers.
- QuTiP is an open source library for quantum computing and quantum information processing.
- Pennylane is an open source quantum machine learning library developed by Xanadu.
- QuantumFlow is an open source library for quantum computing, developed by Google.
- Ocean SDK is D-Wave’s suite of open source Python tools for solving hard problems with quantum computers.
There are also several open source quantum computing hardware projects, such as the Open Quantum Hardware project, which is developing open source quantum computing hardware based on superconducting qubits.
GESDA (Geneva Science and Diplomacy Anticipator) is launching the Open Quantum Institute with Microsoft, aiming to provide global access to quantum computing technology and research in areas relevant to the O&G sector, including seismic computing, weather forecasting, transport optimisation, process optimisation, and chemical engineering.
How open source software can address security concerns in the O&G industry
The use of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) in the O&G sector has led to an increase in the data generated by sensors, which needs to be analysed to improve operational and business decision making.
In legacy systems, data generated at the edge is sent to data centres for analysis in a raw, unencrypted format, risking security breaches. Edge computing enhances security by performing data analysis at the edge and transferring only encrypted, selective data to data centres.
These edge computing devices mostly use open source software and operating systems, which ensures a more secure environment.
Also, an intelligent gateway with the power to run a full, enterprise open source OS (like Linux) offers better security than the IIoT devices with their thin embedded real-time operating system (RTOS).
Why does an open source software system ensure better security?
Typically, open source software is supported by a sizable community, which regularly monitors security vulnerabilities and quickly works on fixing them. This is demonstrated in the form of frequent releases with an updated security status.
On the other hand, for proprietary software, the updated releases typically follow a cycle and are hardly ad hoc. This gives hackers an opportunity to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities.
Also, open source communities provide a level of code maintenance that would be impossible for one company to do on its own.
Organisations and forums promoting open source adoption in the O&G industry
There are a few organisations and forums that are working to promote the adoption of open source software/platforms/tools in the O&G industry.
- Energy Web Foundation: The Energy Web Foundation fosters value creation in the energy sector by building and promoting an open, decentralised software infrastructure built around blockchain technology.
Its objectives are:
1. To develop an ecosystem of users, application developers and infrastructure providers
2. To work jointly to identify and assess blockchain use cases in energy
3. To build an open source IT infrastructure upon which these use cases can be implemented
4. To educate regulators and other stakeholders, and provide inputs to standardisation bodies
- Open Subsurface Data Universe (OSDU) Forum: The OSDU Forum aims to increase efficiency and innovation in the energy sector through the creation and promotion of open data standards and a common data platform. Its goal is to break down data silos, enable better decision making through digital solutions, and create an open, standards-based ecosystem to foster innovation within the industry.
This forum aims to deliver:
- A scalable data platform and related (common) services
- Enable the OSDU platform in any technical setting — cloud, on-premise and edge
- One set of APIs (application programming interface) and therefore provide stable platform services to applications being developed on top
- A broad set of OSDU services to enable utilisation for a wider group of energy companies
- Services using the latest developments in order to improve and monitor data quality
- Open source is impacting every industry today, and O&G is no exception. The IT solutions addressing the challenges in O&G can leverage open source technologies to be more robust, secure, effective, and efficient.
Companies developing solutions for O&G should consider open source software to not only save costs, but also build a more flexible, secure, and reliable solution.
Association with organisations promoting open source adoption in O&G can help in staying updated with the latest open source developments and solutions for the industry.